-
California braces for out-of-control wildfires

The lack of precipitation over the past two winters has California and federal officials concerned about the impact wildfires could have in the summer months. California has already recorded 845 wildfires this year, a 60 percent increase compared with the average for the previous five years.
-
-
Draft of the 2013 U.S. National Climate Assessment is out
As mandated by the U.S. Global Change Research Act (GCRA), the U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP) is currently producing a National Climate Assessment (NCA). The NCA is a report to inform the president, the Congress, and the American people about the current state of scientific knowledge regarding climate change effects on U.S. regions and key sectors, now and in the coming decades. The National Research Council (NRC) says that as the United States continues to engage with the threats, opportunities, and surprises of climate change in its many manifestations, the 2013 NCA should prove to be a valuable resource.
-
-
Finding the right balance for natural hazard mitigation
Uncertainty issues are paramount in the assessment of risks posed by natural hazards and in developing strategies to alleviate their consequences.Researchers describe a model that estimates the balance between costs and benefits of mitigation — efforts to reduce losses by taking action now to reduce consequences later — following natural disasters, as well as rebuilding defenses in their aftermath.
-
-
Former lawmakers to hold hearings on aliens
Six former member of Congress have agreed to hold a congressional style hearing on the existence of aliens in space. “It’s a huge universe out there,” former Representative Roscoe Bartlett (D-Maryland) said. “You have to be kind of presumptuous and arrogant to assume we’re the only intelligent life in the universe.”
-
-
River beds keep moving, increasing flood risk
A detailed study of shifting river beds could hold the key to more accurate flood prevention. It is commonly believed that the elevation of river beds is more or less constant, so any change in flood risk is due to changes in hydrology. Researchers find, however, that there is a significant trends in the elevation of river beds, an indication that river channels are filling in with sediment or that sediment is being eroded through time.
-
-
Calculating the risk of tsunami for the U.S. East Coast
The greatest threat of a tsunami for the U.S. east coast from a nearby offshore earthquake stretches from the coast of New England to New Jersey. The potential for an East Coast tsunami has come under greater scrutiny after a 2012 earthquake swarm which occurred offshore about 170 miles east of Boston. The largest earthquake in the 15-earthquake swarm, most of which occurred on 12 April 2012, was magnitude (M) 4.0.
-
-
Larger fire-fighting crews save lives, limit damage in high-rise fires
Between 2005 and 2009 there were, on average, 15,700 high-rise structure fires annually in the United States. Average annual losses totaled 53 civilian deaths, 546 civilian injuries, and $235 million in property damage. When responding to fires in high-rise buildings, firefighting crews of five or six members — instead of three or four — are significantly faster in putting out fires and completing search-and-rescue operations, concludes a major new study.
-
-
Aging national power grid leaves U.S. vulnerable to storm-related outages
In parts of the United States where the grid system is “out in the open” and exposed to the elements — especially in our older cities — the risk increases for widespread power outages as a result of weather-related events, leading to lengthy, costly repairs.
-
-
Direct CO2 removal could lower costs of climate mitigation
Two broad strategies are typically offered to protect infrastructure from the consequences of climate change: reducing to emissions of CO2 into the atmosphere by using less fossil fuels, and mitigation (building sea walls, dams, and levees; changing building codes, etc.). Both approaches are costly. Scientists suggest that directly removing CO2 from the air could alter the costs of climate change mitigation. It could allow prolonging greenhouse-gas emissions from sectors like transport which are difficult, and thus expensive, to turn away from using fossil fuels.
-
-
New Jersey to launch emergency, preparedness awareness campaign
The New Jersey Office of Homeland Security and Preparedness is currently looking for a PR firm to help it launch a multifaceted awareness campaign. The campaign, worth about $4 million over three years, would aim to increase the level of emergency awareness and preparedness of residents, businesses, and communities in New Jersey.
-
-
Mississippi towns build tornado-proof domes
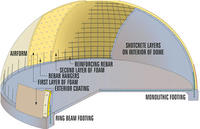
Following a devastating tornado two years ago, the town of Smithville, Mississippi, has started construction on a tornado-proof dome. The dome, to be built on the grounds of the local high school, will double as a gym and a storm shelter. Other towns in Mississippi have also begun their own dome projects.
-
-
L.A County to turn rain water into drinking water
Residents of Los Angeles County know that on the rare occasion that it rains, staying away from the beach is a good idea. Runoff from rain typically brings heavy metals, pesticides, cigarette butts, animal waste, and other pollutants into the streams and rivers which go into the Pacific Ocean. Now, local officials are getting together to find a solution to the water pollution and water scarcity, with an ambitious plan to make the runoff water drinkable.
-
-
Supercomputers allow for more realistic earthquake simulations
A team of researchers has developed a highly scalable computer code that promises dramatically to cut both research times and energy costs in simulating seismic hazards throughout California and elsewhere. The team performed GPU-based benchmark simulations of the 5.4 magnitude earthquake that occurred in July 2008 below Chino Hills, near Los Angeles.
-
-
Oregon citizens preparing for the Big One

A new study concludes that an earthquake of a magnitude 8.0 or above will strike off the coast of the state within the next fifty years. The Cascadia Fault, which runs from Northern California to British Columbia, Canada, causes a massive earthquake every 300 years or so, and the last time an earthquake hit the region was in the year 1700.
-
-
UN event highlights importance of mobile technology during disasters
A United Nations event, organized in conjunction with the Turkish government, the other day highlighted the role of innovative mobile technology in saving lives when conflicts and disasters strike.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
