-
U.S.: Russia may be testing low-yield nukes, in violation of treaty
A top U.S. military official has said that U.S. intelligence agencies believe Russia may be conducting low-yield nuclear testing that may be violation of a major international treaty. Lieutenant General Robert Ashley said in a speech on 29 May that Russia could be doing tests that go “beyond what is believed necessary, beyond zero yield.”
-
-
Inside the secret dinners where Congress figures out how to stop a nuclear apocalypse
Washington is home to countless private soirees and high powered dinner clubs, but there’s only one gathering devoted to nukes. They take place once every couple of months at a restaurant or townhome on Capitol Hill and are organized by former Democratic congressman John Tierney, who heads a group that advocates nuclear nonproliferation. Attendance is usually strong—at least a couple of dozen lawmakers show up—and they’re joined by experts like former Secretary of State John Kerry and former Energy Secretary Ernest Moniz. Sam Brodey writes in the Daily Beast that with global nuclear threats on the rise, and with Congress’ general knowledge of those threats on the decline since the end of the Cold War, those involved with the dinner say it’s more important than ever for lawmakers to have an informal venue where they can bolster their nuclear bona fides.
-
-
Iran suspending some nuclear deal commitments

Iranian President Hassan Rouhani announced Wednesday his country will suspend its compliance with prohibitions on stockpiles of enriched uranium and heavy water that were imposed as part of the 2015 international agreement on its nuclear program.
-
-
Detecting radioactive material remotely
Physicists have developed a powerful new method to detect radioactive material. By using an infrared laser beam to induce a phenomenon known as an electron avalanche breakdown near the material, the new technique is able to detect shielded material from a distance. The method improves upon current technologies that require close proximity to the radioactive material.
-
-
Easier access to radioactive waste
At the Hanford Site, waste retrieval has been completed in 17 of 149 large concrete underground single-shell tanks. The tanks were constructed of carbon steel and reinforced concrete between 1943 and 1964 to store a radioactive mix of sludge and saltcake waste from past nuclear processing activities. Hanford is installing new access holes in the tank domes for future retrieval efforts.
-
-
U.S. should reject partial North Korean “concessions”: Experts
The failure to reach an agreement at last week’s Hanoi meeting between President Donald Trump and the North Korean leader Kim Jong-un in Hanoi is but the latest indication that the differences between the United States and North Korea over the latter’s nuclear weapons capability are deep and complex.
-
-
Lessons learned from Hawaii false nuclear attack alarm
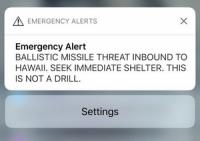
When people in the Hawaiian Islands received a false alarm text message that said “Ballistic missile threat inbound to Hawaii. Seek immediate shelter. This is not a drill” in January 2018, the result was not panic, according to new research. The researchers found that people sought information that could verify their risk and help them decide what to do next.
-
-
Better monitoring of nuclear power plants, nuclear proliferation
The United Kingdom is investing nearly £10 million (about $12.7 million) in a joint project with the United States to harness existing particle physics research techniques to remotely monitor nuclear reactors. Expected to be operational in 2024, the Advanced Instrumentation Testbed (AIT) project’s 6,500-ton detector will measure the harmless subatomic particles called antineutrinos that are emitted by an existing nuclear power plant 25 kilometers, or about 15.5 miles, away.
-
-
Britain’s MI6 chief visited Israel to discuss Iran’s nuclear threat

The chief of Britain’s MI6 intelligence service recently visited Israel to discuss the threat posed by Iran’s nuclear program. Israeli intelligence believes that Iran is “making preparations” to develop nuclear weapons without blatantly violating the 2015 deal. However, the Islamic Republic has not yet made the political decision to break out, according to the Israeli assessment.
-
-
Weapons experts: Archives show that Iran was likely developing nuclear warheads
Documents in the Iranian nuclear archive captured by Israel last year show that Iran built an underground facility, which was likely used for the development of nuclear warheads, a paper published Friday by the Institute for Science and International Security charged.
-
-
Weapons experts: Iranian nuclear archive shows that Iran lied about uranium mine
Nuclear weapons experts, who have reviewed the Iranian nuclear archive that Israel recovered from a Tehran warehouse, concluded that Iran lied that a uranium mine was under control of its civilian atomic energy agency.
-
-
U.S. must start from scratch with a new nuclear waste strategy: Experts
The U.S. government has worked for decades and spent tens of billions of dollars in search of a permanent resting place for the nation’s nuclear waste. Some 80,000 tons of highly radioactive spent fuel from commercial nuclear power plants and millions of gallons of high-level nuclear waste from defense programs are stored in pools, dry casks and large tanks at more than seventy-five sites throughout the country. “No single group, institution or governmental organization is incentivized to find a solution,” says one expert.
-
-
What should we do with nuclear waste?
The failure to develop a strategy for permanent storage and disposal of this fuel costs Americans billions of dollars a year and jeopardizes the future of nuclear power as a carbon-free source of energy, according to nuclear security expert Rodney C. Ewing. He recommends a new not for profit independent corporation that’s owned and supported by the utilities that operate nuclear power plants. The new organization would deal only with spent fuel from commercial reactors. Defense waste is an entirely different issue and should, at this time, remain the responsibility of the federal government.
-
-
Weapons experts: Satellite images confirm Netanyahu’s claims about Iran’s nuclear warehouse
Satellite images obtained over the summer confirm charges made by Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu in September that Iran had a secret nuclear warehouse in Tehran, a team of weapons inspectors wrote in a paper.
-
-
Nuclear experts: Archive shows that Iran had “advanced capabilities” to produce nukes
The documents in an archive seized by Israel show that Iran had “more advanced capabilities to make nuclear weapons themselves,” according to a paper being prepared by an anti-proliferation think tank, experts say. Foreign Policy, which saw an early draft of the paper being produced by the Institute for Science and International Security, reported that the information contained in the archive “demonstrates that Washington and the IAEA were constantly underestimating how close Tehran was to a bomb.”
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
