-
WHO missed several opportunities last spring to prevent outbreak from spreading
The global response to the Ebola epidemic has been slow and inadequate, according to aid organizations and governments in West Africa. The World Health Organization(WHO), the United Nationsagency tasked with coordinating international response to disease outbreaks, missed opportunities to prevent the disease from spreading when it was first diagnosed last spring, according to a draft internal WHO report.
-
-
Responses to Ebola markedly different from responses to AIDS
While there are some similarities between the AIDS epidemic and the Ebola outbreak, the response to the diseases by health officials and governments are completely different. The global response to Ebola has been swift compared to the response to AIDS, which was identified in 1981 but which did not receive international intervention until the mid-1990s, when the United Nations’ UNAIDS program was launched.
-
-
Some steps taken by schools, businesses for fear of Ebola seen as excessive
The plane carrying Amber Joy Vinson, the second Texas nurse to be diagnosed with Ebola, on the trip she took to from Cleveland to Dallas,is now in isolation in a Denver hangar.The 800 passengers who flew on the same planes as Vinson are being asked to self-quarantine for roughly twenty-one days. Navarro College in Corsicana, Texas has postponed recruiting applicants from Africa. Some see these and similar measures as excessive.
-
-
21-day quarantine for Ebola may not be enough to prevent spread of virus: Study
As medical personnel and public health officials are responding to the first reported cases of Ebola Virus in the United States, many of the safety and treatment procedures for treating the virus and preventing its spread are being reexamined. One of the tenets for minimizing the risk of spreading the disease has been a 21-day quarantine period for individuals who might have been exposed to the virus. A new study looks at the murky basis for our knowledge about the virus, namely previous outbreaks in Africa in 1976 (Zaire) and 2000 (Uganda), as well as the first nine months of the current outbreak, and suggests that twenty-one days might not be enough completely to prevent spread of the virus.
-
-
Medical advances should not lead to complacency regarding possible flu pandemic: Scientists
There have been five such pandemics in the past 100 years, the worst of which — the 1918 Spanish Flu — cost fifty million lives worldwide. As our ability to assess the pandemic risk from strains of influenza virus increases with the latest scientific developments, we must not allow ourselves to become complacent that the most substantial threats have been identified, argue an international consortium of scientists.
-
-
CDC assigns risk management teams to hospitals
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has announced that it would send a team of experts to any hospital in the country with a confirmed Ebola case, saying that if such a precaution had been taken at the recent botched infection case on 8 October in Dallas, Texas that facility staff would not have been at risk for infection. These disease control specialists will be able to manage situations including infection control, lab science, personal protective equipment, and the overall management of Ebola units and wards.
-
-
CDC’s disease detectives help deal with Ebola crisis
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Epidemic Intelligence Service(EIS) is the federal government’s intelligence gathering arm for mysterious or unidentified diseases anywhere in the world.The program is staffed with postdoctoral fellows who often go on to hold significant positions in public health or medical academia. The United States Public Health Service (now the CDC) established the EIS in 1951 out of concerns about biological warfare against the U.S. homeland during the Korean War.
-
-
IAEA to provide nuclear detection technology to help diagnose Ebola in West Africa
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) said it would provide specialized diagnostic equipment to help Sierra Leone in its efforts to combat the Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) outbreak. Later, the support is planned to be extended to Liberia and Guinea. The support is in line with a UN Security Council appeal and responds to a request from Sierra Leone. The IAEA assistance will supplement the country’s ability to diagnose EVD quickly using a diagnostic technology known as Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR). RT-PCR is a nuclear-derived technology which allows EVD to be detected within a few hours, while other methods require growing on a cell culture for several days before a diagnosis is determined.
-
-
How are nurses becoming infected with Ebola?
WHO, CDC, and health authorities in many countries recommend health workers treating Ebola wear surgical masks for protection, along with other personal protective equipment such gowns, gloves, and goggles. A glaring inconsistency of these guidelines is that lab scientists working with Ebola are recommended to use respirators, which offer more protection than surgical masks, while masks are deemed adequate for doctors and nurses at the front line. The hospital ward, however, is a far more contaminated and volatile environment than the sterile, highly controlled lab, and nurses have the closest contact with patients, and deserve all available protection for their occupational health and safety. In most responses, lack of knowledge about infection control may not be critical, but in the case of Ebola it may cost lives. The price of getting it wrong with flu guidelines might be a week in bed, but for Ebola it is far more likely to be death. The risk analysis equation we need to use must consider not only the probability of Ebola turning up on our shores, but also the consequences.
-
-
U.S. seeking innovative solutions for protecting healthcare workers on Ebola front lines
The U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) has issued a Broad Agency Announcement (BAA), saying the agency is looking for opportunities to co-create, co-design, co-invest, and otherwise collaborate in the development, testing, and scaling of practical and cost-effective innovations to help healthcare workers on the front lines provide better care and stop the spread of Ebola. USAID notes that this funding mechanism will not support research that does not provide a clear path to development and testing of prevention and intervention strategies. Awards are in the range of $100,000 to $1million.
-
-
New tool can be used as a universal Ebola drug target
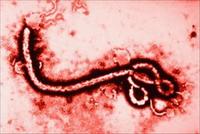
University of Utah biochemists have reported a new drug discovery tool against the Ebola virus. According to a study published in this week’s online edition of Protein Science, they have produced a molecule, known as a peptide mimic, which displays a functionally critical region of the virus that is universally conserved in all known species of Ebola. This new tool can be used as a drug target in the discovery of anti-Ebola agents which are effective against all known strains and likely future strains. The same group of biochemists has previously developed highly potent and broadly acting D-peptide inhibitors of HIV entry, currently in preclinical studies, and is now adapting this approach to Ebola using the mimics developed in this study.
-
-
CDC chief: U.S. “rethinking” Ebola strategy after Dallas nurse’s infection
U.S. federal health officials have urged hospitals to “think Ebola” as officials in Texas are anxiously trying to identify all staff involved in the care of America’s patient zero following the news that a nurse — Nina Pham, 26 — who was involved in his care is the first person to contract the disease in the United States. “We have to rethink the way we address Ebola infection and control because even a single infection is unacceptable,” Tom Frieden, director of the CDC, said on Monday. CDC officials are now watching the Dallas hospital personnel as they put on and take off their protective garb, retraining the staff and evaluating the type of protective equipment being used. The CDC officials were considering using cleaning products that kill the virus to spray down workers who come out of the isolation unit where the nurse is being treated. CDC will update its infection control guidance document, mostly likely next week. The agency’s guidance is just that – a guidance – since the agency does not have the authority to compel hospitals to follow its recommended procedures.
-
-
More research needed to address synthetic biology security concerns
Synthetic biology involves the design of new biological components, devices, or systems that do not exist in nature, or the redesign of existing natural biological systems. Synthetic biology aims to make biological systems work more efficiently or to design biological tools for specific applications — such as developing more effective antibiotics. A new paper examines security risks and policy questions related to the growing field of synthetic biology. While the author does not think the field is ripe for exploitation by terrorists, it does highlight significant gaps in our understanding of the nuts and bolts of lab work in synthetic biology that can contribute to security risks.
-
-
Simulations reveal California’s resilience to extreme droughts
The results from a series of several-year-old computer simulations reveal that the state of California may be more resilient to long-term drought conditions than previously believed. “The results were surprising,” said one of the scientists involved in the study. “California has a remarkable ability to weather extreme and prolonged droughts from an economic perspective.”
-
-
Ebola vaccine trials begin in Mali
The Center for Vaccine Development (CVD) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UM SOM), in conjunction with the Center for Vaccine Development of Mali (CVD-Mali) and the Ministry of Health of Mali, have begun a clinical trial in health care workers (and other front-line workers) to evaluate a promising experimental Ebola vaccine. The trial began on Wednesday, 8 October, with the vaccination of the first subject, followed by two additional participants on 9 October — all three being Malian health care workers. In the coming weeks, thirty-seven more health care workers will receive the vaccine.
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
