-
New, drug-resistant pandemic swine flu may go global

Health experts in Australia have expressed concerned about the threat of a new type of drug-resistant pandemic flu which is circulating in the population at large. These experts say that the new strain of swine flu has learned how to dodge the antiviral Tamiflu. While it is still rare, it is now spreading outside of hospitals. U.K. health officials, who have already recorded eight cases of the new strain in the United Kingdom, agree with their Australian counterparts that the new virus has the potential to turn global.
-
-
A better cyanide antidote for terrorist attacks, mass casualty events
The current procedure for treating cyanide poisoning requires highly trained paramedical personnel and takes time. Cyanide, however, is a fast-acting poison. In a situation involving mass casualties, only a limited number of victims could be saved with IV medication. Scientists are reporting discovery of a promising substance that could be the basis for development of a better antidote for cyanide poisoning.
-
-
Mankind is still at risk of the plague
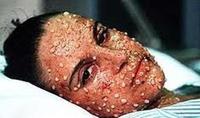
The plague has affected global population levels, with around seventy-five million people perishing during the fourteenth century’s Black Death. A new study finds that a number of factors show we are still at risk of plague today. The study also provides lessons for how best to control the plague.
-
-
“Dirty blizzard” accounts for missing Deepwater Horizon oil
The Deepwater Horizon disaster spilled more than 200 million gallons of oil into the Gulf of Mexico. Microbes likely processed most of the oil within months of the spill, but these microbes do not account for all of the spilled oil. Scientists have now found what happened to the oil not processed by microbes: the oil acted as a catalyst for plankton and other surface materials to clump together and fall to the sea floor in a massive sedimentation event that researchers are calling a “dirty blizzard.” The oily sediments deposited on the sea floor could cause significant damage to ecosystems and may affect commercial fisheries in the future.
-
-
Debate rages over U.S. purchases of smallpox medicine
The U.S. government paid Siga Technologies $463 million to buy enough smallpox drugs to treat two million people. Expert sharply disagree about the wisdom of the move: some say it was a reasonable purchase at a reasonable price, while others say the government purchased too large a quantity of the drug and too high a price.
-
-
Researchers trick bacteria to generate a safer vaccine
Vaccines which employ weakened but live pathogens to trigger immune responses have inherent safety issues but Yale researchers have developed a new trick to circumvent the problem — using bacteria’s own cellular mistakes to deliver a safe vaccine.
-
-
Antimicrobial resistance poses “catastrophic threat” to mankind
The U.K. Department of Health says that global action is needed to tackle the catastrophic threat of antimicrobial resistance, which in twenty years could see any one of us dying following minor surgery. A new report, providing a comprehensive overview of the threat of antimicrobial resistance and infectious diseases, highlights a “discovery void” with few new antibiotics developed in the past two decades. It highlights that, while a new infectious disease has been discovered nearly every year over the past thirty years, there have been very few new antibiotics developed, leaving our armory nearly empty as diseases evolve and become resistant to existing drugs.
-
-
June workshop on approaches to CBRNE incidents
NIST-organized workshop will explore ways to improve an all-of-government approach that increases resilience to international chemical, biological, radiological, nuclear, or explosive (CBRNE) incidents.
-
-
Marburg drug shows promise
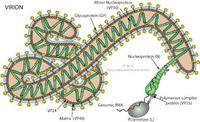
Marburg hemorrhagic fever is a severe and highly lethal disease with no effective treatments, and it has been classified as a Category A bioterrorism agent by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Sarepta Therapeutics announced positive results from a non-human primate study of AVI-7288, the company’s lead drug candidate for the treatment of Marburg virus infection.
-
-
Using plants for herbal defluoridation of drinking water

A filtration system based on a medicinal herb can quickly and easily remove “fluoride” from drinking water, say researchers in India. The technology uses parts of the plant Tridax procumbens as a biocarbon filter for the ion.
-
-
Arsenic in groundwater in Bangladesh naturally occurring
Human activities are not the primary cause of arsenic found in groundwater in Bangladesh. Instead, a team of researchers found that the arsenic in groundwater in the region is part of a natural process that predates any recent human activity, such as intensive pumping.
-
-
Sea surface temperature indicates onset of malaria epidemics
An estimated nine million malaria cases occur in India annually. Researchers find that sea surface temperatures in the tropical South Atlantic Ocean can be used accurately to forecast, by up to four months, malaria epidemics thousands of miles away in northwestern India.
-
-
Much less additional land available for biofuel production
Amid efforts to expand production of biofuels, scientists are reporting new estimates that downgrade the amount of additional land available for growing fuel crops by almost 80 percent.
-
-
Audits find “troubling” security flaws in CDC labs
Laboratories at the Centers for Disease Control Prevention (CDC) have been cited in government audits for failing to secure bioterror agents such as anthrax and plague. The audits also found that employees handling these agents have not been trained properly to do so.
-
-
DHS awards contract for utility plant at the Kansas biolab
DHS has awarded a $40 million contract to build a utility plant at a $1.15 billion animal research lab in Kansas. The 87,000 square foot facility will replace an animal research lab on Plum Island in New York and will be used to research deadly animal diseases that affect livestock.
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
