-
Chemical, physical traits of post-nuclear detonation fallout identified
Post-detonation nuclear forensics relies on advanced analytical techniques and an understanding of the physio-chemical processes associated with a nuclear detonation to identify the device type and the source of the nuclear material in the device. Researchers have begun to develop a technique that provides a practical approach for looking into the complex physical and chemical processes that occur during fallout formation following a nuclear detonation.
-
-
Antibiotic “smart bomb” targets specific strains of bacteria
Researchers have developed a de facto antibiotic “smart bomb” that can identify specific strains of bacteria and sever their DNA, eliminating the infection. The technique offers a potential approach to treat infections by multi-drug resistant bacteria.
-
-
The 9 January chemical leak in West Virginia is the latest in a long history of industrial accidents
The chemical spill that affected the water source in nine West Virginia counties in early January is part of a long history of industrial accidents resulting from the concentration of chemical and coal-mining operations in the region. The 9 January spill, which saw coal-cleansing chemical which leaked from Freedom Industries’ storage tank into the Elk River, leaving more than 300,000 residents without access to clean tap water for days, is the latest in a history of pollution which has poisoned groundwater, spewed toxic gas emissions, and caused fires and explosions.
-
-
Federal, state chemical safety agencies increasingly hampered by budget cuts
The budgets of state and federal agencies tasked with responding to the Elk River chemical spill have recently been cut, and these cuts have limited these agencies’ ability to prevent or respond to disasters such as the water crisis in West Virginia. “We do less,” said a CDC financial official, when asked the results of cuts. “What [the CDC director] has often been quoted as saying is that threats are not going down and so it is concerning to not be able to grow with the public health threats.”
-
-
Faster way to spot bacteria-tainted food -- and prevent illness
The regular appearance of food poisoning in the news, including a recent event that led to the recall of more than 33,000 pounds of chicken, drives home the need for better bacterial detection long before meats and produce make it to the dinner table.
-
-
Cause of one of the most devastating pandemics in human history found

An international team of scientists has discovered that two of the world’s most devastating plagues — the plague of Justinian and the Black Death, each responsible for killing as many as half the people in Europe — were caused by distinct strains of the same pathogen, one that faded out on its own, the other leading to worldwide spread and re-emergence in the late 1800s. These findings suggest a new strain of plague could emerge again in humans in the future.
-
-
New strategy for controlling epidemics in big cities
Influenza places a huge burden upon society, both physically and economically. It is estimated that influenza costs the United States economy over $87 billion annually. In a large city like Washington, D.C., with about 50,000 visitors on any given day who stay for just a few days, there is a constant influx of new people who are susceptible to infections. Further, they visit highly populated tourist destinations, where they come into contact with other visitors as well as residents. Researchers, for the first time, model in detail how transient populations impact the spread of an illness, and how outbreaks such as influenza can be curbed by encouraging healthy behaviors in high-traffic tourist destinations.
-
-
Drug alternatives to antibiotics come with their own problems
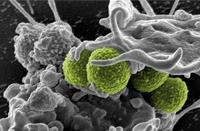
Researchers have been probing the long-term effectiveness of drugs currently being developed by the pharmaceutical industry. These drugs are intended for use in place of antibiotics, and they work by limiting the symptoms caused by a bug or virus in the body, rather than killing it outright. These treatments are designed to avoid the problem of infections becoming resistant to treatment, which has become widespread with antibiotics, but scientists caution that people given damage limitation treatments may appear healthy, but carry high levels of infection and so may be more likely to pass on disease. In addition, people with lesser symptoms could remain undiagnosed and add to the spread of disease.
-
-
Substitute for conventional antibiotics: Researchers discover a protein that kills bacteria
Bacterial resistance is a natural process. Over the past sixty years or so, however, the misuse and overuse of antibiotics has pushed more and more bacteria to become more and more resistant, undermining one of the pillars of modern health care. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics has developed faster than the production of new antibiotics, making bacterial infections increasingly difficult to treat. Scientists worry that a particularly virulent and deadly “superbug” could one day join the ranks of existing untreatable bacteria, causing a public health catastrophe comparable with the Black Death. Now, researchers have discovered a protein that kills bacteria. The isolation of this protein, produced by a virus that attacks bacteria, is a major step toward developing a substitute for conventional antibiotics.
-
-
Masking human sounds in water to protect swimmers, surfers from sharks
Researchers will attempt to “mask” the noise of swimmers from sharks after receiving a grant from the Australia’s Shark Hazard Mitigation Strategy. The project will first look at characterizing noises produced from swimming, surfing, and kayaking that are detectable by a number of large shark species. Researchers will then compare shark behavior when the human noises are detectable to when they are masked, to see whether masking typical swimmer noises can be effective at disrupting detection of humans.
-
-
China exports air pollution, as well as consumer goods, to the U.S.

Chinese air pollution blowing across the Pacific Ocean is often caused by the manufacturing of goods for export to the United States and Europe, according to findings of a new study. The study is the first to quantify how much of the pollution reaching the American West Coast is from the production in China of cellphones, televisions, and other consumer items imported here and elsewhere.
-
-
Tracking Internet searches to predict disease outbreak
The habit of Googling for an online diagnosis before visiting a GP can provide early warning of an infectious disease epidemic. A new study found that Internet-based surveillance has been found to detect infectious diseases such Dengue Fever and Influenza up to two weeks earlier than traditional surveillance methods. Researchers say that when investigating the occurrence of epidemics, spikes in searches for information about infectious diseases could accurately predict outbreaks of that disease.
-
-
Salmonella biofilms extraordinarily difficult, if not impossible, to kill
In the United States, an estimated million-plus cases of Salmonella occurs annually, with 23,000 hospitalizations and 450 fatalities reported each year. Researchers find that once Salmonella bacteria get into a food processing facility and have an opportunity to form a biofilm on surfaces, it is likely to be extraordinarily difficult, if not impossible, to kill it.
-
-
Carbon nanotube sponge helps in water clean-up
A carbon nanotube sponge capable of soaking up water contaminants, such as fertilizers, pesticides, and pharmaceuticals, more than three times more efficiently than previous efforts has been presented in a new study published today. The carbon nanotube (CNT) sponges, uniquely doped with sulphur, also demonstrated a high capacity to absorb oil, potentially opening up the possibility of using the material in industrial accidents and oil spill clean-ups.
-
-
Toxins-breathing bacteria to help industry, environment
Preliminary tests suggest that the bacteria could be used to remove these pollutants from the wastewater and protect the surrounding ecosystems. Buried deep in the mud along the banks of a remote salt lake near Yosemite National Park are colonies of bacteria with an unusual property: they breathe a toxic metal to survive. Researchers believe that this unusual organism may one day become a useful tool for industry and environmental protection – for example, the bacteria could be used simply to clean up the water, but it might also be possible for the bacteria to help humans recover and recycle the valuable elements in the water.
-
More headlines
The long view
What We’ve Learned from Survivors of the Atomic Bombs
Q&A with Dr. Preetha Rajaraman, New Vice Chair for the Radiation Effects Research Foundation in Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan.
Combatting the Measles Threat Means Examining the Reasons for Declining Vaccination Rates
Measles was supposedly eradicated in Canada more than a quarter century ago. But today, measles is surging. The cause of this resurgence is declining vaccination rates.
Vaccine Integrity Project Says New FDA Rules on COVID-19 Vaccines Show Lack of Consensus, Clarity
Sidestepping both the FDA’s own Vaccines and Related Biological Products Advisory Committee and the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), two Trump-appointed FDA leaders penned an opinion piece in the New England Journal of Medicine to announce new, more restrictive, COVID-19 vaccine recommendations. Critics say that not seeking broad input into the new policy, which would help FDA to understand its implications, feasibility, and the potential for unintended consequences, amounts to policy by proclamation.
