-
Former IAEA deputy director criticizes nuclear agency’s Iran investigations
Olli Heinonen, the former deputy director-general of the International Atomic Energy Agency has criticized the agency for “reduc[ing] the level of transparency and details in its reporting” on Iran’s nuclear program, making it “practically impossible” to confirm that Iran is complying with the terms of the nuclear deal.
-
-
Sandia’s radiation security team helps protect the public in large events
Sandia National Laboratories’ Radiological Assistance Program (RAP) team is one of several Department of Energy (DOE)/National Nuclear Security Administration (NNSA) teams in nine U.S. regions. The teams provide radiological detection support for large public events in Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, New Mexico, and Arizona. They also help with major public events around the United States, such as Super Bowls or visits from the pope.
-
-
Exercising the U.S. nuclear forensics capabilities
The Domestic Nuclear Detection Office (DNDO) plays an important role in the field of nuclear forensics. In addition to advancing technical capabilities and supporting expertise development, DNDO coordinates with other partners to exercise the U.S. government’s ability to collect nuclear debris samples in the event of a detonation and transport them to laboratories for analysis.
-
-
Immobilizing radioactive waste in glass for millions of years
How do you handle nuclear waste that will be radioactive for millions of years, keeping it from harming people and the environment? It is not easy, but researchers have discovered ways to immobilize such waste – the offshoot of decades of nuclear weapons production – in glass and ceramics.
-
-
Nuclear CSI: Noninvasive procedure could spot criminal nuclear activity
Determining whether an individual – a terrorist, a smuggler, a criminal — has handled nuclear materials, such as uranium or plutonium, is a challenge national defense agencies currently face. The standard protocol to detect uranium exposure is through a urine sample; however, urine is able only to identify those who have been recently exposed. Scientists have developed a noninvasive procedures that will better identify individuals exposed to uranium within one year.
-
-
Nanomaterials help solve the problem of nuclear waste
In the last decades, nanomaterials have gained broad scientific and technological interest due to their unusual properties compared to micrometer-sized materials. Nuclear fuels production, structural materials, separation techniques, and waste management may all benefit from more knowledge in the nano-nuclear technology.
-
-
Developing tests for radiation absorbed in nuclear emergency
In a large-scale nuclear or radiological emergency, such as a nuclear detonation, hundreds of thousands of people may need medical care for injuries or illness caused by high doses of radiation. To help save as many people as possible and better prepare the nation for the health impacts of such catastrophic emergencies, HHS will sponsor late-stage development of two tests, known as biodosimetry tests, which can determine how much radiation a person’s body has absorbed.
-
-
HHS bolsters U.S. health preparedness for radiological threats
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ (HHS) Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response (ASPR) says that as a part of its mission to help protect Americans’ health following even the most unthinkable of disasters, it is purchasing two medical products to treat injuries to bone marrow in victims of radiological or nuclear incidents. Bone marrow is essential to producing blood.
-
-
Assessing the risk from Africa as Libya loses its chemical weapons
Libya’s remaining chemical weapons left over from the Gaddafi regime are now being safely disposed of in a German facility. This eliminates the risk of them falling into the wrong hands. But can these same hands acquire weapons of mass destruction from the rest of Africa? The disposal of Libya’s chemical weapons has lowered the risk of weapons of mass destruction in Africa. But we have seen how far non-state actors are willing to go to either produce or steal such weapons. For example, analysts envision militants known as “suicide infectors” visiting an area with an infectious disease outbreak like Ebola purposely to infect themselves and then using air travel to carry out the attack. Reports from 2009 show forty al-Qaeda linked militants being killed by the plague at a training camp in Algeria. There were claims that they were developing the disease as a weapon. The threat WMD pose cannot be ignored. African countries, with help from bilateral partners and the international community, have broadened their nonproliferation focus. They will need to keep doing so if the goal is effectively to counter this threat.
-
-
Risk of another Chernobyl- or Fukushima-type accident worryingly plausible

The biggest-ever statistical analysis of historical nuclear accidents suggests that nuclear power is an underappreciated extreme risk and that major changes will be needed to prevent future disasters. The researchers’worrying conclusion is that, while nuclear accidents have substantially decreased in frequency, this has been accomplished by the suppression of moderate-to-large events. They estimate that Fukushima- and Chernobyl-scale disasters are still more likely than not once or twice per century, and that accidents on the scale of the 1979 meltdown at Three Mile Island (a damage cost of about $10 billion) are more likely than not to occur every 10-20 years.
-
-
DHS takes delivery of RadSeeker which identifies threat materials in shielded, masked, or concealed situations
The first regular shipments of the Smiths Detection RadSeeker featuring Symetrica’s Discovery Technology Sub-System will begin this fall as the first part of a contract with the Department of Homeland Security (DHS). Symetrica’s Discovery Technology at the heart of RadSeeker identifies threat materials in shielded, masked, or concealed situations.
-
-
FBI’s WMD Directorate marks its first decade
If you can imagine a disaster involving explosives or the release of nuclear, biological, chemical, or radioactive material, there is a pretty good chance a group of subject-matter experts within the FBI has built an elaborate scenario around it and tested how well emergency responders face up to it. It is the main jobs of the Weapons of Mass Destruction (WMD) Directorate — to imagine worst-case scenarios and then devise ways to prevent and prepare for them. The Directorate was created ten years ago, on 26 July 2006.
-
-
Iran received secret exemptions from complying with some facets of nuclear deal

The nuclear deal between the P5+1 powers and Iran – the official named is the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA) — placed detailed limitations on facets of Iran’s nuclear program that needed to be met by Implementation Day, which took place on 16 January 2016. Most of the conditions were met by Iran, but some nuclear stocks and facilities were not in accordance with JCPOA limits on Implementation Day. In anticipation, the Joint Commission had earlier and secretly exempted them from the JCPOA limits. “Since the JCPOA is public, any rationale for keeping these exemptions secret appears unjustified,” say two experts. “Moreover, the Joint Commission’s secretive decision making process risks advantaging Iran by allowing it to try to systematically weaken the JCPOA. It appears to be succeeding in several key areas.”
-
-
A new generation of low-cost, networked, nuclear-radiation detectors
A DARPA program aimed at preventing attacks involving radiological “dirty bombs” and other nuclear threats has successfully developed and demonstrated a network of smartphone-sized mobile devices that can detect the tiniest traces of radioactive materials. Combined with larger detectors along major roadways, bridges, other fixed infrastructure, and in vehicles, the new networked devices promise significantly enhanced awareness of radiation sources and greater advance warning of possible threats.
-
-
Looking from space for nuclear detonations
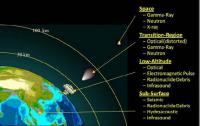
Sandia has been in the business of nuclear detonation detection for more than fifty years, starting with the 1963 launch of the first of twelve U.S. Vela satellites to detect atmospheric nuclear testing and verify compliance with the Limited Test Ban Treaty of 1963 and subsequently the Threshold Test Ban Treaty of 1974. That marked the start of the U.S. Nuclear Detonation Detection System that supports treaty monitoring. The Global Burst Detection (GBD) system launched 5 February from Cape Canaveral aboard the 70th Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite. The GBD looks for nuclear detonations around the world, offering real-time information about potential activity to U.S. policymakers. The launch was the 12th and final of the Block IIF (GPSIIF) series of GPS satellites in medium Earth orbit.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
