-
New technology increases awareness of landslide risks

Engineers have created a new way to use lidar technology to identify and classify landslides on a landscape scale, which may revolutionize the understanding of landslides in the United States and reveal them to be far more common and hazardous than often understood. The new, non-subjective technology can analyze and classify the landslide risk in an area of fifty or more square miles in about thirty minutes — a task that previously might have taken an expert several weeks to months. It can also identify risks common to a broad area rather than just an individual site.
-
-
Transforming planes into flying aircraft carriers
Military air operations typically rely on large, manned, robust aircraft, but such missions put these expensive assets — and their pilots — at risk. While small unmanned aircraft systems (UAS) can reduce or eliminate such risks, they lack the speed, range, and endurance of larger aircraft. These complementary traits suggest potential benefits in a blended approach — one in which larger aircraft would carry, launch, and recover multiple small UAS. A flying carrier would allow the United States to use of drones in areas where the United States has no access to nearby airfields, but recovering a drone in mid-air remains a daunting technical challenge.
-
-
New acoustic sensor for chemical, biological detection
Testing for ovarian cancer or the presence of a particular chemical could be almost as simple as distinguishing an F sharp from a B flat, thanks to a new microscopic acoustic device that has been dramatically improved by scientists at the Argonne National Laboratory. The device, known as a surface acoustic wave (SAW) sensor, detects frequency changes in waves that propagate through its crystalline structure. This makes it ideal for detecting the presence of chemicals or biomarkers present in a liquid or gas.
-
-
Wi-Fi signals enable through-wall detection
Engineers prove the concept that local Wi-Fi signals can be used to monitor moving objects and bodies that are otherwise visually obscured. Although fundamentally similar to traditional radar systems, their novel approach is entirely passive — utilizing the wireless signals that already swamp our urban airways. This technology has a wide range of applications from healthcare monitoring, security and emergency disaster relief, to finding earthquake survivors in fallen buildings.
-
-
New app turns smartphones into sensors for an earthquake early-warning system
The MyShake app, still in test mode, uses smartphone accelerometers and locators to augment the data on incoming quakes issued by the 400 seismometers which are part of California’s ShakeAlert program.Registered phones act as additional earthquake sensors, as the app runs an algorithm which detects when the phone is still or shaking. Should several registered phones in the same area begin to shake at the same time, an earthquake alert is issued.
-
-
Generating fuel from sunlight
Researchers have made significant progress towards developing a process of Artificial Photosynthesis (AP) that could replace the use of fossil fuels in the future. AP is the industrial process of preparing fuels and chemicals from nothing more than carbon dioxide, water and sunlight. It is a vital process that would be the foundation of a world that would no longer need fossil fuels.
-
-
Boeing completes testing of new anti-jamming technology

Boeing says it has proven its new anti-jamming communications technology is capable of operating as either a ground-based user terminal or satellite-based networking hub, enabling the military to send and receive secure communications at a significantly lower cost by using existing terminals and satellites.
-
-
Cockroach cyborgs use microphones to detect, trace sounds in collapsed buildings
Researchers have developed technology that allows cyborg cockroaches, or biobots, to pick up sounds with small microphones and seek out the source of the sound. The technology is designed to help emergency personnel find and rescue survivors in the aftermath of a disaster. The researchers have also developed technology that can be used as an “invisible fence” to keep the biobots in the disaster area. “In a collapsed building, sound is the best way to find survivors,” says one of the researchers.
-
-
Mental-health apps may reduce number of mass shooting events
Between 1982 and 2011, mass shootings occurred every 200 days on average. S since 2011, mass shootings have occurred every sixty-four days on average. Mass shootings have one thing in common: the culprits all suffered from mental illness and the condition was known to at least one person. New mobile app educates the public about mental illness and provides local and national resources for early intervention and treatment.
-
-
Sandia Lab’s mobile neutron imager shines in urban emergency response exercise

A nuclear device has been hidden in a high-rise building in a major metropolitan area. Emergency responders have intelligence that narrows down the location to a single city block, but it is not safe to search door-to-door. Can they identify the exact location of the device quickly without the culprits realizing a search is on? The answer is a definite yes. Sandia Lab’ mobile imager of neutrons for emergency responders (MINER) system did just that at an emergency response exercise in downtown Chicago earlier this year. The exercise used a sealed laboratory radiation source that mimics the radioactive signature of more nefarious material.
-
-
New smart key software enhances security for homes businesses
Computer scientists and security specialists have created an innovative electronic smart key system that aims to provide a safer and more flexible security system for homes and businesses. eLOQ is a new software system for the creation and management of electronic keys and locks which cannot be copied or picked.
-
-
Students point to future of ocean robotics in new global game
College students from around the world demonstrated they could have a hand in shaping the future of ocean robotics as they competed in the first Maritime RobotX Challenge, which was held 24-26 October in Singapore. “Developing autonomy for surface vessels is still in its early stages, and these students have the opportunity to come up with solutions that could set new standards in this field,” said Assistant Chief of Naval Research Capt. Rob Palisin, who helped judge the competition. “In turn, the Navy gets the chance to observe the best young engineers in action and learn from their approaches.”
-
-
Next-generation technology for first responders: intuitive, instinctive, and interoperable
DHS’s Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) has a vision for a new age of first responders, a vision which will enable first responders and their technology to be more intuitive, instinctive, and interoperable.TheNext-Generation First Responder suit will incorporates wearables, the Internet, and cellular connectivity, along with multiple environmental and biological sensors to help firefighters, law enforcement, and aid workers, better perform their jobs safely.
-
-
Light frequencies help sniff out deadly materials from a distance
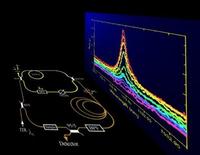
Spectroscopic chemical sensing, which measures the frequency of light absorbed or scattered from a substance to help determine its molecular identity, can be used to detect traces of biological and chemical agents and residue from explosive materials. New program aims to develop chip-sized, optical frequency combs which accurately identify even tiny traces of dangerous biological and chemical substances several football fields away.
-
-
Building a better lie detector
The Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA), within the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI), announced the other day the winner of its first public challenge contest, Investigating Novel Statistical Techniques to Identify Neurophysiological Correlates of Trustworthiness (INSTINCT). The winning solution, JEDI MIND — Joint Estimation of Deception Intent via Multisource Integration of Neuropsychological Discriminators — uses a combination of innovative statistical techniques to improve predictions approximately 15 percent over the baseline analysis.
-
More headlines
The long view
Risk Assessment with Machine Learning
Researchers utilize geological survey data and machine learning algorithms for accurately predicting liquefaction risk in earthquake-prone areas.
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
New Approach Detects Adversarial Attacks in Multimodal AI Systems
New vulnerabilities have emerged with the rapid advancement and adoption of multimodal foundational AI models, significantly expanding the potential for cybersecurity attacks. Topological signatures key to revealing attacks, identifying origins of threats.
