-
“Second skin” uniform protects soldiers from biological, chemical agents in the field
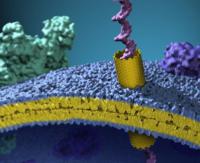
In work that aims to protect soldiers from biological and chemical threats, scientists have created a material that is highly breathable yet protective from biological agents. This material is the first key component of futuristic smart uniforms that also will respond to and protect from environmental chemical hazards.
-
-
Using gels for biological decontamination

Removing chemical, biological, radiological, and toxic contaminants from a range of surface types could be as easy as peeling off a sticker thanks to research conducted by scientists at the U.S. Army’s Edgewood Chemical Biological Center (ECBC) and industry partner CBI Polymer.The researchers explored how a HydroGel can be modified to decontaminate surfaces contaminated with biological agents.
-
-
Testing NYC subway biodefenses

Researchers took to the New York City subway system 9-13 May to study how a surrogate for a biological agent, such as anthrax, might disperse throughout the nation’s largest rapid transit system as a result of a terrorist attack or an accidental release. The study is part of a five-year DHS project called Underground Transport Restoration (UTR) and was conducted in accordance with the National Environmental Policy Act.
-
-
Pennsylvania superbug infection could mean "the end of the road" for antibiotics: Researchers
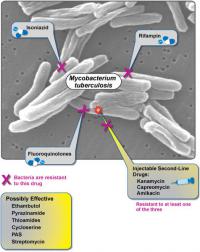
Researchers have, for the first time, found a person in the United States carrying a bacteria resistant to antibiotics of last resort. Top U.S. public health officials say this is alarming, and could mean “the end of the road” for antibiotics. Researchers say that the discovery “heralds the emergence of a truly pan-drug resistant bacteria.”
-
-
New paper filter removes viruses from water
More than 748 million people around the world lack access to safe drinking water and basic sanitation. Water-borne infections are among the global causes for mortality, especially in children under age of five, and viruses are among the most notorious water-borne infectious microorganisms. They can be both extremely resistant to disinfection and difficult to remove by filtration due to their small size. Scientists have developed a simple paper sheet which can improve the quality of life for millions of people by removing resistant viruses from water.
-
-
Rapid detection of E. coli in water
Tragedies like the E. coli outbreak in Ontario’s Walkerton in May 2000 could be averted today with a new invention by researchers at York University that can detect the deadly contaminant in drinking water early. Anew technology has cut down the time taken to detect E. coli from a few days to just a couple of hours.
-
-
Airflow study to be conducted in NYC Subway
The Department of Homeland Security (DHS) Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) will conduct a week-long airflow study in portions of the New York City (NYC) subway system to gather data on the behavior of airborne particles in the event contaminants were released. This study poses no risk to the general public and will run from 9 to 13 May.
-
-
Cellphone-sized device detects the Ebola virus quickly

The worst of the recent Ebola epidemic is over, but the threat of future outbreaks lingers. Monitoring the virus requires laboratories with trained personnel, which limits how rapidly tests can be done. Now scientists report in ACS’ journal Analytical Chemistry a handheld instrument that detects Ebola quickly and could be used in remote locations.
-
-
New Yorker sentenced to 16 years for trying to buy ricin
It was a scary scenario: Chinese national Cheng Le, living in New York City, attempted to order ricin through the so-called dark Web. Ricin is a highly potent and potentially fatal toxin with no known antidote. What did Le plan to do with the ricin? Nothing good. According to U.S. Attorney for the Southern District of New York Preet Bharara, “In Le’s own words, established at trial, he was looking for ‘simple and easy death pills’ and ways to commit ‘100 percent risk-free’ murder.”
-
-
Paper-based test to help prevent food poisoning
The foodborne bacteria Salmonella alone led to nearly 20,000 hospitalizations and almost 400 deaths in 2013. Economists estimate that the treatment of all these patients and the related productivity losses cost more than $3 billion annually. And those numbers account for just one of the fifteen pathogens responsible for most of the food poisoning cases. Scientists have developed a simple, paper-based test that could help detect pathogens hitchhiking on food before they reach store shelves, restaurants and, most importantly, our stomachs.
-
-
Cloud-based biosurveillance ecosystem

The Departments of Defense and Homeland Security are developing a system which lets epidemiologists scan the planet for anomalies in human and animal disease prevalence, warn of coming pandemics, and protect soldiers and others worldwide.
-
-
U.S. bioterrorism detection program unreliable: GAO
DHS’s BioWatch program aims to provide early indication of an aerosolized biological weapon attack. Until April 2014, DHS pursued a next-generation autonomous detection technology (Gen-3), which aimed to enable collection and analysis of air samples in less than six hours, unlike the current system (Gen-2), which requires manual intervention and can take up to thirty-six hours to detect the presence of biological pathogens. A GAO report found that DHS lacks reliable information about BioWatch Gen-2’s technical capabilities to detect a biological attack, and therefore lacks the basis for informed cost-benefit decisions about upgrades to the system.
-
-
Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) technology for on-site detection
Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) technology currently is applied using chemical analysis of materials, such as scanning at airports to identify what materials may be inside of glass vials. Researchers want to expand SERS for use in biological applications that could employ antibodies for purposes such as identifying viruses, water toxins, or pathogens in food samples. The researchers work on developing a small hand-held device that allows users to take a sample, put it in a glass vial and insert into the instrument for rapid identification.
-
-
The history of biological weapons use
Few comprehensive, definitive histories of biological warfare have been written, many events reported in the literature never happened, and few details are available about some uses of biological weapons which most certainly did occur. A new review of the literature on actual and alleged instances of biological warfare finds that the incidence of illicit biological agent use has been greater than many people may realize, even as the effects have been relatively limited.
-
-
Highly sensitive test to detect and diagnose infectious disease, superbugs
Infectious diseases such as hepatitis C and some of the world’s deadliest superbugs — C. difficile and MRSA among them — could soon be detected much earlier by a unique diagnostic test, designed to easily and quickly identify dangerous pathogens. Researchers have developed a new way to detect the smallest traces of metabolites, proteins or fragments of DNA. In essence, the new method can pick up any compound that might signal the presence of infectious disease, be it respiratory or gastrointestinal.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
