-
Shale may offer long-term home for nuclear waste
About 77,000 tons of spent nuclear fuel currently sit in temporary above-ground storage facilities, and it will remain dangerous for tens or hundreds of thousands of years or longer. Experts say that since the U.S. government abandoned plans to develop a long-term nuclear-waste storage site at Yucca Mountain in Nevada in 2009, finding new long-term storage sites must be a priority. Shale deep under the Earth’s surface could be a solution. France, Switzerland, and Belgium already have plans to use shale repositories to store nuclear waste long-term.
-
-
Storm surges, rising sea levels threaten New Jersey’s beach-centered tourism industry
Sea level at the Jersey Shore could rise by thirty-one inches by the year 2050, posing a threat to New Jersey’s $38 billion tourism industry. Experts say that the potential for more harsh storms and sea level rise calls for better promotion of what else New Jersey has to offer tourists aside from the beach.
-
-
NERC drill finds U.S. grid preparedness insufficient
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) reported that its recent GridEx II exercise has highlighted the fact that nearly all the utilities which took part in the two-day drill last November – a drill aiming to test the preparedness of the U.S. power grid to withstand cyber and physical attacks – admitted that their planning for such attacks was insufficient. NERC’s president, Gerry Cauley, said that protecting utilities against cyber and physical attacks should be considered in the context of measures taken to protect the grid from other threats. He noted that utilities are already hardening their systems against storms like Hurricane Sandy, while working to determine their vulnerability to solar activity that changes the earth’s magnetic field.
-
-
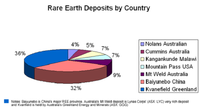
China's share of rare earths minerals declining amid falling demand

China still dominates the world’s rare earth elements market, but its share in global production has been steadily decreasing in recent years. A new study which shows a dramatic decline in these minerals’ prices has shaken he industry. In 2013, China accounted for 92.1 percent of high-tech rare earth oxides produced in the world. The percentage is still high, but it is a decline from 2010, when China accounted for 97.6 percent of global production of the mineral and fell to 95.1 percent in 2011.
-
-
Value of U.S. mineral production decreased in 2013
Last year, the estimated value of mineral production in the United States was $74.3 billion, a slight decrease from $75.8 billion in 2012. According to the U.S. Geological Survey’s annual Mineral Commodity Summaries 2014 report, the 2013 decrease follows three consecutive years of increases. Net U.S. exports of mineral raw materials and old scrap contributed an additional $15.8 billion to the U.S. economy.
-
-
Washington, D.C. area leads nation in cybersecurity jobs

The Washington, D.C metropolitan area had more than 23,000 cybersecurity job postings in 2013, making the region the leading destination for cybersecurity jobs, followed by the New York metro area with 15,000 cybersecurity job postings in 2013. On a state-by state basis, Virginia ranks second and Maryland ranks sixth, with Virginia reporting 25.1 cybersecurity job postings per 10,000 residents and Maryland posting 18.1 jobs per 10,000 residents.
-
-
S.C. politicians want decision to halt work on Savannah River plutonium plant reversed
Three Republican lawmakers from South Carolina — Senator Lindsey Graham and Representatives Tim Scott and Joe Wilson have – have asked South Carolina governor Nikki Haley to “explore any legal avenues” to prevent the mixed-oxide fuel (MOX) project at the Savannah River Sitefrom shutting down. The administration has decided to put the project on hold after repeated delays and cost overruns averaging 60 percent over the original estimates.
-
-
Libyan PM escapes country after assembly ousts him over oil tanker fiasco
Libya’s General National Congress has approved a no-confidence motion against Prime Minister Ali Zeidan and designated the defense minister as acting prime minister. Zeidan left Libya after the vote, in all likelihood for Italy. The no-confidence vote came after a North Korean-flagged tanker named Morning Glory managed to sail away from the port of al Sidra, carrying 234,000 barrels of crude oil from rebel-held oil fields. Last summer, armed militias in east Libya took over most of the country’s oil fields – and also three ports, with partial control of a fourth — bringing oil exports, which had amounted to 1.6 million barrels a day, to a halt. U.S. describes oil sale by the militias as “theft” from the Libyan people.
-
-
Blackstone to acquire Accuvant, an enterprise information security specialist
Denver, Colorado-based Accuvant, a specialist in enterprise information security, has reached a definitive agreement under which Blackstone will acquire a majority stake in Accuvant as part of their private equity portfolio. The transaction is expected to close in April pending relevant regulatory approvals.
-
-
Innovative nuclear radiation detector reaches the market

A handheld radiation camera developed by University of Michigan engineering researchers offers nuclear plant operators a faster way to find potentially dangerous hot spots and leaky fuel rods. The new Polaris-H detector lays a gamma-ray map over an image of a room, pinpointing radiation sources with unprecedented precision. At least four U.S. nuclear power plants are using versions of the camera, which is now available commercially through the U-M spinoff company H3D.
-
-
Iona College to Launch BS, BA, MS concentrations in cybersecurity
Iona College announced the launch in fall 2014 of undergraduate and graduate programs in computer science with a concentration in cyber security. The concentration will be offered for the Bachelor of Science, Bachelor of Arts, and the Master of Science degrees. The programs will provide students with fundamental cyber security skills, theoretical as well as hands-on experience. Students are exposed to new research ideas across many cyber security areas including software security, Web application security, mobile security, networking security, database security, and cryptography.
-
-
Small biomass power plants could help rural economies, stabilize national power grid

As energy costs rise, more Americans are turning to bioenergy to provide power to their homes and workplaces. Bioenergy is renewable energy made from organic sources, such as biomass. Technology has advanced enough that biomass power plants small enough to fit on a farm can be built at relatively low costs. Researchers have found that creating a bioenergy grid with these small plants could benefit people in rural areas of the country as well as provide relief to an overworked national power grid.
-
-
Allowing Terrorism Risk Insurance Act to expire could hurt national security: Study
The current terrorism risk insurance program has a $27.5 billion threshold for aggregate losses that are paid by the insurance industry and commercial policyholders before the government program begins paying. The program will expire in 2014 and Congress again is considering the appropriate government role in terrorism insurance markets. Allowing the federal terrorism risk insurance act to expire could have negative consequences for U.S. national security, according to a new study from the RAND Corporation.
-
-
High level of “brain waste” among highly educated immigrants
Many highly educated immigrants coming to the United States without a job lined up have been unable to find work at their level of education, leading to considerable “brain waste,” researchers have found. The prevalence of such “brain waste” exceeded 40 percent for immigrants with a bachelor’s degree, 50 percent for those with a doctoral or professional degree, and 75 percent for those with a master’s degree.
-
-
Biometric security for mobile devices becoming mainstream
Biometric security such as fingerprint, face, and voice recognition is set to hit the mainstream as global technology companies market the systems as convenient and easy to use. The latest biometric technologies are not without their security issues, but they are marketed as more convenient than traditional methods rather than more secure, and encourage adoption by people who currently do not have any security on their phone at all.
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
