-
Cost of plutonium disposal facility skyrockets
The Mixed Oxide (MOX) nuclear fuel factory at the Savannah River Site in South Carolina, being built to help dispose of cold war-era weapon-grade plutonium, would cost up to $30 billion in addition to the $4 billion spent on construction so far. The staggering cost overruns have led many to call for a new, less expensive solution. Matthew Bunn, a former Clinton White House official who helped develop the plutonium disposal program, agrees that the cost of the MOX factory is excessive. “The things we’re trying to accomplish aren’t worth that amount of money,” he said.
-
-
Damage to coastal infrastructure from storm surges, floods may reach 9% of global GDP
Damage to the world’s coastal infrastructure as a result of flooding, sea level rise, and coastline development is expected to cost as much as 9 percent of global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) according to a new report published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences(PNAS).
-
-
Improving livestock diets to bolster food security, combat climate change
Livestock production is responsible for 12 percent of human-related greenhouse gas emissions, primarily coming from land use change and deforestation caused by expansion of agriculture, as well as methane released by the animals themselves, with a lesser amount coming from manure management and feed production. A new study shows that within the current systems, farmers would find it more profitable in coming years to expand livestock production in mixed systems — where livestock are fed on both grass as well as higher quality feed — rather than in pure grass-based systems. This development, would lead to a 23 percent reduction of emissions from land use change in the next two decades without any explicit climate mitigation policy.
-
-
Facebook-WhatsApp deal raises security concerns
Facebook’s acquisition of WhatsApp made headlines for its sheer size — $4 billion in cash and $15 in Facebook stock, for a total of about $19 billion – but security experts are worried about the security aspects of the deal. Even security specialists advising WhatApp’s customers not to panic about the deal, use language which is not exactly reassuring. Serge Malenkovich of Kaspersky Labs says: “There are no new [emphasis in original] reasons to worry about messaging privacy. Honestly speaking, WhatsApp was never meant to be a true confidential messaging tool; there were even multiple breaches in the past, including some attacks, which make eavesdropping possible.”
-
-
Not much is known about long-term health effects of chemical leaked in W.Va.
In January, 10,000 gallons an obscure chemical called 4-methylcyclohexanemethanol, or MCHM, used in processing coal, leaked from storage tanks into the nearby Elk River in the Charleston, West Virginia area, contaminating the water of more than 300,000 residents for days. To what degree MCHM affects long-term human and fetal health is a major concern for residents because of the lack of complete toxicology and other studies on the chemical.
-
-
50-state roadmap to renewable energy unveiled
Researchers recently developed detailed plans to transform the energy infrastructure of New York, California, and Washington states from fossil fuels to 100 percent renewable resources by 2050. The new roadmap to renewable energy for all fifty states was presented on 15 February at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS) in Chicago. The online interactive roadmap is tailored to maximize the resource potential of each state.
-
-
Iran-Russia oil deal threatens nuclear negotiations
Iran said that in exchange for Iranian oil, Russia could build a second reactor at Iran’s Bushehr nuclear power plant. Russia could also provide Iran with trucks, railroad tracks, mini-refineries, grain, and other goods for Iranian oil. In a deal worth $1.5 billion a month, Iran would export 500,000 barrels of oil per day to Russia. The deal would increase Iran’s oil exports, which have been reduced to about one million barrels a day by American and European sanctions aimed at curbing Iran’s nuclear program.
-
-
Secure Communities triggers deportation of undocumented immigrants with no criminal records
The U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement’s (ICE) Secure Communitiesprogram sends fingerprint data from local law enforcement and the Federal Bureau of Investigationto immigration officers to identify and deport illegal immigrants who commit major crimes. The program has expanded from fourteen jurisdictions in 2008 to more than 3,000 today. Immigration advocates say that the program’s emphasis on identifying and deporting undocumented immigrants who have committed crimes in the United States notwithstanding, it has also triggered the deportation of 5,964 undocumented immigrants with no criminal records.
-
-
QR codes threaten Internet security
Internet security experts have raised concerns about the growing use of Quick Response codes, also known as QR codes. Because the codes can only be read by a machine, such as a smart phone, it is difficult for people to determine what they are about to download. The codes, which are often used in marketing campaigns, could also be used to subscribe people to unwanted services, such as premium SMS.
-
-
Researchers tackle rare Earth materials shortage
The demand for rare Earth materials is growing much faster than production. Rare Earth metals do occur in the earth’s crust, but not in sufficiently high concentrations. This is why only one country — China — has so far been supplying the entire world with these elements. In recent years, however, China has begun to restrict its export of these materials. European research organizations have teamed up to address growing rare Earth materials by examining a more focused approach to recycling scrap.
-
-
Lockheed Martin launches updated, expanded Engineers in the Classroom (EITC) toolkit
This week is National Engineers Week, and Lockheed Martin, a company which employs 60,000 of them, is marking the week by launching an updated and expanded Engineers in the Classroom (EITC) toolkit created in partnership with National Geographic. These materials, which can be found on Lockheed Martin’s EITC Web site, will help engineers and scientists engage students in hands-on, creative activities with a goal of inspiring them to consider careers in STEM.
-
-
Skeptics doubt voluntary Cybersecurity Framework will achieve its goal
The Framework for Improving Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity, developedby NIST following Executive Order 13636to promote cybersecurity, has been received with both support and skepticism from critical infrastructure industries. The 41-page document, put together by industry and government experts, offers guidelines on cybersecurity standards and best practices to critical infrastructure firms. It says its role is to be a complement to industries’ existing risk management practices.Skepticssay that without incentives, legislation, or enforcement, the guidelines will not be adopted.”The marketplace will punish any company that implements anything that could be considered excessive security, because it will increase their costs,” says an industry insider.
-
-
Power cuts will be more common in the future

U.S. figures show that since 2007, commercial and domestic air-conditioning alone consumed 484billion kilowatt hours of electricity — not much more than the country’s total energy consumption in the mid-1950s. The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) has warned that U.S. generation systems could collapse by 2020 without $100 billion of new investment in power stations. Demands of high-powered electrical appliances, a growing world population, and inadequate investment in the power sector will create more frequent power blackouts in Western societies.
-
-
Resistance shapes the discovery of new insecticides
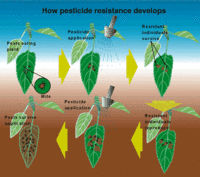
Recent news around the world has focused on the dangers of antibiotic resistance. – and the CDC estimates over two-million illnesses and 23,000 deaths occurred in 2013 as a result of antibiotic resistance in bacteria and fungus. But what of another type of resistance which can also have a huge impact on the population: that to insecticides? Livestock, for example, are affected by buffalo flies; farmers and customers are familiar with the total devastation caused by fruit flies; malaria mosquitoes and bed bugs are becoming more resistant to existing chemicals. Even our pets are affected: fleas and ticks are continuing their march, leading to a need for newer, often more expensive synthetic chemistries. The price of insecticide resistance — in the form of R&D costs for new compounds — is passed from chemical companies, to farmers, to consumers.
-
-
Cuba to lose its U.S. banking service today
Today (Monday) Cuba’s bank in the United States, Buffalo-based M&T Bank, will stop accepting Cuba’s deposits. The bank will close Cuba’s accounts on 1 March 2014. One result will be that travel between Cuba and the United States will become more difficult because banking services are necessary for issuing travel visas. Cuba’s diplomatic mission in Washington, D.C., and the Cuban Permanent Mission to the United Nations in New York have been unable to find an American bank to handle the country’s U.S.-based accounts.
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
