-
FDA allows use of antibiotics in livestock despite “high risk” to humans

The Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has recently confirmed the link between antibiotic use on industrial farms and the rise of antibiotic resistance, saying there is “strong scientific evidence of a link between antibiotic use in food animals and antibiotic resistance in humans,” and warns of “potentially catastrophic consequences” if resistance is not slowed. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA), however, has quietly allowed thirty potentially harmful antibiotics, including eighteen rated as “high risk,” to remain on the market as additives in farm animal feed and water. The FDA first recognized the risks from the use of antibiotics in animal feed in 1977, when it proposed to withdraw approvals for animal feed containing penicillin and most tetracyclines. The agency has not followed through on its own findings – and has fought court orders to do so — and today 70 percent of all medically important antibiotics sold in the United States are sold for use in livestock production — not on humans.
-
-
The world likely to face more frequent, and more severe, blackouts
U.S. household electricity usage increased by 1,300 percent between 1940 and 2001. In the last few decades, air conditioning has been the greatest factor in increased electrical consumption, and one of the greatest sources of systematic strain, with considerably more blackouts occurring in the summer months than during winter. The electricity used to fuel America’s air conditioning is currently of a similar volume to the U.S. entire energy consumption in the 1950s. A new study reveals that today’s occasional blackouts are dress rehearsals for the future, when they will occur with greater frequency and increased severity. Power cuts will become more regular around the globe as electrical supply becomes increasingly vulnerable and demand for technology continues to grow at an unprecedented rate.
-
-
ExxonMobil to pay fines for violations at its Baton Rouge chemical facilities
In a settlement with Louisiana’s Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ), ExxonMobil is ordered to pay $2.329 million to address violations from 2008 to 2013 at its greater Baton Rouge facilities. ExxonMobil was cited for a series of problems at its refinery and resin-finishing and chemical plants in East Baton Rouge Parish, and its tank-farm facility in West Baton Rouge.
-
-
Halting bugs’ crop destruction in India saves up to $309 million
Researchers who first discovered a devastating pest in India and devised a natural way to combat it have now put an economic value on their counterattack: up to $309 million the first year and more than $1 billion over five years. This is the amount of damage the papaya mealybug would have wreaked on farmers and consumers in India without scientists’ intervention. The winning intervention centered on three natural enemies of the mealybug — three parasitic wasps from Mexico— which the U.S. government first employed in Florida after the pest spread there in the late 1990s.
-
-
Aussie police uncovers vast money laundering operation used by terrorists, criminals

Terror groups are known to rely on money laundering operations to finance their activities. A recent operation by an Australian government taskforce has revealed the scope of money laundering operations within the country’s borders. The investigation, which has uncovered forty money laundering operations in Australia, has so far seized $26 million in cash, seized $30 million worth in houses and other assets, and has intercepted drug shipments worth at least $530 million.
-
-
U.S. power plant emissions down

Power plants that use natural gas and a new technology to squeeze more energy from the fuel release far less of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide than coal-fired power plants do, according to a new analysis. The so-called “combined cycle” natural gas power plants also release significantly less nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide, which can worsen air quality.
-
-
Many VSATs operated with no security, leaving them vulnerable to hacking
Very-small-aperture terminals, or VSATs, are used by the oil and gas industry, utilities, financial firms, and news media to transmit information, often sensitive, from remote locations to headquarters. There are more than 2.9 million VSATs in operation around the world, with about two-thirds based in the United States. New security report says that at least 10,500 VSATs are operated with minimal or no security, and are wide open to being hacked.
-
-
China exports air pollution, as well as consumer goods, to the U.S.

Chinese air pollution blowing across the Pacific Ocean is often caused by the manufacturing of goods for export to the United States and Europe, according to findings of a new study. The study is the first to quantify how much of the pollution reaching the American West Coast is from the production in China of cellphones, televisions, and other consumer items imported here and elsewhere.
-
-
California lawmakers propose restricting use of antibiotics in livestock

The growth of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in humans has been attributed to the increasing use of antibiotics in livestock. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC) estimates that antibiotic-resistant bacteria infect more than two million Americans a year,killing at least 23,000 of them. California legislators are proposing new laws to restrict the use of antibiotics in livestock.
-
-
Economists propose market-driven solutions to the problem of antibiotic use in agriculture
Fifty-one tons of antibiotics are consumed daily in the United States, of which 80 percent are used in agriculture. To minimize the overuse of antibiotics in livestock, Aidan Hollis of the University of Calgary is proposing the imposition of an antibiotic tax on food producers, thus encouraging them to distinguish between good and bad use of antibiotics, since the fee would force farmers to purchase antibiotics only when needed to treat sick animals and not for non-illness purposes.Timothy Richards of Arizona State University says that more regulations or a tax would run the risk of harming the agriculture industry. He says that farmers and ranchers should clearly label their products as containing or not containing antibiotics, and then market dynamics would operate by “letting people follow labels and buy or not buy meats where antibiotics are used.”
-
-
New L.A. fault map threatens Hollywood development projects
The state of California recently released new geological maps which reveal the presence of an active earthquake fault along the path of major developments in Hollywood. The maps established a zone of 500 feet on both sides of the fault, and state law will require new developments within the zone to conduct underground seismic testing to determine whether the fault runs beneath planned development sites. Building on top of faults is prohibited. Three prominent Hollywood developments — the Millennium Hollywood skyscraper project, the Blvd6200 development, and an apartment project on Yucca Street — are within the 500-foot fault zone.
-
-
Healthcare industry to conduct cyberattack drill in March
The American health care industry, in partnership with the federal government, will in March conduct simulated cyberattacks targeting industry networks and resources in an effort to test the industry’s vulnerability to cyberattacks. This will be the first time insurers, hospitals, pharmaceutical manufacturers, and HHS will run coordinated drills. Healthcare is one of seventeen critical infrastructure sectors which, if attacked, could have damaging consequences for the country.
-
-
Massachusetts takes steps to withstand climate change impacts
Governor Deval Patrick of Massachusetts earlier this week unveiled a $50 million plan to help prepare Massachusetts for the challenges climate change poses to energy supplies, public health, transportation, and basic infrastructure in his state. A $40 million grant from the state’s Department of Energy Resources will help cities and towns develop protections around energy services, and $10 million will go toward shoring up critical coastal infrastructure and dam repair.
-
-
Time to replace GDP with new metrics: experts
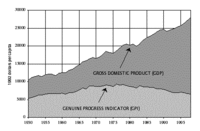
Gross Domestic Product is a misleading measure of national success, say public policy experts. “When it was instituted seven decades ago, GDP was a relevant signpost of progress,” they say. “Increased economic activity was credited with providing employment, income and amenities to reduce social conflict and prevent another world war. But the world today is very different compared to how it was then.”
-
-
NRC: storing spent nuclear fuel in cooling pools is safe
The nuclear reactors now in service in the United States were built with the assumption that the spent fuel would be removed from nuclear the facilities after a few years, but because the government has failed to provide a centralized place to store the spent fuel, utility companies have had to store an ever-growing quantity of it in spent fuel pools on the grounds of the facilities. Scientists argue that it would be safer to move some of the spent fuel into giant steel and concrete casks, where it can be stored dry, with no reliance on water, pumps, or filters to keep them cool. The nuclear industry and the NRC do not agree.
-
More headlines
The long view
Need for National Information Clearinghouse for Cybercrime Data, Categorization of Cybercrimes: Report
There is an acute need for the U.S. to address its lack of overall governance and coordination of cybercrime statistics. A new report recommends that relevant federal agencies create or designate a national information clearinghouse to draw information from multiple sources of cybercrime data and establish connections to assist in criminal investigations.
Trying to “Bring Back” Manufacturing Jobs Is a Fool’s Errand
Advocates of recent populist policies like to focus on the supposed demise of manufacturing that occurred after the 1970s, but that focus is misleading. The populists’ bleak economic narrative ignores the truth that the service sector has always been a major driver of America’s success, for decades, even more so than manufacturing. Trying to “bring back” manufacturing jobs, through harmful tariffs or other industrial policies, is destined to end badly for Americans. It makes about as much sense as trying to “bring back” all those farm jobs we had before the 1870s.
The Potential Impact of Seabed Mining on Critical Mineral Supply Chains and Global Geopolitics
The potential emergence of a seabed mining industry has important ramifications for the diversification of critical mineral supply chains, revenues for developing nations with substantial terrestrial mining sectors, and global geopolitics.
Are We Ready for a ‘DeepSeek for Bioweapons’?
Anthropic’s Claude 4 is a warning sign: AI that can help build bioweapons is coming, and could be widely available soon. Steven Adler writes that we need to be prepared for the consequences: “like a freely downloadable ‘DeepSeek for bioweapons,’ available across the internet, loadable to the computer of any amateur scientist who wishes to cause mass harm. With Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4 having finally triggered this level of safety risk, the clock is now ticking.”
