-
Terrorists used encrypted apps to plan, coordinate Paris attacks
The leaders of U.S. and European law enforcement and intelligence agencies have been explicit in their warnings: commercially available communication devices equipped with end-to-end encryption software make it impossible for security services to track terrorists plotting an attack – or monitor the terrorists’ communication while the attack is under way. Sources close to the investigation of the 13 November Paris terrorist attacks have now confirmed that the terrorists used the encrypted WhatsApp and Telegram messengers apps to communicate for a period before the attacks – and with each other during the attacks. What was said in those encrypted messages, and who sent and received these messages, may never be known, because the companies themselves do not have the key – or back door – to decrypt these messages. Thus, security services could not monitor such messages before an attack in order to prevent it, and cannot read these message after an attack to learn more about the terrorists’ network and support system.
-
-
Safer cyberspace through experimental cybersecurity research
How do cybersecurity experts discover how properly to defend a system or build a network which is secure? As in other domains of science, this process involves hypothesis, experimentation, and analysis — or at least it should. In reality, cybersecurity research can happen in an ad hoc fashion, often in crisis mode in the wake of an attack. A group of researchers has imagined a different approach, one in which experts can test their theories and peers can review their work in realistic but contained environments — not unlike the laboratories found in other fields of science. The researchers issued a report calling for a new generation of experimental cybersecurity research.
-
-
The mind of a cyberterrorist, a neglected aspect of cybersecurity
A new study is delving into an aspect of cybersecurity rarely explored before now: the human component. The reason why this topic is lesser known, a leading expert says, is that security professionals become very focused on the technological side of responding to attacks and lack the social psychology background to analyze and understand the human being on the other side of that attack.
-
-
U.S. officials barred from reviewing social media postings of visa applicants
Officials from DHS and the Department of State, as a general policy, do not check social media postings of applicants out of civil liberties concerns. With this policy in place, the department’s officials who handled Tashfeen Malik’s application could not have seen her pro-ISIS postings and note her growing radicalization. Officials from United States Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) and U.S. Immigration and Customs Enforcement (ICE) pressed for a change in DHS policy in light of the fact that social media is increasingly used by followers of jihadist groups to declare their allegiance, but the disclosures by Edward Snowden about NSA surveillance programs was behind the reluctance of DHS high officials to change the policy for fears such a change would further damage the administration’s standing with civil rights groups and European allies.
-
-
Protecting the U.S. electrical grid from cyberattack

Across the United States, 3,200 separate organizations own and operate electrical infrastructure. The widely dispersed nature of the nation’s electrical grid and associated control systems has a number of advantages, but since the late 1990s, cost pressures have driven the integration of conventional information technologies into these independent industrial control systems, resulting in a grid which is increasingly vulnerable to cyberattack, either through direct connection to the Internet or via direct interfaces to utility IT systems. DARPA is soliciting proposal for creating automated systems to restore power within seven days or less after a cyberattack on the grid.
-
-
DHS questioned over pressure it put on a library to disable Tor node
Back in September, Kilton Public Library in Lebanon, New Hampshire briefly disabled its Tor relay after local police, following a tip from agents with Homeland Security’s investigations branch that the network may be used by criminals or terrorists. A Congresswoman from California wants to know why DHS officials pressured the New Hampshire library to take down the relay node, and whether DHS has leaned on other organizations to do so.
-
-
Following indictments, China’s military reduces its commercial cybeespionage against American companies

The People’s Liberation Army (PLA) has reduced its cyberespionage activity targeting American companies since five PLA officers were indicted by the Department of Justice in May 2014. “The indictments had an amazing effect in China, more than we could have hoped for,” said one expert. In April, Obama signed an executive order calling for impose economic sanctions on individuals and entities that take part in or benefit from illicit cyber-activities such as commercial espionage. “If the indictments had the effect of getting the PLA to scale down, then sanctions likely will have a wider effect on other Chinese state-sponsored groups,” says another expert.
-
-
FBI unable to break 109 encrypted messages Texas terror attack suspect sent ahead of attack

FBI director James Comey told lawmakers this week that one of the suspects in the foiled terror attack in Garland, Texas, in May had exchanged 109 messages with sources in a “terrorist location” overseas ahead of the attack. U.S. intelligence and law enforcement agencies, however, have not been able to break into and read those messages because they were exchanged on devices equipped with end-to-end encryption software which, security services in the United States and Europe argue, make it impossible to monitor and track terrorists and criminals.
-
-
Low-cost malware detection

The battle between malware authors and security researchers has changed dramatically in the last few years. The purpose behind malware was often for the sake of a prank, to expose vulnerabilities, or for the sake of spite. Today, malware is more about stealing sensitive data and exploiting information for fraud, identity theft, and other criminal intent. An add-on for antivirus software that can scan across a computer network and trap malicious activity missed by the system firewall is being developed by an international team.
-
-
Untraceable communication -- guaranteed
Anonymity networks, which sit on top of the public Internet, are designed to conceal people’s Web-browsing habits from prying eyes. The most popular of these, Tor, has been around for more than a decade and is used by millions of people every day. Recent research, however, has shown that adversaries can infer a great deal about the sources of supposedly anonymous communications by monitoring data traffic though just a few well-chosen nodes in an anonymity network. Researchers have developed a new, untraceable text-messaging system designed to thwart even the most powerful of adversaries.
-
-
Concerns over attacks on the U.S. electrical grid increase after Paris attacks
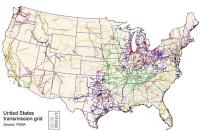
In the aftermath of the 13 November attacks in Paris, U.S. government agencies involved with grid security and utilities are preparing to thwart a major attack on the U.S. electrical grid. Government agencies and utilities believe an attack or series of attacks on the electrical grid of the United States is imminent — more so in the aftermath of the attacks on Paris. They are carrying out drills and exercises to brace for them.
-
-
EU Internet Forum launched to fight radicalization, terrorist content online
The EU earlier this week launched the EU Internet Forum. The aim of the forum is to bring together EU interior ministers, high-level representatives of major Internet companies, Europol, the EU counterterrorism coordinator, and the European Parliament. The EU says that the goal is to reach a joint, voluntary approach based on a public-private partnership to detect and address harmful material online.
-
-
Good apps talking to bad Web sites behind your back

In one of the first studies to analyze behind-the-scenes behaviors of good applications, researchers conducted a large-scale analysis of URLs embedded in 13,500 free android apps downloaded from Google Play. The apps tested were created by reputable developers and downloaded by many people, among them popular social media, shopping, news and entertainment apps. The researchers found that almost 9 percent of popular apps downloaded from Google Play interact with Web sites that could compromise users’ security and privacy; 15 percent talked to bad Web sites (with intentions that vary from harming devices, stealing confidential data or annoying users with spam); and 73 percent talked to low-reputation Web sites(those receiving a Web of Trust rating lower than 60/100).
-
-
New cybersecurity legislation would shield companies from public records laws
A legislation which passed both houses of Congress, but has not yet signed into law by the president, aims to encourage companies and organizations to share with the U.S. government information about cyberattacks and cyberthreats they experience –but critics say there is a catch: the legislation would severely restrict what the public can learn about the program.
-
-
USD launches a new Center for Cyber Security Engineering and Technology

To address the threats cyberattacks pose to the security, prosperity, and privacy of the United States and its citizens, the University of San Diego announced the creation of its Center for Cyber Security Engineering and Technology. The Center will focus on cybersecurity challenges through education, training, and research.
-
More headlines
The long view
Researchers Develop AI Agent That Solves Cybersecurity Challenges Autonomously
New framework called EnIGMA demonstrates improved performance in automated vulnerability detection using interactive tools.
