EnergyCompressing air for renewable energy storage
Enough Northwest wind energy to power about 85,000 homes each month could be stored in porous rocks deep underground for later use, according to a new, comprehensive study. Researchers identified two unique methods for this energy storage approach and two eastern Washington locations to put them into practice.
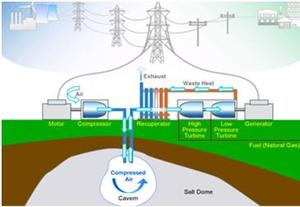
Air is compressed into underground storage, to be released later to power generators // Source: snecn.com
Enough Northwest wind energy to power about 85,000 homes each month could be stored in porous rocks deep underground for later use, according to a new, comprehensive study. Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL) and Bonneville Power Administration identified two unique methods for this energy storage approach and two eastern Washington locations to put them into practice.
A PNNL release reports that compressed air energy storage plants could help save the region’s abundant wind power — which is often produced at night when winds are strong and energy demand is low — for later, when demand is high and power supplies are more strained. These plants can also switch between energy storage and power generation within minutes, providing flexibility to balance the region’s highly variable wind energy generation throughout the day.
“With Renewable Portfolio Standards requiring states to have as much as 20 or 30 percent of their electricity come from variable sources such as wind and the sun, compressed air energy storage plants can play a valuable role in helping manage and integrate renewable power onto the Northwest’s electric grid,” said Steve Knudsen, who managed the study for the BPA.
Geologic energy savings accounts
All compressed air energy storage plants work under the same basic premise. When power is abundant, it is drawn from the electric grid and used to power a large air compressor, which pushes pressurized air into an underground geologic storage structure. Later, when power demand is high, the stored air is released back up to the surface, where it is heated and rushes through turbines to generate electricity. Compressed air energy storage plants can re-generate as much as 80 percent of the electricity they take in.
The world’s two existing compressed air energy storage plants — one in Alabama, the other in Germany — use man-made salt caverns to store excess electricity. The PNNL-BPA study examined a different approach: using natural, porous rock reservoirs that are deep underground to store renewable energy.
Interest in the technology has increased greatly in the past decade as utilities and others seek better ways to integrate renewable energy onto the power grid. About 13 percent, or nearly 8,600 megawatts, of the Northwest’s power supply comes from of wind. This prompted BPA and PNNL to investigate whether the technology could be used in the Northwest.
The release notes that to find potential sites, the research team reviewed the Columbia
