-
Tech companies, telecoms clash over cybersecurity executive order
Last August a cybersecurity bill died in Congress amid partisan bickering. On 12 February this year, President Obama packed many of that bill’s elements into a cybersecurity executive order. To make the order more acceptable to some of its congressional and industry critics, the president introduced an exemption which would take large technology companies off the list of companies subject to the new cybersecurity standards. This exemption placated some of the original cybersecurity bill’s critics, but angered others, chief among them telecommunication companies.
-
-
Marburg drug shows promise
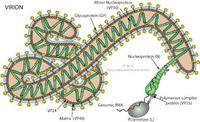
Marburg hemorrhagic fever is a severe and highly lethal disease with no effective treatments, and it has been classified as a Category A bioterrorism agent by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Sarepta Therapeutics announced positive results from a non-human primate study of AVI-7288, the company’s lead drug candidate for the treatment of Marburg virus infection.
-
-
Precious metal recovery technique ideal for rare Earth elements purification
Researchers have come up with a new approach to make the recovery of high value precious metals faster and more economically viable. The new technique could be ideal for the purification of rare earth elements, which are vital commodities for ‘green’ technologies such as hybrid cars and novel batteries.
-
-
Coal and U.S electric power generation

Coal is an important fuel source in the United States today. Responsible for approximately 39 percent of the country’s electrical generation, coal is vital to the day-to-day operation of people’s lives. The United States is rich in coal deposits, with large resources. One of the most important and largest of those deposits is found in the Powder River Basin (PRB) of Wyoming and Montana, which, in 2012, produced more than 42 percent of the nation’s coal.
-
-
TSA would allow knives on planes beginning 25 April
The Transportation Security Administration (TSA) yesterday announced that, starting 25 April, the prohibition against carrying knives on board would be lifted. TSA would also allow other items banned since 9/11, such as lacrosse sticks, ski poles, and small, souvenir baseball bats. The flight attendants union was quick to condemn to move, calling the decision “dangerous” and “designed to make the lives of TSA staff easier, but not make flights safer.”
-
-
U.S. nuclear industry resists stricter, post-Fukushima safety measures
Since the March 2011 Fukushima disaster, members of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) have been debating whether or not to impose even stricter safety measures on the thirty-one U.S. boiling water reactors (BWRs). Utility companies have been fighting any new safety regulations, arguing that the security measures they have are more than enough.
-
-
New source for rare earth elements: discarded consumer products
In a new twist on the state’s mining history, a group of Idaho scientists will soon be crushing consumer electronics rather than rocks in a quest to recover precious materials. Two national labs in the state will apply expertise gained in recycling fissionable material from nuclear fuel to separate rare earth metals and other critical materials from crushed consumer products.
-
-
World’s first zero emission sports car is built-at-home electric car

A new partnership has developed the world’s first build at home electric race car kit, an all-electric sports car designed and engineered to support a growing demand for zero emission racing vehicles. The iRacer kit, available from £13,999, can be transformed quickly between hybrid, pure electric, or internal combustion engines.
-
-
Enabling small ships to launch and retrieve long-endurance UAVs
About 98 percent of the world’s land area lies within 900 nautical miles of ocean coastlines. Enabling small ships to launch and retrieve long-endurance UAVs on demand would greatly expand the U.S. military’s situational awareness and ability quickly and flexibly to engage in hotspots over land or water. DARPA is seeking companies to develop these systems.
-
-
New ways to store data securely with untrusted cloud providers
Cloud storage security is an especially important issue for anyone dealing with large amounts of data that are supposed to be stored for a long period, such as archival and backup data. Researchers received a top honor for their ideas on better ways to ensure the integrity and long-term reliability of data stored at potentially untrusted cloud storage providers.
-
-
Global warming opening new shipping routes in Arctic Ocean
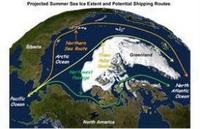
The Arctic Ocean has captured the imagination of explorers because of the possibility it offers for traveling between the Pacific and the Atlantic oceans through the Bering Strait. Until recently, however, sea ice has blocked access to the potential shortcut between Asia and North America or Europe. In the past two years, the ice has begun to melt in late summer to such an extent that even ordinary seagoing vessels have been able to enter its frigid waters. For vessels traveling between Rotterdam in the Netherlands and Yokohama, Japan, the Northern Sea Route is approximately 40 percent shorter than the traditional route through the Suez Canal.
-
-
Police budget cuts a boon to private security picks
In cities across the United State, local law enforcement, facing deep budget cuts, has had to do more police work with fewer officers. New Jersey alone lost 4,200 officers between 2008 and 2011. The reduction in police force has been a boon to the U.S. private security industry, which is expected to earn more than $19 billion by 2016.
-
-
RFI for cybersecurity framework for critical infrastructure
In his 12 February 2013 Executive Order, President Obama called for the development of a Cybersecurity Framework to reduce cyber risks to critical infrastructure such as power plants and financial, transportation, and communications systems. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) the other day issued a Request for Information (RFI) in the Federal Register as its first step in the process to developing that framework.
-
-
Developing the next-generation of VTOL aircraft

One of the greatest challenges of the past half century for aerodynamics engineers has been how to increase the top speeds of aircraft that take off and land vertically without compromising the aircraft’s lift to power in hover or its efficiency during long-range flight. DARPA’s new VTOL X-Plane project aims to achieve higher speeds, increased efficiency, and elegant design.
-
-
Saving money and time in developing phased RF arrays
Phased radio frequency (RF) arrays use numerous small antennas to steer RF beams without mechanical movement. These electronics are invaluable for critical DoD applications such as radar, communications, and electronic warfare. These arrays, however, come with a high price tag. Current phased arrays are extremely expensive and can take many years to engineer and build.
-
More headlines
The long view
Ransomware Attacks: Death Threats, Endangered Patients and Millions of Dollars in Damages
By Dino Jahic
A ransomware attack on Change Healthcare, a company that processes 15 billion health care transactions annually and deals with 1 in 3 patient records in the United States, is continuing to cause massive disruptions nearly three weeks later. The incident, which started on February 21, has been called the “most significant cyberattack on the U.S. health care system” by the American Hospital Association. It is just the latest example of an increasing trend.
Chinese Government Hackers Targeted Critics of China, U.S. Businesses and Politicians
An indictment was unsealed Monday charging seven nationals of the People’s Republic of China (PRC) with conspiracy to commit computer intrusions and conspiracy to commit wire fraud for their involvement in a PRC-based hacking group that spent approximately 14 years targeting U.S. and foreign critics, businesses, and political officials in furtherance of the PRC’s economic espionage and foreign intelligence objectives.
European Arms Imports Nearly Double, U.S. and French Exports Rise, and Russian Exports Fall Sharply
States in Europe almost doubled their imports of major arms (+94 per cent) between 2014–18 and 2019–23. The United States increased its arms exports by 17 per cent between 2014–18 and 2019–23, while Russia’s arms exports halved. Russia was for the first time the third largest arms exporter, falling just behind France.
LNG Exports Have Had No Impact on Domestic Energy Costs: Analysis
U.S. liquified natural gas (LNG) exports have not had any sustained and significant direct impact on U.S. natural gas prices and have, in fact, spurred production and productivity gains, which contribute to downward pressure on domestic prices.
