-
iPhones replacing Blackberries at more U.S. agencies
The security features of Blackberry phones kept them as the favorites with government agencies even as iPhones and Samsung’s Galaxy models were offering more features, but this security advantage appears to have disappeared, and iPhones are replacing Blackberry phones at more and more government agencies
-
-
Scientists improving process to recycle rare-earth materials
Recycling keeps paper, plastics, and even jeans out of landfills. Could recycling rare-earth magnets do the same? Perhaps, if the recycling process can be improved; scientists are working more effectively to remove the neodymium, a rare earth element, from the mix of other materials in a magnet; initial results show recycled materials maintain the properties that make rare-earth magnets useful
-
-
Large-scale production of algae-based biofuels poses sustainability concerns

Scaling up the production of biofuels made from algae to meet at least 5 percent — approximately thirty-nine billion liters — of U.S. transportation fuel needs would place unsustainable demands on energy, water, and nutrients, says a new report from the National Research Council; these concerns, however, are not a definitive barrier for future production, and innovations that would require research and development could help realize algal biofuels’ full potential
-
-
New biorenewables technology about to reach the marketplace
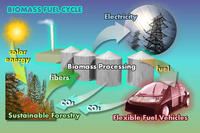
Innovative technology provides a new way to transform cellulosic biomass into renewable fuels and high-value chemicals; ,the technology uses ionic liquids to break down cellulosic or non-food plant biomass without using enzymes or costly pretreatment steps
-
-
Entrepreneurial approach to Japan’s disaster recovery
The 9.0 magnitude earthquake hit off the east coast of Japan in March 2011 killed more than 12,000 people, sent tsunami waves six miles inland, and damaged or completely flattened more than a million buildings; combined with the tsunami and the nuclear meltdown at Fukushima, it was the most economically damaging disaster in world history, costing Japan an estimated $235 billion, according to the World Bank; a Japanese organizations tries a new approach to disaster recovery: entrepreneurship
-
-
Looming sequestration causes Navy to looking at future technology, fleet size

Adm. Mark Ferguson, vice chief of naval operations, offered a revealing look at the potential future for the Navy if sequestration, or automatic defense cuts, goes into effect in January; without some sort of adjustment by Congress, currently the subject of discussion on Capitol Hill, the nearly 10 percent across-the-board Department of Defense budget cuts are slated to commence in 2013 and continue for ten years
-
-
TSA replaces backscatter scanners with millimeter wave scanners at some airports

TSA is replacing some backscatter scanners at large U.S. airports with millimeter wave scanners; backscatter scanners were criticized for violating travelers’ privacy, and risking travelers’ health by emitting high levels of radiation
-
-
Cybersecurity bill supporters want a vote on bill in this Congress
Last week, lawmakers and top White House officials appeared in different events, conferences, and industry gatherings to promote the cyber security bill which has been stalled in the Senate since August; administration’s officials and lawmakers supporting the bill warned that the current situation leaves U.S. critical infrastructure and businesses vulnerable to attack from hackers and spies
-
-
Los Alamos lab accelerates shipment of nuclear waste to permanent storage site

Los Alamos National Laboratory broke its own records in the first year of accelerated shipping effort of nuclear waste from the Lab to permanent disposal facilities located twenty-six miles outside of Carlsbad, New Mexico
-
-
Cyber criminals target small businesses
A recent study conducted by the National Cyber Security Alliance and Symantec found that 77 percent of small business owners in the United States think their company is safe from cyber criminals; trouble is, 83 percent of them do not have a cyber security plan
-
-
Sen. Rockefeller asks Fortune 500 CEOs for cybersecurity best practices

Last month, Senator Jay Rockefeller (D-West Virginia) sent a letter to the CEOs of fortune 500 companies asking them what cybersecurity practices they have adopted, how these practices were adopted, who developed them, and when they were developed; many saw Rockefeller’s letter as an admission that the Obama administration does not have a basis for trying to impose cybersecurity practices on the private sector through the Cybersecurity Act of 2012, now stalled in Congress
-
-
More companies adopt cloud disaster recovery solutions

More and more companies adopt a cloud disaster recovery solution; in a recent 2012 TechTarget Cloud Pulse survey, a majority of the 926 companies that responded have said they are now using a cloud disaster recovery system or plan to in the next six months
-
-
U.S. energy policy should emphasize supply security, not energy independence
America’s policymakers need to consider whether energy independence is really necessary to achieve adequate, reliable and affordable energy supplies, according to a new report from Deloitte; the United States already enjoys significant energy independence for most sectors and much of our economy
-
-
Sequestration-related defense budget cuts in 2013 to increase from $50.5 to $60.6 billion

Defense contractors are already worried about $50 billion dollars which would be cut from the defense budget on 3 January 2013 if the White House and Congress fail to reach an agreement on a deficit reduction plan; budget analysts point out that due to a provision in the Budget Control Act, another $10 billion will be added to that amount, bringing the total in defense cuts in 2013 to $60.6 billion
-
-
China’s Mekong River dams undermine neighbors’ economies, food production

Five Chinese dams on the Mekong River’s upper portions have caused rapid changes in water level, and other adverse effects, downstream, especially in Vietnam, Cambodia, Thailand, and Laos, where millions of people rely on the river for water, food, and transportation
-
More headlines
The long view
Ransomware Attacks: Death Threats, Endangered Patients and Millions of Dollars in Damages
A ransomware attack on Change Healthcare, a company that processes 15 billion health care transactions annually and deals with 1 in 3 patient records in the United States, is continuing to cause massive disruptions nearly three weeks later. The incident, which started on February 21, has been called the “most significant cyberattack on the U.S. health care system” by the American Hospital Association. It is just the latest example of an increasing trend.
Chinese Government Hackers Targeted Critics of China, U.S. Businesses and Politicians
An indictment was unsealed Monday charging seven nationals of the People’s Republic of China (PRC) with conspiracy to commit computer intrusions and conspiracy to commit wire fraud for their involvement in a PRC-based hacking group that spent approximately 14 years targeting U.S. and foreign critics, businesses, and political officials in furtherance of the PRC’s economic espionage and foreign intelligence objectives.
European Arms Imports Nearly Double, U.S. and French Exports Rise, and Russian Exports Fall Sharply
States in Europe almost doubled their imports of major arms (+94 per cent) between 2014–18 and 2019–23. The United States increased its arms exports by 17 per cent between 2014–18 and 2019–23, while Russia’s arms exports halved. Russia was for the first time the third largest arms exporter, falling just behind France.
LNG Exports Have Had No Impact on Domestic Energy Costs: Analysis
U.S. liquified natural gas (LNG) exports have not had any sustained and significant direct impact on U.S. natural gas prices and have, in fact, spurred production and productivity gains, which contribute to downward pressure on domestic prices.
