-
Bolstering pre-disaster resilience significantly reduces post-disaster recovery cost
A new study finds that the federal government spends six times more on post-disaster disaster recovery efforts than on helping communities become more resilient to extreme weather which is predicted to become more intense and frequent. The study, citing Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) estimates, calculates that for every $1 invested in “pre-disaster” mitigation, the cost of damage from extreme weather is reduced by $4.
-
-
$110 billion in damages makes 2012 second only to 2005 in terms of weather-related disasters

The U.S. National Climatic Data Center’s (NCDC) says that 2012 saw eleven weather and climate disaster events each with losses exceeding $1 billion in damages. This makes 2012 the second costliest year since 1980, with a total of more than $110 billion in damages throughout the year. The 2012 total damages rank only behind 2005, which incurred $160 billion in damages due in part to four devastating land-falling hurricanes.
-
-
USDA announces additional emergency watershed protection funding
USDA’s Natural Resources Conservation Service will send an additional $66.8 million in Emergency Watershed Protection Program funds to help disaster recovery efforts in fifteen states.
-
-
Storm predictions for Navy, civilian planners
With the arrival of the Atlantic hurricane and Pacific typhoon season, and the often dangerous storms that can accompany it, new technology sponsored by the Office of Naval Research (ONR) will be used to help Navy and civilian officials alike plan for stormy weather, officials announced the other day.
-
-
Weather reports aid life-or-death decisions in Africa
The people living in sub-Saharan Africa have a life-or-death dependency on information about the weather. Knowing when, where, and what to grow or graze animals can be the difference between a bumper harvest and facing starvation. Although sub-Saharan Africa depends more directly on rainfall than any other region on Earth, the region has the fewest number of rain monitoring stations. There are also significant delays in the time between measurements being made and the resulting data being made available.
-
-
Texas to appeal FEMA decision not to declare West, Texas a disaster area
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) said President Obama would not declare West, Texas a disaster area in the wake of the massive fertilizer plant explosion there two months ago, and Texas governor Rick Perry is not happy. FEMA said Texas did not make the case the state lacked funds for cleanup and recovery efforts.
-
-
New Jersey faces costly water infrastructure upgrades

Before Hurricane Sandy hit New Jersey, state officials knew they had much work ahead of them to update the state’s water infrastructure. The damage Sandy inflicted only highlighted the inadequacies of New Jersey’s outdated wastewater, stormwater, and drinking water infrastructure. Upgrading the system will be costly, but not doing so will be costlier.
-
-
Engineers on a wind load reconnaissance visit to tornado-hit Moore, Oklahoma
Eight days after an EF5 tornado struck Moore, Oklahoma, an 8-member team from the American Society of Civil Engineers’ (ASCE) Structural Engineering Institute (SEI) visited the area to assess the performance of critical facilities that either resisted or suffered significant damage from the estimated 200+ mph winds. The team studied four elementary schools and a hospital, and also examined the failures of long-span roof structures.
-
-
FEMA issues annual National Preparedness Report
Presidential Policy Directive 8: National Preparedness requires an annual National Preparedness Report (NPR) that summarizes national progress in building, sustaining, and delivering the thirty-one core capabilities outlined in the National Preparedness Goal. The 2013 NPR presents an opportunity to reflect on the progress that that has been made in strengthening national preparedness and to identify where preparedness gaps remain.
-
-
U.S. cities preparing for disasters

In the last year the United States, among other challenges, faced Hurricane Sandy, the Sandy Hook shooting, the Boston Marathon bombings, and Tornadoes in Oklahoma. The future is unpredictable, so cites across the United States are taking steps to be in a better position to respond to disasters.
-
-
Identifying regions with multiple forest threat potential, including wildfires
A recent study offers emergency managers a tool to help them identify regions exposed to multiple forest threats. The tool uses a novel 15-mile radius neighborhood analysis to highlight locations where threats are more concentrated relative to other areas, and identifies where multiple threats may intersect. It is a technique that may have never been used before to describe forest threats, according to the researchers.
-
-
Insurers face minimum $4 billion payout from May U.S. storm damage
Total economic losses from the Oklahoma tornado – in fact, the event comprised at least sixty-one confirmed tornado touchdowns — are preliminarily estimated at $5.0 billion, amid insured losses of at least $2.5 billion. Total economic losses from flash flooding in the Plains and Midwest, and from damaging winds in the Northeast, are expected to exceed $2.0 billion, with insured losses above $1.0 billion.
-
-
Earthquake acoustics can indicate a massive tsunami is coming
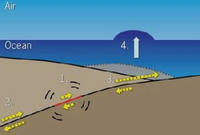
Although various systems can detect undersea earthquakes, they cannot reliably tell which will form a tsunami, or predict the size of the wave. There are ocean-based devices that can sense an oncoming tsunami, but they typically provide only a few minutes of advance warning. Scientists have now identified key acoustic characteristics of the 2011 Japan earthquake that indicated it would cause a large tsunami. The technique could be applied worldwide to create an early warning system for massive tsunamis.
-
-
Thousands of U.S. bridges in “fracture critical” condition
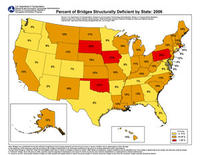
There are currently 66,749 structurally deficient bridges and 84,748 functionally obsolete bridges in the United States – about a quarter of the nation’s 607,000 bridges. With declining federal funds for bridge repair, the burden of maintenance has shifted to states, which spent $28.5 billion last year on bridge work – up from $12.3 billion in 1998.
-
-
U.S. hurricane supercomputers need an upgrade
During the hurricane season, which began last week, the U.S. National Weather Service (NWS) will use models from several supercomputers from around the world to generate predictions about hurricanes’ landfall, path, and intensity. Meteorologists say that the two American supercomputers used for storm modeling are underpowered and inferior to European computers.
-
More headlines
The long view
Using Drone Swarms to Fight Forest Fires
Forest fires are becoming increasingly catastrophic across the world, accelerated by climate change. Researchers are using multiple swarms of drones to tackle natural disasters like forest fires.
How Climate Change Will Affect Conflict and U.S. Military Operations
“People talk about climate change as a threat multiplier,” said Karen Sudkamp, an associate director of the Infrastructure, Immigration, and Security Operations Program within the RAND Homeland Security Research Division. “But at what point do we need to start talking about the threat multiplier actually becoming a significant threat all its own?”
