-
Future of coal in Australia riskier than renewables
Coal-fired electricity may have little or no economic future in Australia, even if carbon capture and storage becomes commercially available, a new analysis has found. The study shows that coal with carbon capture and storage scenarios are likely to struggle to compete economically with 100 percent renewable electricity in a climate-constrained world, even if carbon capture and storage is commercialized by 2030.
-
-
Flexible vehicle-arrest system stops cars involved in crime, terrorism

Researchers have developed a mathematical model that could help engineers design a flexible vehicle-arrest system for stopping cars involved in criminal activity or terrorism, such as suspect car bombers attempting break through a check point, without wrecking the car or killing the occupants.
-
-
New detectors for chemical, biological threats
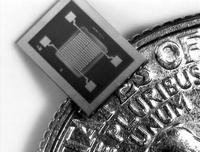
In the late 1990s, Sandia scientists developed a simple-to-use handheld chemical detector for the military, the MicroChemLab. Ever since, Sandia has improved such microfluidics- and microelectromechanical (MEMS) systems-based instruments that identify chemicals based on gas chromatography, or GC, and resonator-style instruments such as surface acoustic wave (SAW) detectors. The lab’s researchers are building on this sensor work to invent tiny detectors that can sniff out everything from explosives and biotoxins to smuggled humans.
-
-
Global warming increasing risk of record heat: scientists
Drought shriveled crops in the Midwest, massive wildfires raged in the West, and East Coast cities sweltered. The summer of 2012 was a season of epic proportions, especially July, the hottest month in the history of U.S. weather record keeping. As the world warms, it is likely that we will continue to see such calamitous weather. Scientists caution against trying to determine whether global warming caused any individual extreme event, but they say that the observed global warming clearly appears to have affected the likelihood of record heat.
-
-
High performance concrete to rescue Brittany's lighthouses

Lighthouses in Brittany, France, have stood at the intersection of violent currents, blinding storms, and breaking surf for over a century. A lighthouse turret off the coast of Lorient in Brittany has been enhanced with technology developed for bridges. This trial run will test the application of Ultra-High Performance Concrete (UHPC).
-
-
Limestone powder enhances performance of “green” concrete

Adding limestone powder to “green” concrete mixtures — those containing substantial amounts of fly ash, a byproduct of coal-burning power plants — can significantly improve performance. The promising laboratory results suggest a path to increasing greatly the use of fly ash in concrete, leading to sizable reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, energy use, construction costs and landfill volumes.
-
-
Top Five most awesome robots
In the last decade, robots have often been employed on the battlefields of Iraq and Afghanistan, usually to seek out hidden bombs. More and more of these the robots are now being adopted by first response agencies to help in search-and-rescue operations in the wake of disasters. The growing interest in – and usefulness of — robotics have also inspired a series of competitions and challenges, some of which are directed at high-school and college students, to encourage budding scientists to go into the field of robotics.
-
-
Norwich University receives $10 million for cybersecurity research
Norwich University in Vermont has secured another round of funding for cybersecurity research. $9.9 million in federal funds will go toward a project aiming to ensure that private and public sector groups can better plan for cyberattacks. The university’s Applied Research Institute (NUARI) will direct the money for its Distributed Environment for Critical Infrastructure Decision-making Exercises (DECIDE) program.
-
-
Crop pests spread as Earth warms, threatening global food security
Currently 10-16percent of global crop production is lost to pests. Losses of major crops to fungi, and fungi-like microorganisms, amount to enough to feed nearly 9 percent of today’s global population. These figures will increase further as global temperatures continue to rise, and a new study shows that global warming is resulting in the spread of crop pests toward the North and South Poles at a rate of nearly three km a year.
-
-
Using desalination to secure water in the desert
Researchers are working on an innovative project to secure water supplies in desert communities which suffer from having an acute shortage of fresh water, but abundant hypersaline groundwater. Hypersaline water is even saltier than seawater.
-
-
Wildfires to worsen with climate change

Air quality has vastly improved over much of the United States in the past forty years as a result of government efforts to regulate emissions. Gradual climate change may contribute in the coming years to increases in significant, disruptive events like severe storms, floods, and wildfires. A Harvard model predicts wildfire seasons by 2050 will be three weeks longer, up to twice as smoky, and will burn a wider area in the western United States. These increasing wildfires may erase some of the progress made on air quality.
-
-
Sandy Task Force issues sixty-nine rebuilding recommendations
The Hurricane Sandy Rebuilding Task Force, appointed by President Obama and chaired by Housing and Urban Development secretary Shaun Donovan, last week release its much-anticipated report, in which it lays out sixty-nine policy recommendations for improving areas affected by Hurricane Sandy last October. The report stressed the importance of investment in new and better construction to withstand increasingly dangerous storms and surges caused by climate change.
-
-
Jersey shore towns build protection against future storms

Mantoloking and Brick townships in New Jersey were among the hardest hit by Superstorm Sandy. The storm also destroyed the natural dune barriers which offered a measure of protection. The two cities have decided to take action to minimize the damage of inflicted by a future storm: a $40 million project will see a steel wall —extending sixteen feet above the beach with a depth of thirty-two feet below the ground, and covered in sand to form an artificial dune — will run along the length of the two towns.
-
-
Fukushima radioactive plume to reach U.S. next year
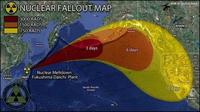
The radioactive ocean plume from the 2011 Fukushima nuclear plant disaster will reach the shores of the United States within three years from the date of the incident, but is likely to be harmless, according to a new study. While atmospheric radiation was detected on the U.S. west coast within days of the incident, the radioactive particles in the ocean plume take considerably longer to travel the same distance.
-
-
Understanding the effects of wildfire smoke improves climate change models
Where there is wildfire, there is smoke — a lot of it. Those vast, carbon-laden clouds released by burning biomass can play a significant role in climate change. Not much is known, however, about the different types of particles in wildfire smoke and how they affect climate. Now researchers have uncovered some of their secrets. In particular, they studied an important component of smoke that has so far been absent from most models of climate change.
-
More headlines
The long view
Autonomous Vehicle Technology Vulnerable to Road Object Spoofing and Vanishing Attacks
Researchers have demonstrated the potentially hazardous vulnerabilities associated with the technology called LiDAR, or Light Detection and Ranging, many autonomous vehicles use to navigate streets, roads and highways. The researchers have shown how to use lasers to fool LiDAR into “seeing” objects that are not present and missing those that are – deficiencies that can cause unwarranted and unsafe braking or collisions.
Tantalizing Method to Study Cyberdeterrence
Tantalus is unlike most war games because it is experimental instead of experiential — the immersive game differs by overlapping scientific rigor and quantitative assessment methods with the experimental sciences, and experimental war gaming provides insightful data for real-world cyberattacks.
Prototype Self-Service Screening System Unveiled
TSA and DHS S&T unveiled a prototype checkpoint technology, the self-service screening system, at Harry Reid International Airport (LAS) in Las Vegas, NV. The aim is to provide a near self-sufficient passenger screening process while enabling passengers to directly receive on-person alarm information and allow for the passenger self-resolution of those alarms.
Falling Space Debris: How High Is the Risk I'll Get Hit?
An International Space Station battery fell back to Earth and, luckily, splashed down harmlessly in the Atlantic. Should we have worried? Space debris reenters our atmosphere every week.
Testing Cutting-Edge Counter-Drone Technology
Drones have many positive applications, bad actors can use them for nefarious purposes. Two recent field demonstrations brought government, academia, and industry together to evaluate innovative counter-unmanned aircraft systems.
Strengthening the Grid’s ‘Backbone’ with Hydropower
Argonne-led studies investigate how hydropower could help add more clean energy to the grid, how it generates value as grids add more renewable energy, and how liner technology can improve hydropower efficiency.
