-
Student teams compete in U.S. Navy’s RoboBoat competition

In a race against one another and the clock, robotic boats are battling it out at the 6th International RoboBoat Competition, which began 8 July and ends 14 July. The Office of Naval Research (ONR)-co-sponsored competition takes place on a pond at the Founder’s Inn and Spa in Virginia Beach, Virginia. The event features fifteen student teams racing their custom-designed and built boats.
-
-
DARPA’s disaster robot competition moves to final stage

On Monday, 8 July 2013, the seven teams which progressed from DARPA’s Virtual Robotics Challenge (VRC) arrived at the headquarters of Boston Dynamics in Waltham, Massachusetts to meet and learn about their new teammate, the ATLAS robot. ATLAS is one of the most advanced humanoid robots ever built, but is essentially a physical shell for the software brains and nerves that the teams will continue to develop and refine. The robot will have to perform a series of tasks similar to what might be required in a disaster response scenario.
-
-
U.S. power plants use more coal, bucking the trend toward natural gas
Power plants in the United States are burning more coal to produce electricity, bucking the trend toward using natural gas, and in the process emitting more greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere, a new government report says. Burning coal to produce electricity was popular just a few years ago, but hydraulic fracturing led to a natural gas boom, driving down gas prices and making natural gas more competitive with coal. The demand for natural gas got so high, however, that its price began to creep up at the same time that the price of coal dropped because of weakening demand for it.
-
-
Japan to restart nuclear power plants

Japan’s fifty nuclear power plants were taken off-line in the wake of the 2011 Fukushima nuclear disaster, but the government Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, which took office in December, said it was planning to restart Japan’s nuclear power generation program.
-
-
Assessing the social, economic effects of Deepwater Horizon spill
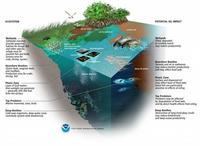
Numerous studies are under way to determine the impacts of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill on the Gulf of Mexico, but the extent and severity of these impacts and the value of the resulting losses cannot fully be measured without considering the goods and services provided by the Gulf, says a new report from the National Research Council (NRC). The report offers an approach that could establish a more comprehensive understanding of the impacts and help inform options for restoration activities.
-
-
Wildfires contribute more to global warming than previously thought
Wildfires produce a witch’s brew of carbon-containing particles. A range of fine carbonaceous particles rising high into the air significantly degrade air quality, damaging human and wildlife health, and interacting with sunlight to affect climate.
-
-
Oil-devouring microbe communities a mile deep in the Gulf
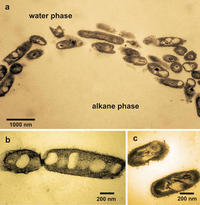
The Deepwater Horizon explosion on 20 April 2010, caused the largest marine oil spill in history, with several million barrels of crude oil released into the Gulf of Mexico over the course of three months. Soon after the spill began, a massive oil slick was visible from orbiting satellites, yet once the underwater gusher was sealed, obvious traces of the crude oil disappeared much sooner than nearly all observers predicted. Some of the oil evaporated; some was skimmed off. Microbes “ate” much of the oil as well.
-
-
Treating oil spills with chemical dispersants may do more damage than good
Treating oil spills at sea with chemical dispersants is detrimental to European fisheries. Post-spill chemical dispersants may reduce problems for surface animals, but the increased contamination under the water reduces the ability for fish and other organisms to cope with subsequent environmental challenges.
-
-
Researchers highlight problem of legacy mercury in the environment
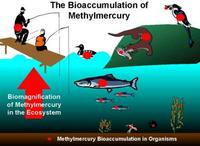
Researchers have published evidence that significant reductions in mercury emissions will be necessary just to stabilize current levels of the toxic element in the environment. So much mercury persists in surface reservoirs (soil, air, and water) from past pollution, going back thousands of years, that it will continue to persist in the ocean and accumulate in fish for decades to centuries, they report.
-
-
U.S. geological carbon dioxide storage potential
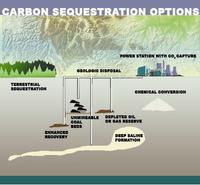
The United States has the potential to store a mean of 3,000 metric gigatons of carbon dioxide (CO2) in geologic basins throughout the country. Technically accessible storage resources are those that can be accessed using today’s technology and pressurization and injection techniques. The most common method of geologic carbon storage involves pressurizing CO2 gas into a liquid, and then injecting it into subsurface rock layers for long-term storage.
-
-
Growing cybersecurity opportunities for young Americans
With the growing number of cyberattacks on U.S. companies, government agencies, and critical infrastructure, and the likelihood that such attacks will only increase, there has been a corresponding increase in the number of cybersecurity programs and educational opportunities for young Americans.
-
-
Highly portable X-ray imaging system developed
Los Alamos National Laboratory and Tribogenics have developed the MiniMAX (Miniature, Mobile, Agile, X-ray) camera to provide real-time inspection of sealed containers and facilities.MiniMAX is an alternative to the large, expensive, and fixed facilities presently required for security inspections using X-ray imaging. The complete MiniMAX portable radiography system weighs less than five pounds.
-
-
Increasing food production from existing farmland
A policy known as sustainable intensification could help meet the challenges of increasing demands for food from a growing global population. The goal of sustainable intensification is to increase food production from existing farmland. Sustainable intensification would minimize the pressure on the environment in a world in which land, water, and energy are in short supply.
-
-
Research network to search for extraterrestrial intelligence launched in U.K.
A network has been launched to promote academic research in the United Kingdom relating to the search for extraterrestrial intelligence. The network brings together academics from eleven institutions across the country, and it covers a broad spectrum of research topics, including potential methods for detecting signals, the linguistic challenge of deciphering messages, the probability of an extraterrestrial civilization interacting with Earth, and the longevity of civilizations.
-
-
Earthquake-proofing precast buildings
Precast or ready-made building structures offer a number of advantages when compared to more traditional construction techniques in terms of time and cost savings. The vulnerability of joints and connections between assembled precast elements, however, is widely recognized as a potential safety issue, especially in earthquake-prone areas. An EU-funded project has set out to develop new procedures and guidelines for designing precast structure joints and connections that can stand up to seismic forces.
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
Risk Assessment with Machine Learning
Researchers utilize geological survey data and machine learning algorithms for accurately predicting liquefaction risk in earthquake-prone areas.
Foundation for U.S. Breakthroughs Feels Shakier to Researchers
With each dollar of its grants, the National Institutes of Health —the world’s largest funder of biomedical research —generates, on average, $2.56 worth of economic activity across all 50 states. NIH grants also support more than 400,000 U.S. jobs, and have been a central force in establishing the country’s dominance in medical research. Waves of funding cuts and grant terminations under the second Trump administration are a threat to the U.S. status as driver of scientific progress, and to the nation’s economy.
The True Cost of Abandoning Science
“We now face a choice: to remain at the vanguard of scientific inquiry through sound investment, or to cede our leadership and watch others answer the big questions that have confounded humanity for millennia —and reap the rewards.”
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
New Approach Detects Adversarial Attacks in Multimodal AI Systems
New vulnerabilities have emerged with the rapid advancement and adoption of multimodal foundational AI models, significantly expanding the potential for cybersecurity attacks. Topological signatures key to revealing attacks, identifying origins of threats.
