-
Georgia wants to redraw its northern border to tap Tennessee River water
Lawmakers in Georgia are renewing efforts to claim Georgia’s right to tap into the Tennessee River’s water supply. The lawmakers hope to achieve this by raising questions about the exact demarcation of the border between the two states.
-
-
Russian fireball largest ever detected by nuke monitoring organization
Infrasound has been used as part of the Comprehensive Nuclear Test Ban Treaty Organization’s (CTBTO) monitoring tools to detect atomic blasts since April 2001 when the first station came online in Germany. Infrasonic waves from the meteor that broke up over Russia’s Ural Mountains last week were the largest ever recorded by the CTBTO’s International Monitoring System.
-
-
Cockroaches gait informs search-and-rescue robot design
More than 70 percent of Earth’s land surface is not navigable by wheeled or tracked vehicles, so legged robots could potentially bridge the gap for ground-based operations like search and rescue and defense. New insights on how cockroaches stabilize could help engineers design steadier robots for operating on difficult terrain.
-
-
Battle-tested technologies no employed by the police
Technologies employed in the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan are now hitting local streets across the United States, changing how local law enforcement investigates crimes by focusing on where crimes are most likely to happen instead of where a crime has taken place.
-
-
Scientists warn of sequestration’s impact on basic research
With less than a week left before sequestration is to take effect, America’s research community has repeated its call for an end to the across-the-board cuts to discretionary spending which will restrict the U.S. ability to invest in the basic scientific research. A coalition of American research and education institutions says that it is this basic research which drives innovation and produces economic growth.
-
-
Climate change as a national security issue
In a new report, Harvard researcher is pointing toward a new reason to worry about the effects of climate change — national security. During the next decade, the report concludes, climate change could have wide-reaching effects on everything from food, water, and energy supplies to critical infrastructure and economic security. “The imminent increase in extreme events will affect water availability, energy use, food distribution, and critical infrastructure — all elements of both domestic and international security,” the report’s author says.
-
-
New explosives vapor detection technology

Novel explosives detection method focuses on direct, real-time vapor detection rather than collection of explosives particles. It could change paradigm for explosives screening.
-
-
Self-healing protective coating for concrete
Scientists are reporting development of what they describe as the first self-healing protective coating for cracks in concrete, the world’s most widely used building material. The coating is inexpensive and environmentally friendly.
-
-
U.S. responds to China’s cyberattacks with anti-theft trade strategy
The Obama administration yesterday (Wednesday) unveiled the details of a broad strategy to counter the systemic theft by Chinese government agencies of U.S. trade and technology and trade secrets. The administration’s plan calls for new diplomatic push to discourage intellectual property theft abroad and better coordination at home to help U.S. companies protect themselves.
-
-
Chinese set to buy yet another U.S. taxpayer-backed hi-tech firm
Lawmakers yesterday expressed their concerns about the likelihood that U.S. taxpayer dollars could end up bolstering the Chinese economy. The lawmakers reacted to reports that a Chinese firm, Zhejiang Geely Holding Group, is leading the list of companies bidding for a majority stake in government-backed Fisker Automotive, and that the only serious rival of that Chinese company is a Chinese auto maker. Fisker’s main battery supplier — U.S. government-backed A123 Systems – has already been acquired by a separate Chinese firm.
-
-
Improving detection of, responses to biological warfare
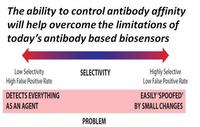
Biological warfare agents pose more than a hypothetical threat to U.S. soldiers. Troops operate in hostile areas where they could come under attack from adversaries wielding bio-agents like anthrax and toxins. The first step in reacting to any such attack is knowing that it occurred. Quickly and accurately identifying the presence of airborne antigens can be difficult given their complexity, the presence of numerous similar microorganisms in the environment, and the fact that even minute quantities of a threat agent can cause infection. Researches seek to advance sensitivity and durability of antibody-based biosensors better to protect soldiers.
-
-
Earthquake catastrophes and fatalities to rise in 21st century
Predicted population increases in this century can be expected to translate into more people dying from earthquakes. There will be more individual earthquakes with very large death tolls as well as more people dying during earthquakes than ever before, according to a new study.
-
-
High school students to compete in DOE National Science Bowl

The U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) created the National Science Bowl in 1991 to encourage students to excel in math and science and pursue careers in related fields. More than 200,000 students have participated in the National Science Bowl in the twenty-three years since its inception. Students from Los Alamos High School will represent New Mexico at the Department of Energy’s National Science Bowl in April.
-
-
Water managers can now consult new U.S. water evaporation maps
The amount of water available for people and ecosystems is the amount of annual precipitation — that is, snow or rain — minus the amount of annual evapotranspiration. Evapotranspiration itself is the amount of water lost to the atmosphere from the ground surface. Scientists map the long-term U.S. evapotranspiration rates for the first time.
-
-
Prof. strips, stabs stuffed animal to teach quantum mechanics
Students who showed up for Monday’s quantum physics class of Professor Emlyn Hughes, a Columbia University physics professor, found out they were in for a new approach to teaching the week’s topic.
As the students entered the classroom, they were greeted with the tune of Lil Wayne’s “Drop It Like It’s Hot.” As the students were taking their seats, Hughes removed his clothes, then changed into a black T-shirt and pants. He then sat down and hugged his knees in a fetal position before airing video footage of the 9/11 2001 terror attacks, and videos of aerial bombardments from the Second World War.
-
More headlines
The long view
New Technology is Keeping the Skies Safe
DHS S&T Baggage, Cargo, and People Screening (BCP) Program develops state-of-the-art screening solutions to help secure airspace, communities, and borders
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Artificial General Intelligence Could Affect the Rise and Fall of Nations
Visions for potential AGI futures: A new report from RAND aims to stimulate thinking among policymakers about possible impacts of the development of artificial general intelligence (AGI) on geopolitics and the world order.
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
