-
Nanostructured material stronger than a speeding bullet
Providing protection against impacts from bullets and other high-speed projectiles is more than just a matter of brute strength; while traditional shields have been made of bulky materials such as steel, newer body armor made of lightweight material such as Kevlar has shown that thickness and weight are not necessary for absorbing the energy of impacts; new tests of nanostructured material could lead to better armor against everything from gunfire to micrometeorites
-
-
DARPA seeks multi-band, portable sensor to provide soldiers with clear images
Clip-on or helmet-mounted camera system would fuse useful aspects of visible, near infrared, and infrared images into a single shot under all weather and visibility conditions; the Pixel Network for Dynamic Visualization program, or PIXNET, technology would ingest the most useful data points from each component sensor and fuse them into a common, information-rich image that can be viewed on the soldier’s heads-up display, and potentially be shared across units
-
-
The limitations of climate models

How accurate is the latest generation of climate models? Climate physicists have compared them with old models and draws a differentiated conclusion: while climate modeling has made substantial progress in recent years, we also need to be aware of its limitations
-
-
Scientists resurrect process to convert sugar directly to diesel

A long-abandoned fermentation process once used to turn starch into explosives can be used to produce renewable diesel fuel to replace the fossil fuels now used in transportation; the retooled process produces a mix of products that contain more energy per gallon than ethanol that is used today in transportation fuels and could be commercialized within 5-10 years
-
-
Inflatable giant plugs could have saved NYC subway system

Inflatable plugs being developed with funding from DHS, could have saved some of New York’s subway and highway tunnels from flooding during Hurricane Sandy, according to the developers of the plugs; DHS successfully tested a plug earlier this year, using a 16-foot diameter prototype to hold back pressurized water at a test tunnel in Morgantown, West Virginia; the idea was originally intended to protect tunnels from terrorist attacks
-
-
Dutch flood-protection may be suitable for New York, other East Coast cities

Megastorms and disasters are not going to continue to be once in a lifetime storms, but instead become more of an annual occurrence; experts say that the combination of more frequent megastorms and rising sea levels across the east coast would forcemany cities to get serious about flood protection
-
-
New strategy for fingerprint visualization
Identifying fingerprints on paper is a commonly used method in police forensic work, but it is not easy to make those fingerprints visible. Now, scientists have developed a new approach for making such fingerprints more readily readable
-
-
Long-term sea level rise could cost Washington, D.C. billions
New study projects that the city of Washington, D.C., and federal property in the city, could suffer billions of dollars in damage if sea level rise as a result of global warming increases over the next century. Potential for significant damage will be even greater in the event of extreme weather like Hurricane Sandy
-
-
2011 Virginia quake triggered landslides very far away
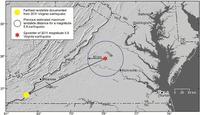
The 2011 Mineral, Virginia M-5.8 earthquake was felt over an extraordinarily large area; a new study details landslides triggered by the earthquake at distances four times greater and over an area twenty times larger than previously documented for M-5.8 earthquakes worldwide
-
-
Indian monsoon failure more frequent with warming
Global warming could cause frequent and severe failures of the Indian summer monsoon in the next two centuries, new research suggests; the effects of these unprecedented changes would be extremely detrimental to India’s economy which relies heavily on the monsoon season to bring fresh water to the farmlands
-
-
NY, NJ brace for nor’easter
East Coast resident are still coping with the destruction wreaked by Hurricane Sandy, but now they have to prepare for another potentially destructive storm – a nor’easter which is expected to hit New York and new Jersey on Wednesday; the nor’easter will likely stay 50-100 miles off shore, but its western edges will bring winds of up to 55 mph, coastal flooding, up to two inches of rain along the shore, and several inches of snow to Pennsylvania and New York
-
-
Many NYC buildings to remain closed for weeks, months for clean-up, repairs
Water and winds produced by Hurricane Sandy destroyed mechanical and electrical systems in many commercial and residential buildings in Lower Manhattan; as a result, many buildings in the area are weeks or months away from being repaired and fully operational
-
-
Protecting New York City from storms, surges
Almost a week after Hurricane Sandy hit New York City; people are still picking up the pieces of their former lives; for New York officials, the next step is decide how best to protect New York City from a similar disaster in the future; there are many ideas and proposals, ranging from moveable sea gates, to expanding protective marshlands and wetlands, to creating a system of artificial reefs in the channel along the Red Hook and Gowanus neighborhoods of Brooklyn, made out of rocks, shells, and fuzzy rope that will promote the growth of oysters
-
-
Nuclear energy facilities proved themselves resilience during Hurricane Sandy

There are thirty-four nuclear energy facilities in the area hit by Hurricane Sandy; all of them have responded well and safely to the powerful storm; the industry says that careful planning and preparations days in advance of the storm paid off at all of these facilities
-
-
Hurricane Sandy offered support for reliance on nuclear power
A Scientific American writer is impressed with the way nuclear power facilities were able safely to withstand the wrath of Hurricane Sandy; the lesson he draws from this experience: “Global warming is increasing the probability and destructiveness of extreme weather events like Sandy. (I don’t see the point of dithering over this claim any more.) The last thing we should do in the face of this threat is abandon nuclear energy. If anything, we need more nuclear power, not less, to curb global warming”
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
Risk Assessment with Machine Learning
Researchers utilize geological survey data and machine learning algorithms for accurately predicting liquefaction risk in earthquake-prone areas.
Foundation for U.S. Breakthroughs Feels Shakier to Researchers
With each dollar of its grants, the National Institutes of Health —the world’s largest funder of biomedical research —generates, on average, $2.56 worth of economic activity across all 50 states. NIH grants also support more than 400,000 U.S. jobs, and have been a central force in establishing the country’s dominance in medical research. Waves of funding cuts and grant terminations under the second Trump administration are a threat to the U.S. status as driver of scientific progress, and to the nation’s economy.
The True Cost of Abandoning Science
“We now face a choice: to remain at the vanguard of scientific inquiry through sound investment, or to cede our leadership and watch others answer the big questions that have confounded humanity for millennia —and reap the rewards.”
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
New Approach Detects Adversarial Attacks in Multimodal AI Systems
New vulnerabilities have emerged with the rapid advancement and adoption of multimodal foundational AI models, significantly expanding the potential for cybersecurity attacks. Topological signatures key to revealing attacks, identifying origins of threats.
