-
Thriving in toxic environments
Not long ago, a group claimed that these microorganisms, which live in an environment that is rich in the arsenic-based compound arsenate, could take up that arsenate and use it — instead of the phosphate on which all known life on Earth depends; the claim, since disproved, raised another question: How do organisms living with arsenate pick and choose the right substance? Scientists reveal how bacteria living in toxic environments identify and expel the poison
-
-
Twenty-year anniversary of U.S. last full-scale nuclear test
The first U.S. nuclear test, code named Trinity, took place in southern New Mexico forty-seven years earlier, on 16 July 1945; in all, the United States conducted 1,030 nuclear tests – the last one, code-named Divider, took place twenty years ago, on 23 September 1992
-
-
Los Alamos lab accelerates shipment of nuclear waste to permanent storage site

Los Alamos National Laboratory broke its own records in the first year of accelerated shipping effort of nuclear waste from the Lab to permanent disposal facilities located twenty-six miles outside of Carlsbad, New Mexico
-
-
Cosmic rays help gather information from inside the Fukushima nuclear reactors
Researchers have devised a method to use cosmic rays to gather detailed information from inside the damaged cores of the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear reactors which were heavily damaged in March 2011 by a tsunami that followed a great earthquake
-
-
A Mississippi river diversion helped build Louisiana wetlands
The extensive system of levees along the Mississippi River has done much to prevent devastating floods in riverside communities; the levees, however, have also contributed to the loss of Louisiana’s wetlands; by holding in floodwaters, they prevent sediment from flowing into the watershed and rebuilding marshes, which are compacting under their own weight and losing ground to sea-level rise
-
-
Corps: absolute flood protection along the Missouri River is impossible
A U.S. Army Corps of Engineers report said that absolute flood protection along the Missouri River is impossible, so the basin needs to prepare and plan for flooding in the future
-
-
Ozone causes forests to use more water, reducing availability in the Southeast

Scientists have found that rising levels of ozone, a greenhouse gas, may amplify the impacts of higher temperatures and reduce streamflow from forests to rivers, streams, and other water bodies; such effects could potentially reduce water supplies available to support forest ecosystems and people in the southeastern United States
-
-
New app uses scattered public information to put together a digital footprint of individuals, organizations
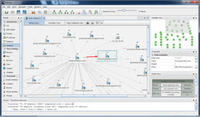
A new app application can collect scattered online clues to provide a picture of individuals or organizations; the application draws on public data sources in order to put together a graphical digital footprint
-
-
New military apparel repels chemical, biological agents
Scientists are developing a new military uniform material that repels chemical and biological agents using a novel carbon nanotube fabric; the material will be designed to undergo a rapid transition from a breathable state to a protective state; the highly breathable membranes would have pores made of a few-nanometer-wide vertically aligned carbon nanotubes that are surface modified with a chemical warfare agent-responsive functional layer
-
-
Scientists say it is too late to stop global warming: better to focus on adaptation, mitigation
Two scientists argue that governments and institutions should focus on developing adaption policies to address and mitigate against the negative impact of global warming, rather than putting the emphasis on carbon trading and capping greenhouse-gas emissions; they say that attempts to limit greenhouse-gas emissions through carbon cap-and-trade schemes and to promote renewable and sustainable energy sources are probably too late to arrest the inevitable trend of global warming
-
-
Evidence suggests that three-strikes law does not deter crime
Contrary to what police, politicians, and the public believe about the effectiveness of California’s three-strikes law, researchers have found that the get-tough-on-criminals policy voters approved in 1994 has done nothing to reduce the crime rate; a criminologist finds that decline in alcohol consumption is most responsible for decreasing crime rate
-
-
Different technologies aim to replace dogs as explosives detectors
Bomb-sniffing dogs are the best and most popular way for airport security quickly to detect anyone planning to bring explosives to an airport; scientists are trying to change that; Dr. Denis Spitzer and his colleagues, for example, are working on a sensor that will detect vapors of TNT and other explosives in very faint amounts; the device they are trying to create would replace dogs as the top bomb detecting method in the field
-
-
DARPA seeking tools for identifying hidden explosives at standoff
The threat to U.S. soldiers from improvised explosive devices (IEDs) is as varied as the makers of IEDs are resourceful in how they design and conceal the explosives; interdisciplinary teams needed to develop proof-of-concept demonstrations of technology for identifying presence of embedded explosives in opaque, high-water-content substances
-
-
Mice genetically modified to detect landmines
In another advancement in explosives detection, scientists have genetically modified mice to enable them to sniff out landmines; the GM mouse, known as MouSensor, may one day become a significant tool to help deal with the dangerous legacies of past wars
-
-
“Student-centered” approach to science education more effective
A group of educational researchers are drawing widespread attention after their paper measuring the superior results of a more “student-centered” approach to teaching science was published in the journal Science; the researchers say that the stakes are extraordinarily high, so it is critical that the United States find more effective ways of teaching the so-called STEM fields (science, technology, engineering, mathematics) in K-12 classrooms
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
Risk Assessment with Machine Learning
Researchers utilize geological survey data and machine learning algorithms for accurately predicting liquefaction risk in earthquake-prone areas.
Foundation for U.S. Breakthroughs Feels Shakier to Researchers
With each dollar of its grants, the National Institutes of Health —the world’s largest funder of biomedical research —generates, on average, $2.56 worth of economic activity across all 50 states. NIH grants also support more than 400,000 U.S. jobs, and have been a central force in establishing the country’s dominance in medical research. Waves of funding cuts and grant terminations under the second Trump administration are a threat to the U.S. status as driver of scientific progress, and to the nation’s economy.
The True Cost of Abandoning Science
“We now face a choice: to remain at the vanguard of scientific inquiry through sound investment, or to cede our leadership and watch others answer the big questions that have confounded humanity for millennia —and reap the rewards.”
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
New Approach Detects Adversarial Attacks in Multimodal AI Systems
New vulnerabilities have emerged with the rapid advancement and adoption of multimodal foundational AI models, significantly expanding the potential for cybersecurity attacks. Topological signatures key to revealing attacks, identifying origins of threats.
