-
Speeding skyscraper construction -- and making them stronger
Researchers are working on a new technique that could speed construction of skyscrapers while also providing enough stiffness and strength to withstand earthquakes and forces from high winds
-
-
Proton-based transistor could let machines communicate with humans
Devices humans use, from light bulbs to iPods, send information using electrons; human bodies and all other living things, on the other hand, send signals and perform work using ions or protons; researchers build a novel transistor that uses protons, creating a key piece for devices that can communicate directly with living things
-
-
Future electric vehicle to run unlimited distances

Electrically powered vehicles (EV) are promising environmentally friendly alternatives for combustion engine-based automobiles; batteries used in present-day EV, however, limit the continuous running distance from one charge; researchers propose a potentially revolutionary solution for powering EVs capable of running unlimited distances
-
-
New vest offers GPS tacking and other information
Canadian company Laipac Technology is showing its S911 GPS Vest which the company describes as “a high coverage assault protection designed for military, tactical law enforcement and VIP personnel that demand the highest protection.”
-
-
Tsunami-predicting software to help protect coastal communities

New software has been developed to help protect vulnerable coastal communities from the destruction of a tsunami; the mathematical model has created significant interest in the wake of the 2011 earthquake and tsunami in Japan six months ago
-
-
Laser device detects IEDs

Researchers have developed a laser that could detect roadside bombs — the deadliest enemy weapon U.S. and coalition soldiers encountered in Iraq and Afghanistan; the laser, which has comparable output to a simple presentation pointer, potentially has the sensitivity and selectivity to canvas large areas and detect improvised explosive devices
-
-
Environmentalists worry border environment protection
Environmentalists have taken aim at an amendment to the Senate appropriations bill for DHS that would allow border enforcement agencies ultimate authority within 100-miles of the U.S. border
-
-
Designing a new grid pylon

There are more than 88,000 pylons in the United Kingdom; they stand some 50-meters high, weigh around twenty tons, and carry up to 400,000 volts of electricity over thousands of kilometers of some of the most exposed, weather-beaten parts of Britain; the familiar steel lattice tower has barely changed since the 1920s; National Grid says it is time for a change
-
-
St. Andrews University promoting its certificate in terrorism studies

The University of St. Andrews is promoting a program leading to a certificate in it terrorism studies; the program was established in 2006 in is offered on-line
-
-
Man-made silk mimics spider silk

Spider silk has attracted human interest for thousands of years due to its toughness and ductility; as with most biomaterials, spider silk has evolved over millions of years resulting in a combination of properties that far exceeds any man-made material; until now
-
-
Earth's largest environmental catastrophe: 250 million year anniversary
The eruption of giant masses of magma in Siberia 250 million years ago led to the Permo-Triassic mass extinction when more than 90 percent of all species became extinct
-
-
Saltwater intrusion threatens South Florida’s water supplies
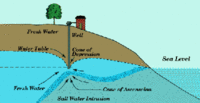
South Florida’s water supply is becoming increasingly endangered by saltwater that is steadily seeping in from the ocean and contaminating supplies; despite the best efforts of local communities to stop the problem, saltwater intrusion is spreading
-
-
Texas drought forces military to change training

A particularly severe drought in Texas has forced the military to change the way it trains its soldiers due to the risk of starting fires; law enforcement agencies would benefit from taking note of additional safety measures put into place
-
-
Severe drought in Georgia, 150 counties declared disaster areas
A severe drought and excessive heat has forced the U.S. Department of Agriculture to declare 150 counties in Georgia as primary natural disaster areas; the drought began on 15 April and has caused farmers to lose more than 30 percent of their pasture, grain crops, cotton, peanuts, tobacco, and forage crops
-
-
Industrial stent-like repairs for failing pipelines
There are thousands of miles of pipe underground in the United States, some more than 100 years old; gas, oil, water, and sewage seep, and sometimes gush, through corroded joints and defective welds every day; new technology uses carbon and glass laminates to repair and replace failing pipelines
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
Risk Assessment with Machine Learning
Researchers utilize geological survey data and machine learning algorithms for accurately predicting liquefaction risk in earthquake-prone areas.
Foundation for U.S. Breakthroughs Feels Shakier to Researchers
By Max Larkin
With each dollar of its grants, the National Institutes of Health —the world’s largest funder of biomedical research —generates, on average, $2.56 worth of economic activity across all 50 states. NIH grants also support more than 400,000 U.S. jobs, and have been a central force in establishing the country’s dominance in medical research. Waves of funding cuts and grant terminations under the second Trump administration are a threat to the U.S. status as driver of scientific progress, and to the nation’s economy.
The True Cost of Abandoning Science
By Steven R. Furlanetto
“We now face a choice: to remain at the vanguard of scientific inquiry through sound investment, or to cede our leadership and watch others answer the big questions that have confounded humanity for millennia —and reap the rewards.”
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
By Kathryn Brimblecombe-Fox
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
New Approach Detects Adversarial Attacks in Multimodal AI Systems
New vulnerabilities have emerged with the rapid advancement and adoption of multimodal foundational AI models, significantly expanding the potential for cybersecurity attacks. Topological signatures key to revealing attacks, identifying origins of threats.
