-
Listening to the sound of bullets

ShotSpotter systems relies on a system of acoustic sensors to identify the location from which a shot has been fired; the alerts are immediately conveyed to police dispatchers, 911 operators, and sometimes to officers in the field via laptops in patrol cars; the system includes a computer program which displays a comprehensive bird’s-eye view of the area, marking the location of the incident with a red dot and indicating the time and number of rounds fired
-
-
Research inspires robotics design for medicine, military
A pathogen that attacks the small intestines of humans and animals is serving as the inspiration for developing robots that can fight disease and aid in military operations; ror 250 years, scientists have tried to understand how the microorganism is able to attach to a multitude of surfaces and swim in harsh environments — enabling it to infect many kinds of species while most parasites have specific hosts
-
-
Blast gauge gives medics, doctors critical information

Researchers are working to enhance the safety of soldiers in the field through the development of a device that monitors the physical impacts of exposure to an explosive blast; 188,270 service members have suffered a traumatic brain injury in the last decade; the extent of injury is often difficult to discern, making diagnosis and selection of appropriate medical treatment challenging
-
-
How smartphones are fighting floods
A new smartphone app is helping the Army Corps of Engineers to strengthen its levees and fight floods in Kansas;filing reports is as simple as using a smartphone to take a picture, adding a note, and uploading the information to a database, which only takes a few seconds; this new system helps reduce the time it takes to gather critical information about levees by as much as thirty-six hours, giving engineers valuable additional time to detect and save a failing levee
-
-
Averting bridge disasters: new sensors could save hundreds of lives
One of every four U.S. highway bridges has known structural problems or exceeded its intended life-span. Most only get inspected once every one or two years; University of Maryland researcher has developed a new sensor that measures indicators of a bridge’s structural health, such as strain, vibration, flexibility, and development of metal cracks; the sensors are expected to last more than a decade, with each costing about $20
-
-
New software to improve explosive detection
New software developed by Peaklet Analysis with the aid of a Western Kentucky University (WKU) math professor could help existing explosives detectors improve their detection abilities
-
-
New invisibility cloak conceals objects from human view
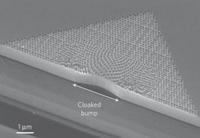
For the first time, scientists have devised an invisibility cloak material that hides objects from detection using light that is visible to humans; the new “carpet cloak” works by concealing an object under layers of silicon oxide and silicon nitride etched in a special pattern, and bending light waves away from the bump that the object makes, so that the cloak appears flat and smooth like a normal mirror
-
-
Transforming acids into bases
Chemists at the University of California, Riverside have accomplished in the lab what until now was considered impossible: transform a family of compounds which are acids into bases; the research offers vast family of new catalysts for use in drug discovery, biotechnology
-
-
California universities prepare homeland security leaders of tomorrow
Fresno State University in California is readying itself for the launch of a new bachelor’s degree program that prepares students for careers in homeland security and emergency management; the program is part of a broader effort by California State University (CSU) leaders as well as local and state officials to boost the state’s security by training more professionals to enter a field that is facing shortages of qualified workers
-
-
Tiny flying machines revolutionize surveillance work
Tiny aerial vehicles are being developed with innovative flapping wings based on those of real-life insects; incorporating micro-cameras, these revolutionary insect-size vehicles will be suitable for many different purposes ranging from helping in emergency situations considered too dangerous for people to enter, to covert military surveillance missions
-
-
Micro-robots emulate water-striding insects

Researchers are working on building nimble micro-robots that are able to skim across the surface of water; the prototype devices emulate water-striding insects such as mosquitoes and water spiders, and could be used for military spy missions, water-pollution monitoring, and other applications
-
-
Designing a more effective crystal ball
A new model for crowdsourcing predictions called Aggregative Contingent Estimation System (ACES) is transforming the way future events are forecast — combining the collective knowledge of many individual opinions in a unique way that improves accuracy beyond what any one person or small group of experts could provide
-
-
The world’s first "printed" aircraft flies
Engineers have designed and flown the world’s first “printed” aircraft, which could revolutionize the economics of aircraft design; the plane is a UAV whose entire structure has been printed, including wings, integral control surfaces, and access hatches; it was printed on an EOS EOSINT P730 nylon laser sintering machine, which fabricates plastic or metal objects, building up the item layer by layer
-
-
Auto theft going extinct?

Thanks to aggressive police work and new technology car theft could eventually become an obsolete problem; new technological developments like high-tech keys, immobilizer systems, and GPS tracking have made it increasingly difficult for thieves to successfully steal cars; new police tactics and technologies like bait cars and license plate scanners have given law enforcement agencies the edge in tracking down stolen cars and catching thieves
-
-
Sensing "skin" protects concrete structures
Scientists have developed a sensing “skin” which is made of stretchy thermoplastic elastomer mixed with titanium dioxde; patches of the skin are painted with black carbon to measure changes in the electrical charge of the skin; the skin will be rolled out in patches across structures such as bridges and dams; the formation of a crack would cause a movement in the concrete under the patch, which would change the capacitance, or stored energy, of the skin; daily check by computers would detect the change the capacitance, and issue and alert
-
More headlines
The long view
Are We Ready for a ‘DeepSeek for Bioweapons’?
Anthropic’s Claude 4 is a warning sign: AI that can help build bioweapons is coming, and could be widely available soon. Steven Adler writes that we need to be prepared for the consequences: “like a freely downloadable ‘DeepSeek for bioweapons,’ available across the internet, loadable to the computer of any amateur scientist who wishes to cause mass harm. With Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4 having finally triggered this level of safety risk, the clock is now ticking.”
A Brief History of Federal Funding for Basic Science
Biomedical science in the United States is at a crossroads. For 75 years, the federal government has partnered with academic institutions, fueling discoveries that have transformed medicine and saved lives. Recent moves by the Trump administration — including funding cuts and proposed changes to how research support is allocated — now threaten this legacy.
Bookshelf: Preserving the U.S. Technological Republic
The United States since its founding has always been a technological republic, one whose place in the world has been made possible and advanced by its capacity for innovation. But our present advantage cannot be taken for granted.
Autonomous Weapon Systems: No Human-in-the-Loop Required, and Other Myths Dispelled
“The United States has a strong policy on autonomy in weapon systems that simultaneously enables their development and deployment and ensures they could be used in an effective manner, meaning the systems work as intended, with the same minimal risk of accidents or errors that all weapon systems have,” Michael Horowitz writes.
Ukraine Drone Strikes on Russian Airbase Reveal Any Country Is Vulnerable to the Same Kind of Attack
Air defense systems are built on the assumption that threats come from above and from beyond national borders. But Ukraine’s coordinated drone strike on 1 June on five airbases deep inside Russian territory exposed what happens when states are attacked from below and from within. In low-level airspace, visibility drops, responsibility fragments, and detection tools lose their edge. Drones arrive unannounced, response times lag, coordination breaks.
Shots to the Dome—Why We Can’t Model US Missile Defense on Israel’s “Iron Dome”
Starting an arms race where the costs are stacked against you at a time when debt-to-GDP is approaching an all-time high seems reckless. All in all, the idea behind Golden Dome is still quite undercooked.
