-
Public support for torture declines as people learn the explicit details of torture techniques
Does the American public condone torture when the goal is to prevent terrorist attacks? News headlines reporting the results of a Pew Research Center poll released on 9 December indicate more than half of Americans do. That finding, however, is not necessarily valid, says Tufts University’s Richard Eichenberg, who argues that the poll is flawed because it is based on a faulty premise. A more accurate picture of the nation’s attitude can be found in responses to polls conducted by Pew, Gallup, and other news organizations and analyzed in a 2010 report. These surveys explained in graphic detail what interrogation techniques were being judged. So while response to more general questions on the use of torture may continue to produce mixed reactions, Eichenberg says public support for torture will decline as more people become aware of the explicit details of torture techniques contained in the Senate report.
-
-
New gas mask filtration materials show promise
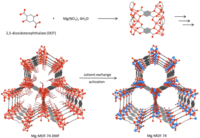
Scientists are examining the possibility of metal-organic framework compounds (MOFs) — porous crystalline materials which are made up metal ions and bridged with organics — as a possible evolution in gas mask filtration technology. Thought MOFs may still be a way from real-world application, the impact that they might have on respiration technologies could be significant.
-
-
FBI moves cyberthreats to top of law-enforcement agenda
FBI director James Comey said combatting cybercrime and other cyber threats are now top FBI priority. “It (the Internet) is transforming human relationships in ways we’ve never seen in human history before,” Comey said. “I see a whole lot of hacktivists, I see a whole lot of international criminal gangs, very sophisticated thieves,” he added. “I see people hurting kids, tons of pedophiles, an explosion of child pornography.” In October Comey urged Congress to require tech companies to put “backdoors” in apps and operating systems. Such a move would allow law enforcement officials to better to monitor suspected criminals who often escape the law using encryption and anti-surveillance computer software.
-
-
U.S. Army seeking to end environmental testing at Indiana nuclear firing range
The U.S. Army wants to end its Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) license at the Jefferson Proving Ground in southern Indiana. The Army’s appeal comes after years of water and soil testing at the site. Currently, an estimated 162,040 pounds of depleted uranium projectiles and shows are still on the firing range. The site was last used in 1995. Uranium munitions, specifically the kind used to penetrate armor during Operation Desert Shield, were used there throughout the 1980s and 1990s.
-
-
Michigan teen-ager faces terrorism charges after posting anonymous threats
A 17-year-old Brandon High School student in Oakland County, Michigan has been arrested and accused of posting online threats using the anonymous app, After School. The Oakland County Sheriff’s office contacted the app provider and served subpoenas to identify the anonymous user who posted seventeen messages and five pictures, ranging from “Tomorrow I am going to shoot and kill every last one of you and it’s going to be bigger than Columbine,” “Death to you all,” and “Bang Bang Brandon Bang Bang,” to stock photos of a person holding a pump-action shotgun.As of Thursday evening, Apple has pulled the After School app from its App Store.
-
-
A first: U.S. Navy shipboard laser operates in Persian Gulf

The U.S. Navy announced that a laser weapon system (LaWS) — a cutting-edge weapon that brings significant new capabilities to America’s Sailors and Marines — was for the first time successfully deployed and operated aboard a naval vessel in the Persian Gulf. The operational demonstrations, which took place from September to November aboard USS Ponce (AFSB[I] 15), were historic not only because they showed a laser weapon working aboard a deployed U.S. Navy ship, but also because LaWS operated seamlessly with existing ship defense systems. During the tests, LaWS hit targets mounted aboard a speeding oncoming small boat, shot a Scan Eagle unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) out of the sky, and destroyed other moving targets at sea.
-
-
Firefighters portable radios may fail at elevated temperatures
Firefighters rely on the radios to report their location and to communicate with other first responders as well as the incident command post or communications center. Performance problems with portable radios have been identified by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health as contributing factors in some firefighter fatalities. New test results from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) confirm that portable radios used by firefighters can fail to operate properly within fifteen minutes when exposed to temperatures that may be encountered during firefighting activities.
-
-
Report details brutal interrogation practices, lax supervision

The long-awaited report on the CIA interrogation practices was release yesterday, causing a political storm. Many congressional Republicans have expressed concern over the release of the Senate report on the CIA’s use of torture on captured al-Qaeda and Islamist militants, claiming it would set off a global backlash, and threaten the security of American troops and diplomatic missions overseas.Obama administration officials agree that the release of the Senate report or its declassified executive summary is a good reason for concern about the security of U.S. facilities and military bases overseas, but they doubt it would lead to the sort of violence that killed four Americans at a diplomatic outpost in Benghazi, Libya in 2012.
-
-
FAA caught between commercial pressures, safety concerns in regulating drone use
Law enforcement agencies in major U.S. cities have expressed concerns about the possible use of drones by terrorists to launch bombs against key U.S. targets, including shopping malls, stadiums, and even banks. The FAA is in a tough spot, says one expert.”If they come out with rules that are not protective enough and then there’s some sort of an accident then they will be criticized for not having been more careful with this technology,” he says. “On the other hand, if they come out with rules that are viewed as overly restrictive in the name of safety then they are going to be criticized as impeding the growth of the industry, so it’s a very difficult balancing act that they have to navigate.”
-
-
Bionic bra one step closer
A Bionic Bra which automatically tightens in response to breast movement is one step closer to reality with the development of a new prototype. The development of the bra is the result of findings by researchers that without the right breast support, the movement of women’s breasts during demanding physical activity – in sports, the military, first response, and more – may cause long-term damage, including numbness in the fingers caused by compression of nerves on the shoulders, as well as neck and back pain. “Unfortunately, the most supportive sports bras tend to be the most uncomfortable to wear.” Making matters worse, “research has found that 85 percent of women are wearing bras that do not fit or support their breasts correctly,” one of the researchers said.
-
-
Israel attacks targets in Syria to prevent advanced arms shipments to Hezbollah

Israeli jets bombed two military targets in Syria – one near the Damascus International Airport, the other near the town of Dima, north of Damascus and near the Syria-Lebanon border – and as has been the case in previous such attacks, there was no confirmation or elaboration from Jerusalem. Syrian general command sources said that several facilities had been hit, both at the Damascus International Airport and in the area of Dimas. This is the tenth Israeli attack against military depots in Syria since January 2013. The attacks have had a specific goal: to prevent the Assad regime and Iran from transferring advanced weapon systems to Hezbollah. When Israel’s intelligence services notice that such systems are gathered for the purpose of shipping them to Hezbollah, the shipments are destroyed before they are delivered to Hezbollah.
-
-
Crime data research sheds new light on British Muslim communities

U.K. Muslim communities may not be as victimized by violent crime, or as dissatisfied with the police as is widely suggested and believed, according to new research. An examination of statistics reveals a surprising counter-narrative to commonly held perceptions of British Muslim communities and their relationships to crime victimization and the criminal justice system. Despite widespread condemnation of police counter-terrorism measures such as stop and search, data from the Crime Survey of England and Wales reveal that a sizeable majority of Muslim respondents not only reported positive attitudes toward a range of subjects such as police fairness, reliability, and relevance to the community but are in many cases more likely to do so than non-Muslim respondents.
-
-
NIST study argues for RFID forensic evidence management

Radio frequency identification (RFID) tags— have become increasingly popular for tracking everything from automobiles being manufactured on an assembly line to zoo animals in transit to their new homes. Now, thanks to a new NIST report, the next beneficiaries of RFID technology may soon be law enforcement agencies responsible for the management of forensic evidence. The release notes that the practical question that agencies must consider is whether RFID technology can produce measurable benefits and a positive return on the funds invested in a new system. The NIST report estimates that RFID systems can pay back their initial set-up cost in about two years.
-
-
Studying the long-term aging of electronics in nuclear weapons

Sandia National Laboratories is studying how environments, including radiation which originates from a nuclear weapon itself, could affect the performance of electronics in the W76-1 warhead as they age. Researchers have studied radiation effects since the early days of nuclear weapons, but a 30-year program, which begun in 2006, will provide real-time data for the first time on how electronics age within the weapon. Studies in the past used techniques that artificially accelerated the aging process based on a range of assumptions resulting from experiments and previous research.
-
-
New report, video detail dynamics of deadly Chicago house fire

A new NIST computer-modeling study of a 2012 Chicago house fire reveals the conditions that unleashed a surge of searing gases, leading to the death of a veteran firefighter. The simulation shows that fire in a covered back porch caused a closed steel-faced, wood-framed door to crumble, releasing pressure and causing hot gases to pour into the adjoining hallway where the victim and another firefighter were advancing a fire hose. The coincidental timing of the responders’ “interior attack” and the door’s failure proved to be deadly. In less than five seconds, the flow of gases caused the hallway temperature to soar, from about 60 degrees Celsius (140 degrees Fahrenheit) to at least 260 degrees Celsius (500 degrees Fahrenheit), the study found.
-
More headlines
The long view
Are We Ready for a ‘DeepSeek for Bioweapons’?
Anthropic’s Claude 4 is a warning sign: AI that can help build bioweapons is coming, and could be widely available soon. Steven Adler writes that we need to be prepared for the consequences: “like a freely downloadable ‘DeepSeek for bioweapons,’ available across the internet, loadable to the computer of any amateur scientist who wishes to cause mass harm. With Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4 having finally triggered this level of safety risk, the clock is now ticking.”
“The Federal Government Is Gone”: Under Trump, the Fight Against Extremist Violence Is Left Up to the States
As President Donald Trump guts the main federal office dedicated to preventing terrorism, states say they’re left to take the lead in spotlighting threats. Some state efforts are robust, others are fledgling, and yet other states are still formalizing strategies for addressing extremism. With the federal government largely retreating from focusing on extremist dangers, prevention advocates say the threat of violent extremism is likely to increase.
Luigi Mangione and the Making of a ‘Terrorist’
Discretion is crucial to the American tradition of criminal law, Jacob Ware and Ania Zolyniak write, noting that “lawmakers enact broader statutes to empower prosecutors to pursue justice while entrusting that they will stay within the confines of their authority and screen out the inevitable “absurd” cases that may arise.” Discretion is also vital to maintaining the legitimacy of the legal system. In the prosecution’s case against Luigi Mangione, they charge, “That discretion was abused.”
Autonomous Weapon Systems: No Human-in-the-Loop Required, and Other Myths Dispelled
“The United States has a strong policy on autonomy in weapon systems that simultaneously enables their development and deployment and ensures they could be used in an effective manner, meaning the systems work as intended, with the same minimal risk of accidents or errors that all weapon systems have,” Michael Horowitz writes.
Ukraine Drone Strikes on Russian Airbase Reveal Any Country Is Vulnerable to the Same Kind of Attack
Air defense systems are built on the assumption that threats come from above and from beyond national borders. But Ukraine’s coordinated drone strike on 1 June on five airbases deep inside Russian territory exposed what happens when states are attacked from below and from within. In low-level airspace, visibility drops, responsibility fragments, and detection tools lose their edge. Drones arrive unannounced, response times lag, coordination breaks.
Shots to the Dome—Why We Can’t Model US Missile Defense on Israel’s “Iron Dome”
Starting an arms race where the costs are stacked against you at a time when debt-to-GDP is approaching an all-time high seems reckless. All in all, the idea behind Golden Dome is still quite undercooked.
