-
Be prepared: What to do if an asteroid is heading our way

Last month, experts from European Space Agency’s (ESA) Space Situational Awareness (SSA) program and Europe’s national disaster response organizations met for a two-day exercise on what to do if an asteroid is ever found to be heading our way. The exercise considered the threat from an imaginary, but plausible, asteroid, initially thought to range in size from twelve meters to thirty-eight meters — spanning roughly the range between the 2013 Chelyabinsk airburst and the 1908 Tunguska event — and travelling at 12.5 km/s. Teams were challenged to decide what should happen at five critical points in time, focused on 30, 26, 5, and 3 days before and one hour after impact.
-
-
New cyber test range trains soldiers for simultaneous cyber and combat operations
A unique mix of training technologies sponsored by the Office of Naval Research (ONR) is preparing front-line soldiers to conduct cyber and combat operations simultaneously, as Marines demonstrated during a recent amphibious exercise off the coast of Virginia. During last month’s Bold Alligator exercise, Marines used ONR’s Tactical Cyber Range to emulate adversary communications hidden in a noisy, dense electromagnetic spectrum —as much a battleground in today’s digital world as any piece of land.
-
-
Helping first-response robots operate for longer periods
Through a project supported by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), Sandia Lab is developing technology which will dramatically improve the endurance of legged robots, helping them operate for long periods while performing the types of locomotion most relevant to disaster response scenarios. One of Sandia’s new robots which showcases this technology will be demonstrated at an exposition to be held in conjunction with the DARPA Robotics Challenge Finals next June.
-
-
Turning deadly chemical warfare agents into harmless soil
Destroying chemical warfare agents in bulk is a challenge for the military and international community. Current methods of eradication, such as incineration or hydrolysis, create toxic waste which requires further processing. The logistics required to transport large stockpiles from storage to a disposal site can be risky and expensive. DARPA is seeking portable system that turns stockpiles of chemical warfare agents into dirt or other safe organic compounds without generating hazardous waste.
-
-
Public support for torture declines as people learn the explicit details of torture techniques
Does the American public condone torture when the goal is to prevent terrorist attacks? News headlines reporting the results of a Pew Research Center poll released on 9 December indicate more than half of Americans do. That finding, however, is not necessarily valid, says Tufts University’s Richard Eichenberg, who argues that the poll is flawed because it is based on a faulty premise. A more accurate picture of the nation’s attitude can be found in responses to polls conducted by Pew, Gallup, and other news organizations and analyzed in a 2010 report. These surveys explained in graphic detail what interrogation techniques were being judged. So while response to more general questions on the use of torture may continue to produce mixed reactions, Eichenberg says public support for torture will decline as more people become aware of the explicit details of torture techniques contained in the Senate report.
-
-
New gas mask filtration materials show promise
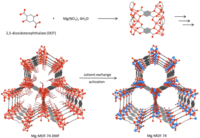
Scientists are examining the possibility of metal-organic framework compounds (MOFs) — porous crystalline materials which are made up metal ions and bridged with organics — as a possible evolution in gas mask filtration technology. Thought MOFs may still be a way from real-world application, the impact that they might have on respiration technologies could be significant.
-
-
FBI moves cyberthreats to top of law-enforcement agenda
FBI director James Comey said combatting cybercrime and other cyber threats are now top FBI priority. “It (the Internet) is transforming human relationships in ways we’ve never seen in human history before,” Comey said. “I see a whole lot of hacktivists, I see a whole lot of international criminal gangs, very sophisticated thieves,” he added. “I see people hurting kids, tons of pedophiles, an explosion of child pornography.” In October Comey urged Congress to require tech companies to put “backdoors” in apps and operating systems. Such a move would allow law enforcement officials to better to monitor suspected criminals who often escape the law using encryption and anti-surveillance computer software.
-
-
U.S. Army seeking to end environmental testing at Indiana nuclear firing range
The U.S. Army wants to end its Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) license at the Jefferson Proving Ground in southern Indiana. The Army’s appeal comes after years of water and soil testing at the site. Currently, an estimated 162,040 pounds of depleted uranium projectiles and shows are still on the firing range. The site was last used in 1995. Uranium munitions, specifically the kind used to penetrate armor during Operation Desert Shield, were used there throughout the 1980s and 1990s.
-
-
Michigan teen-ager faces terrorism charges after posting anonymous threats
A 17-year-old Brandon High School student in Oakland County, Michigan has been arrested and accused of posting online threats using the anonymous app, After School. The Oakland County Sheriff’s office contacted the app provider and served subpoenas to identify the anonymous user who posted seventeen messages and five pictures, ranging from “Tomorrow I am going to shoot and kill every last one of you and it’s going to be bigger than Columbine,” “Death to you all,” and “Bang Bang Brandon Bang Bang,” to stock photos of a person holding a pump-action shotgun.As of Thursday evening, Apple has pulled the After School app from its App Store.
-
-
A first: U.S. Navy shipboard laser operates in Persian Gulf

The U.S. Navy announced that a laser weapon system (LaWS) — a cutting-edge weapon that brings significant new capabilities to America’s Sailors and Marines — was for the first time successfully deployed and operated aboard a naval vessel in the Persian Gulf. The operational demonstrations, which took place from September to November aboard USS Ponce (AFSB[I] 15), were historic not only because they showed a laser weapon working aboard a deployed U.S. Navy ship, but also because LaWS operated seamlessly with existing ship defense systems. During the tests, LaWS hit targets mounted aboard a speeding oncoming small boat, shot a Scan Eagle unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) out of the sky, and destroyed other moving targets at sea.
-
-
Firefighters portable radios may fail at elevated temperatures
Firefighters rely on the radios to report their location and to communicate with other first responders as well as the incident command post or communications center. Performance problems with portable radios have been identified by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health as contributing factors in some firefighter fatalities. New test results from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) confirm that portable radios used by firefighters can fail to operate properly within fifteen minutes when exposed to temperatures that may be encountered during firefighting activities.
-
-
Report details brutal interrogation practices, lax supervision

The long-awaited report on the CIA interrogation practices was release yesterday, causing a political storm. Many congressional Republicans have expressed concern over the release of the Senate report on the CIA’s use of torture on captured al-Qaeda and Islamist militants, claiming it would set off a global backlash, and threaten the security of American troops and diplomatic missions overseas.Obama administration officials agree that the release of the Senate report or its declassified executive summary is a good reason for concern about the security of U.S. facilities and military bases overseas, but they doubt it would lead to the sort of violence that killed four Americans at a diplomatic outpost in Benghazi, Libya in 2012.
-
-
FAA caught between commercial pressures, safety concerns in regulating drone use
Law enforcement agencies in major U.S. cities have expressed concerns about the possible use of drones by terrorists to launch bombs against key U.S. targets, including shopping malls, stadiums, and even banks. The FAA is in a tough spot, says one expert.”If they come out with rules that are not protective enough and then there’s some sort of an accident then they will be criticized for not having been more careful with this technology,” he says. “On the other hand, if they come out with rules that are viewed as overly restrictive in the name of safety then they are going to be criticized as impeding the growth of the industry, so it’s a very difficult balancing act that they have to navigate.”
-
-
Bionic bra one step closer
A Bionic Bra which automatically tightens in response to breast movement is one step closer to reality with the development of a new prototype. The development of the bra is the result of findings by researchers that without the right breast support, the movement of women’s breasts during demanding physical activity – in sports, the military, first response, and more – may cause long-term damage, including numbness in the fingers caused by compression of nerves on the shoulders, as well as neck and back pain. “Unfortunately, the most supportive sports bras tend to be the most uncomfortable to wear.” Making matters worse, “research has found that 85 percent of women are wearing bras that do not fit or support their breasts correctly,” one of the researchers said.
-
-
Israel attacks targets in Syria to prevent advanced arms shipments to Hezbollah

Israeli jets bombed two military targets in Syria – one near the Damascus International Airport, the other near the town of Dima, north of Damascus and near the Syria-Lebanon border – and as has been the case in previous such attacks, there was no confirmation or elaboration from Jerusalem. Syrian general command sources said that several facilities had been hit, both at the Damascus International Airport and in the area of Dimas. This is the tenth Israeli attack against military depots in Syria since January 2013. The attacks have had a specific goal: to prevent the Assad regime and Iran from transferring advanced weapon systems to Hezbollah. When Israel’s intelligence services notice that such systems are gathered for the purpose of shipping them to Hezbollah, the shipments are destroyed before they are delivered to Hezbollah.
-
More headlines
The long view
Factories First: Winning the Drone War Before It Starts
Wars are won by factories before they are won on the battlefield,Martin C. Feldmann writes, noting that the United States lacks the manufacturing depth for the coming drone age. Rectifying this situation “will take far more than procurement tweaks,” Feldmann writes. “It demands a national-level, wartime-scale industrial mobilization.”
How Male Grievance Fuels Radicalization and Extremist Violence
Social extremism is evolving in reach and form. While traditional racial supremacy ideologies remain, contemporary movements are now often fueled by something more personal and emotionally resonant: male grievance.
The Surprising Reasons Floods and Other Disasters Are Deadlier at Night
It’s not just that it’s dark and people are asleep. Urban sprawl, confirmation bias, and other factors can play a role.
Why Flash Flood Warnings Will Continue to Go Unheeded
Experts say local education and community support are key to conveying risk.
