-
Drones being used to track hurricanes

Federal hurricane trackers will start experimenting with unmanned boats and aircrafts to learn more about how to anticipate and track the movements of hurricanes; NASAand the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration(NOAA) are teaming up and using a pair of military-surplus Global Hawk spy drones, which are known more for spying on battlefields than chasing storms
-
-
Underground organisms play a more complex role carbon capturing than previously thought
In a surprising finding, researchers have shown that certain underground organisms thought to promote chemical interactions that make the soil a carbon sink actually play a more complex, dual role when atmospheric carbon levels rise
-
-
Evaluating fresh water sustainability in the southern U.S.
Researchers have embarked on 4-year federal research effort to evaluate freshwater sustainability across the southern United States and develop policy recommendations on what can be done to make the best use of water supplies in the face of population growth and the effects of climate change over the next ten to thirty years
-
-
Hurricane Isaac downgraded from Category 1 hurricane to tropical storm

Hurricane Isaac was downgraded from a category 1 hurricane to a tropical storm. The storms winds have dropped below 70 mph, but the storm is moving very slowly throughout the gulf area at about 6 mph; at this point officials estimate that Isaac is expected to cause $1.5 billion in insured losses
-
-
New Jersey infrastructure badly needs shoring up, and soon
According to experts, changes to the way New Jersey maintains its infrastructure must be made soon, or the state could be vulnerable to catastrophic failures in its water and power systems as well as collapsing roads; the North Jersey Transportation Planning Authority says more than $56.9 billion will be needed just to maintain state roads, rails, and public transportation systems through 2035; when you add in improvements to account for environmental changes and the expanding population in the state, the bill skyrockets to more than $123 billion
-
-
New filter will help clean oil spills
Oil and water disdain each other, but once forced to comingle they are nearly impossible to separate; a new filter separates oil and water using only gravity; the filter could help clean oil spills, or clean water at treatment plants
-
-
Japan awards tsunami buoy contract to SAIC

The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) in Tokyo, Japan, has awarded (SAIC) a contract for the production and delivery of six SAIC Tsunami Buoy (STB) systems; the STB systems will be deployed at locations in the northwest Pacific Ocean approximately 200 nautical miles east of Sendai, Japan
-
-
Heat waves move toward California coasts, become more humid, imperiling health
Scientists detected a trend toward more humid heat waves which are expressed very strongly in elevated nighttime temperatures, a trend consistent with climate change projections; moreover, relative to local warming, the mid-summer heat waves are getting stronger in generally cooler coastal areas; this carries strong public health implications for the twenty-one million Californians living near the ocean whose everyday lives are acclimated to moderate temperatures
-
-
Smart agriculture will increase global food production, reduce environmental impact

Global demand for food is expected to double by 2050 due to population growth and increased standards of living; a new study, based on analysis of agricultural data gathered from around the world, offers hope that with more strategic use of fertilizer and water, we could not only dramatically boost global crop yield, but also reduce the adverse environmental impact of agriculture
-
-
Last year’s east coast earthquake has the region preparing for another one
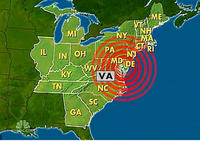
Last year an earthquake that was centered in Virginia shook up the entire east coast, surprising everyone; it did not result in any deaths and was considered relatively light compared to many tremors on the West Coast, but it was bad enough to force some states to prepare themselves in case of another quake
-
-
Activists in arms over plans to ship plutonium to New Mexico
A proposal to ship tons of plutonium to New Mexico, including cores of nuclear warheads which would be dismantled at a structurally questionable lab on top of an earthquake fault zone, has activists and nuclear watchdogs up in arms
-
-
Los Alamos lab responds to radiological incident

The Los Alamos National Laboratory said it is investigating the inadvertent spread of Technetium 99 by employees and contractors at the Lujan Neutron Scattering Center at the Los Alamos Neutron Science Center (LANSCE), a multidisciplinary accelerator facility used for both civilian and national security research; multiple tests indicate no health risks to public or employees
-
-
Cooling coal emissions would clean air, lower health, climate-change costs

In the United States there are about 1,400 electric-generating unit powered by coal, operated at about 600 power plants; the estimated health costs of burning coal in the United States are in the range of $150 billion to $380 billion, including 18,000-46,000 premature deaths, 540,000 asthma attacks, 13,000 emergency room visits, and two million missed work or school days each year; scientists estimate that implementing large-scale cryogenic systems into coal-fired plants would reduce overall costs to society by 38 percent through the sharp reduction of associated health-care and climate-change costs
-
-
Maldives to build floating islands to save country from rising sea levels
The Maldives Islands, a low-lying chain of twenty-six atolls in the Indian Ocean, are sinking; more precisely: due to global warming, the sea level is rising over the islands, most of which sit lower than three feet above the rising water; the Maldives government has embarked on an ambitious project: build floating islands, anchor them to the ocean floor, then relocate most of the population of 300,000 – and some of the tourist attractions – to them
-
-
Electric plants challenged by high temperatures, drought
The hottest July on record since 1895, along with the most wide-spread drought in the country since 1956, have nuclear plants struggling with finding enough water — cool water — to keep key parts of the plants cool; if the water gets too warm, operators have to dial back production — for reactor safety, and also to regulate the temperature of discharge water, which affects aquatic life
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
