-
Engineers to build Australia’s first bushfire resistant straw house
With Australia’s bushfire season fast approaching, construction of the first bushfire resistant straw bale house tested by engineers from CSIRO has begun in rural Victoria; the house is based on design principles that minimize environmental impact and it is set to withstand temperatures equal to that of a worst case bushfire scenario
-
-
Helping communities resist wildfires

In the ten years since 2002, an annual average of nearly 71,000 wildfires near structures and other human development were recorded and 1.9 million hectares (4.7 million acres) burned; federal agencies spend an average of $1.2 billion per year on the suppression of these fires, with state and local agencies contributing millions more
-
-
Target of limiting global warming to 2°C recedes as CO2 emissions grow
A new report shows that global CO2 emissions have increased by 58 percent since 1990, rising 3 percent in 2011, and 2.6 percent in 2012; the most recent figure is estimated from a 3.3 percent growth in global gross domestic product and a 0.7 percent improvement in the carbon intensity of the economy; these latest carbon dioxide emission figures continue to track at the high end of a range of emission scenarios, expanding the gap between current trends and the course of mitigation needed to keep global warming below 2°C
-
-
City officials debate proposals for sea walls to protect New York from storms
Since Hurricane Sandy ripped through the northeast, many people have had to decide what to do with their damaged homes; now elected officials in New York must decide how to protect coastal areas around the city from being run over by storms in the future; New York officials are now proposing similar projects, including a $16 billion barrier for New York Bay, which was proposed by City Council president Christie Quinn
-
-
Improved research tools helped predict impact of last week’s Japan earthquake
On 11 March 2011, a magnitude-9.0 earthquake and ensuing tsunami that slammed into northeastern Japan killed or left missing some 19,000 people, devastating much of the coast; lessons were learned, and improved computational models helped in more accurately predicting the impact of a strong earthquake near Japan last Friday
-
-
Testing new wind energy turbine

An offshore wind test turbine has been erected behind the University of Maine Advanced Structures and Composites Center on campus to evaluate sensor systems and controls in preparation for the installation of a floating turbine in the Gulf of Maine this spring as part of the DeepCwind Consortium project
-
-
Climate models still struggle with medium- term climate forecasts
Scientists have evaluated twenty-three climate models and concluded that there is still a long way to go before reliable regional predictions can be made on seasonal to decadal time scales; none of the models evaluated is able today to forecast the weather-determining patterns of high and low pressure areas such that the probability of a cold winter or a dry summer can be reliably predicted
-
-
Geologists pinpoint powerful-earthquake hot spots
After studying about 1,500 earthquakes, scientists conclude that the world’s largest earthquakes occur at subduction zones — locations where a tectonic plate slips under another; the scientists have found that regions where “scars” on the seafloor, called fracture zones, meet subduction areas are at higher risk of generating powerful earthquakes
-
-
U.S. faces more – and more intense – wildfire

Scientists using NASA satellite data and climate models have projected drier conditions likely will cause increased fire activity across the United States in coming decades; the researchers calculated results for low and high greenhouse gas emissions scenarios; in both cases, results suggest more fire seasons that are longer and stronger across all regions of the United States in the next 30-50 years; specifically, high fire years like 2012 would likely occur two to four times per decade by mid-century, instead of once per decade under current climate conditions
-
-
Geoengineering could disrupt global rainfall patterns
Tackling climate change by reducing the solar radiation reaching our planet using climate engineering, known also as geoengineering, could result in undesirable effects for the Earth and humankind; in particular, new research shows that disruption of global and regional rainfall patterns is likely in a geoengineered climate
-
-
TVA considering raising height of dams to prevent future floods
The dams located on the upper Tennessee River never had flood waters top them, and government officials want to keep it that way, saying that due to recent disasters such as the 2010 Nashville flood and the 2011Fukushima tsunami, they need to prepare the worst possible situation
-
-
Removing sea defenses may reduce impact of coastal flooding
Coastal defenses put in place over the last century or so have re-shaped the U.K. coastline, artificially protecting some areas, but at the expense of beaches in adjacent areas; this man-made situation increases the risk of flooding in low lying coastal settlements where beaches act as a natural flood defense; beach levels can be artificially recharged, but maintaining this indefinitely along large stretches of coastline is costly and likely to be unsustainable
-
-
Pulverized rocks used to strip CO2 from emissions of steel, coal, cement plants
Researchers in Quebec are developing a process which would see steel, coal, and cement plants as well as oil and gas facilities remove most of the carbon dioxide (CO2) from their emissions through chemical reactions with various types of crushed rocks in the stacks
-
-
Huawei rejects U.S. “threat to national security” claims
In October the United States House Intelligence Committee issued a report warning U.S. companies against using two Chinese companies, Huawei and ZTE, for their telecommunication technology needs; the report said that the firms may be too close to China’s Communist Party and its military’ the report also suggested their products and services could pose a threat to the security of the United .States; Huawei vigorously disputes both claims
-
-
Quantum cryptography may soon go main stream
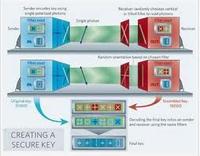
Researchers have perfected a technique that offers a less expensive way to ensure the security of high-speed fiber-optic cables, protecting communication networks from unauthorized snooping; this means that existing telecom networks can now be secured with this ultimate form of encryption
-
More headlines
The long view
Falling Space Debris: How High Is the Risk I'll Get Hit?
An International Space Station battery fell back to Earth and, luckily, splashed down harmlessly in the Atlantic. Should we have worried? Space debris reenters our atmosphere every week.
Using Drone Swarms to Fight Forest Fires
Forest fires are becoming increasingly catastrophic across the world, accelerated by climate change. Researchers are using multiple swarms of drones to tackle natural disasters like forest fires.
