-
U.S. may already have authority to issue infrastructure protection regulations
While the president and Congress continue to debate the cybersecurity bill, the White House Office of Management and Budget may already have sufficient statutory authority to enact new regulations through the normal notice-and-comment rulemaking process; the basis for such regulations would be the Data Quality Act (DQA) which sets the standards for the integrity of data used by federal agencies in public disseminations
-
-
Electric plants challenged by high temperatures, drought
The hottest July on record since 1895, along with the most wide-spread drought in the country since 1956, have nuclear plants struggling with finding enough water — cool water — to keep key parts of the plants cool; if the water gets too warm, operators have to dial back production — for reactor safety, and also to regulate the temperature of discharge water, which affects aquatic life
-
-
Glass offers a better way of storing U.K. nuclear waste

Researchers have shown, for the first time, that a method of storing nuclear waste normally used only for High Level Waste (HLW) could provide a safer, more efficient, and potentially cheaper solution for the storage and ultimate disposal of Intermediate Level Waste (ILW)
-
-
How to act if there is a fire on a high-speed train

Researchers have used computer models to analyze the best way to evacuate the Spanish High Speed Train (AVE) in the case of fire; the involvement of the crew in organizing the fast transfer of passengers, completing the process before the train comes to a halt, and collective collaboration to assist those with reduced mobility are just some of the strategies to be followed
-
-
Mystery of dramatic leveling off of methane in the atmosphere solved

Increased capture of natural gas from oil fields probably accounts for up to 70 percent of the dramatic leveling off seen in atmospheric methane at the end of the twentieth century; methane has twenty times the global warming potential of carbon dioxide, although CO2 is filling the atmosphere in far larger amounts
-
-
Engineering students build U.K. first hydrogen powered locomotive
Engineering students and staff at the University of Birmingham have designed and built a prototype hydrogen powered locomotive, the first of its kind to operate in the United Kingdom
-
-
Invasion at “Fort Knox of Uranium” raises security concerns

The Y-12 National Security Complex in Oak Ridge, Tennessee, is regarded asthe Fort Knox of Uranium, so the fact that three anti-nuclear activists, one of them an 82-year old nun, were able to breach the high-security complex’s protective fences is not reassuring; that they did so using nothing more than bolt cutters, after announcing their arrival from half-a-mile away, and that they could stay, undetected, in a highly secure area on the nuclear complex’s ground for two hours, is even more worrisome
-
-
Y-12 and operator error
Three anti-nuclear activists, led by an 82-year old nun, breached the perimeter security system of the supposedly highly secure Y-2 nuclear facility at Oak Ridge, Tennessee, where nuclear weapons components are manufactured (note that the Oak Ridge National Laboratory [ONRL] is not affiliated with the Y-12 National Security Complex); they then spent several hours in a secure area of the facility, leisurely spray-painting slogans on the facility’s walls – without the facility’s security staff, or the sophisticated $500 million security cameras and sensors, detecting them; to understand what happened at Y-2, we must accept that operator error is an essential problem in national security, and that the problem is pervasive and normal; the only way to deal with the operator error phenomenon is to build redundancies into the system
-
-
Long Beach Police Department purchases underwater inspection system for port
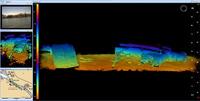
The Port of Long Beach is the second busiest seaport in the United States and is a major gateway for trade with Asia, handling more than six million containers annually; to enhance port security, the City of Long Beach Police Department has purchased an Underwater Inspection System (UIS) from Cod Octopus
-
-
New device dismantles pipe bombs safely, preserving forensic evidence
Thousands of pipe bombs are made each year, and thousands of pipe bomb threats are called into local police and FBI authorities across the country; many are false alarms, but those that are not can be deadly; dismantling a pipe bomb is tricky and serious business, and missteps during the dismantling process can produce catastrophic results
-
-
Drone use spreads to more areas and missions

As security challenges in the United State and around the globe change, many countries have one thing in common: unmanned drones will be a significant part of the future of security; advancements in technology are driving the use of UAVs into newareas
-
-
Geoengineering clouds to slow global warming

Researchers are taking a second look at the possibility of using futuristic ships to shoot salt water high into the sky over the oceans, creating clouds that reflect sunlight and thus counter global warming; The theory behind idea, called “marine cloud brightening,” is that adding particles, in this case sea salt, to the sky over the ocean would form large, long-living clouds
-
-
Bacteria in tap water traced to the water treatment process
Most of the bacteria that remain in drinking water when it gets to the tap can be traced to filters used in the water treatment process, rather than to the aquifers or rivers where they originated; the findings could open the door to more sustainable water treatment processes that use fewer chemicals and, as a result, produce lower levels of byproducts that may pose health risks; eventually, the work could enable engineers to control the types of microbes in drinking water to improve human health
-
-
Aerospace materials for on-site building of pipes of infinite length

Concrete and steel pipes are built in short sections to fit on standard 18-wheel trucks; the heavy industrial manufacturing processes, long-distance trucking, and leak-prone joints used in steel and concrete pipe construction exact a heavy toll on the environment, not to mention bottom line; the solution: a new pipe design, consisting of a central layer of lightweight plastic honeycomb, which can be built onsite as a single section of virtually infinite length
-
-
Greenland melting breaks record four weeks early – with two weeks more to go
Melting over the Greenland ice sheet shattered the seasonal record on 8 August — a full four weeks before the close of the melting season; with more melting yet to come in August, this year’s overall melting will fall way above the old records; researchers devise a “cumulative melting index,” which measures the type of melting which adds to the runoff of melt-water that makes sea levels rise
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
By Natasha Lindstaedt
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
By Katie Myers
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
By David Montgomery
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
By John Domol
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
By Zach Winn
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
