-
Obama considering executive order for infrastructure protection
President Barack Obama is exploring whether to issue an executive order to protect the U.S. critical computer infrastructure from cyber attacks; White House sources say an executive order is being considered after a 2 August procedural vote in the Senate that all but doomed a scyberecurity bill endorsed by Obama as well as current and former national security officials from both Republican and Democratic administrations
-
-
Climatic impacts of megapolitan expansion
Arizona’s Sun Corridor is the most rapidly-growing megapolitan area in the United States. Nestled in a semi-arid environment, it is composed of four metropolitan areas: Phoenix, Tucson, Prescott, and Nogales. With a population projection expected to exceed 9 million people by 2040; a first study of its kind, attempting to quantify the impact of rapidly expanding megapolitan areas on regional climate, showed that local maximum summertime warming resulting from projected expansion of the urban Sun Corridor could approach 4 degrees Celsius
-
-
Engineers solve leaky water pipes problem

Leaky pipes are a common problem for the water industry: according to the U.K. Water Services Regulation Authority (OFWAT), between 20 and 40 percent of our total water supply can be lost through damaged pipes; developing more accurate ways of finding leaks would enable water companies to save revenue and reduce their environmental impact
-
-
Wastewater key to addressing growing global water shortage

Parched cities and regions across the globe are using sewage effluent and other wastewater in creative ways to augment drinking water, but four billion people still do not have adequate supplies, and that number will rise in coming decades
-
-
Water sustainability flows through complex human-nature interactions
The fate of water in China mirrors problems across the world: water is fouled, pushed far from its natural origins, squandered, and exploited; China’s crisis is daunting, though not unique: two-thirds of China’s 669 cities have water shortages, more than 40 percent of its rivers are severely polluted, 80 percent of its lakes suffer from eutrophication — an over abundance of nutrients — and about 300 million rural residents lack access to safe drinking water
-
-
Concerns about U.S. grid grow along with demand for power

The U.S. grid is stretched to capacity and severely outdated; some experts fear that blackouts in the past years in New York, Boston, and San Diego will become more frequent in the near future unless a multi-billion dollar overhaul is worked out
-
-
World facing increasingly challenging water situation
New measure developed for sustainability of global groundwater water supply points to overuse of water in Asia and North America; approximately 1.7 billion people, most residing in Asia, live in areas where groundwater resources or groundwater-dependent ecosystems are under threat
-
-
July flooding in China causes $8.3 billion of economic losses

Insurance industry faces agriculture losses from China to the United States in July 2012: flooding caused more than $8.3 billion in economic losses across China during July, while the worst drought in decades worsened across much of the United States; severe weather also prompted widespread damage in parts of the United States and Europe
-
-
California’s hydropower is vulnerable to climate change
Fifteen percent of California’s electricity comes from hydropower, a cheap and relatively clean energy source; .about 75 percent of this hydropower comes from high-elevation units, located above 1,000 ft.; with most of them located in Northern California and the Sierra Mountains; if California loses snowpack under climate warming, these high-elevation reservoirs might not be able to store enough water for hydropower generation in summer months when the demand is much higher
-
-
Dropping lake levels in Michigan are a cause for concern
In a state that boasts 11,000 lakes, Michigan is going through a year long drought that has residents and businesses scrambling as water levels continue to decrease; the low waters is the result of low snowpack last winter and a hot dry summer this year
-
-
Improved disaster resilience is imperative for U.S: report
A new report from the National Academies says that it is essential for the United States to bolster resilience to natural and human-caused disasters, and that this will require complementary federal policies and locally driven actions that center on a national vision – a culture of resilience; improving resilience should be seen as a long-term process, but it can be coordinated around measurable short-term goals that will allow communities better to prepare and plan for, withstand, recover from, and adapt to adverse events
-
-
UAVs with dexterous arms to help in infrastructure repair and disaster recovery
With current technology, most UAVs perform passive tasks such as surveillance and reconnaissance missions, tasks which are performed well above ground; researchers are interested in how UAVs might interact with objects at or near ground level; a UAV with dexterous arms could perform a wide range of active near-ground missions, from infrastructure repair and disaster recovery to border inspection and agricultural handling
-
-
Extreme summer heat events, global warming linked: research
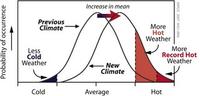
Since the late 1980s researches have been asserting that global warming would reach a point in the coming decades when its connection to extreme events would become more apparent; while some warming should coincide with a noticeable boost in extreme events, the natural variability in climate and weather can be so large as to disguise the trend; to distinguish the trend from natural variability, NASA researchers turned to statistics; the researchers did not focus on the causes of temperature change, analyzing instead surface temperature data
-
-
Study finds correlation between injection wells and small earthquakes
Most earthquakes in the Barnett Shale region of North Texas occur within a few miles of one or more injection wells used to dispose of wastes associated with petroleum production such as hydraulic fracturing fluids, according to new research
-
-
Canadian company offers the first treatment to neutralize red mud

Red mud is the most significant waste product of the traditional Bayer process for aluminum production; the industry produces more than 100 million tons of red mud a year, of which less than 5 percent is be reused; the rest is stored in ponds and reservoirs, posing serious environmental and economic risk; on 4 October 2010, for example, a flood of toxic red mud devastated Hungary after a retaining dyke ruptured, causing an ecological disaster; Canadian company Orbite Aluminae offers a technology to tackle the aluminum industry’s most serious problem
-
More headlines
The long view
Water Wars: A Historic Agreement Between Mexico and US Is Ramping Up Border Tension
As climate change drives rising temperatures and changes in rainfall, Mexico and the US are in the middle of a conflict over water, putting an additional strain on their relationship. Partly due to constant droughts, Mexico has struggled to maintain its water deliveries for much of the last 25 years, deliveries to which it is obligated by a 1944 water-sharing agreement between the two countries.
Trump Is Fast-Tracking New Coal Mines — Even When They Don’t Make Economic Sense
In Appalachian Tennessee, mines shut down and couldn’t pay their debts. Now a new one is opening under the guise of an “energy emergency.”
Smaller Nuclear Reactors Spark Renewed Interest in a Once-Shunned Energy Source
In the past two years, half the states have taken action to promote nuclear power, from creating nuclear task forces to integrating nuclear into long-term energy plans.
Keeping the Lights on with Nuclear Waste: Radiochemistry Transforms Nuclear Waste into Strategic Materials
How UNLV radiochemistry is pioneering the future of energy in the Southwest by salvaging strategic materials from nuclear dumps –and making it safe.
Model Predicts Long-Term Effects of Nuclear Waste on Underground Disposal Systems
The simulations matched results from an underground lab experiment in Switzerland, suggesting modeling could be used to validate the safety of nuclear disposal sites.
