-
U.S. shale gas weakening Russian, Iranian petro-power
Rising U.S. natural gas production from shale formations has already played a critical role in weakening Russia’s ability to wield an “energy weapon” over its European customers, and this trend will accelerate in the coming decades
-
-
Mathematical framework converts junk energy into useful power

Researchers have developed a mathematical framework that could one day form the basis of technologies that turn road vibrations, airport runway noise, and other “junk”energy into useful power;
-
-
Nanotechnology to help purify water
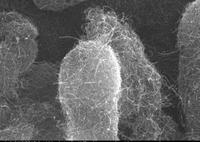
Among many potential applications, carbon nanotubes are great candidate materials for cleaning polluted water; many water pollutants have very high affinity for carbon nanotubes and pollutants could be removed from contaminated water by filters made of this nanomaterial — for example, water soluble drugs which can hardly be separated from water by activated carbon
-
-
Lawmakers blast the Federal Protective Service
Last week lawmakers held a hearing to investigate the Federal Protective Service’s (FPS) progress in addressing its ongoing problems; the agency has made little progress drawing the ire of lawmakers; in recent years, FPS has suffered from a series of high-profile security failures
-
-
Japan halts shipments of radioactive beef
The Japanese government is coming under fire for only halting shipments of contaminated cattle now, four months after the 11 March earthquake and tsunami that led to the nuclear crisis at the Fukushima Daiichi atomic energy station; authorities recently discovered that 637 cattle had been fed hay contaminated with radioactive cesium and then shipped from farms in northern prefectures including Fukushima
-
-
Virginia powerplant holds nuke disaster simulation
On Tuesday, nuclear plant officials and emergency responders recently participated in an exercise to simulate an accident at the Surry atomic power plant in Virginia; Dominion Virginia Power, which operates the state’s four nuclear reactors, regularly holds exercises like these at the Surry plant, but following Japan’s nuclear disaster, the exercises have become even more important
-
-
Studying the Japan quake's impact on soil will improve building design

The 11 March quake that hit Japan weakened subsurface materials by as much as 70 percent; that nonlinear response from the top layer of the Earth’s crust affected how the movement of faults deep beneath the surface was delivered to buildings, bridges, and other structures; understanding how the soil responds to powerful earthquakes could be important to engineers and architects designing future buildings to withstand the level of acceleration measured in this quake
-
-
Sensor network to provide early quake alerts
Researchers from U.S. universities are collaborating to implement a new network of seismic sensors aimed at arming communities with early earthquake detection and warning capabilities; the sensors, no bigger than a Post-it note, are part of a new phase of the Quake-Catcher Network (QCN), a project gathering detailed data to help scientists understand the earthquake process and how to mitigate against its effects
-
-
Bill to allow DHS to seize authority over U.S. coastlines
The House is currently considering a bill that would cede control of America’s coastlines to DHS; under the proposed National Security and Federal Lands Protection Act, the Secretary of the Interior would forfeit authority of all public coast lands to the Secretary of Homeland Security, whenever the DHS chief sees fit
-
-
Placement of wind-turbine increases power tenfold

The power output of wind farms can be increased by an order of magnitude — at least tenfold — simply by optimizing the placement of turbines on a given plot of land; rather than build taller towers and bigger blades, efficient wind-based energy production should focus on the design of the wind farm itself, to maximize its energy-collecting efficiency at heights closer to the ground
-
-
"Amplified" nanotubes for efficient, loss-free grid
The current U.S. copper-based grid leaks electricity at an estimated 5 percent per 100 miles of transmission; Rice University researchers have achieved a breakthrough in the development of a cable that will make an efficient electric grid of the future possible; the armchair quantum wire (AQW) will be a weave of metallic nanotubes that can carry electricity with negligible loss over long distances
-
-
Melting ice sheets chief cause of rising sea levels
There are two causes for rising sea levels — melting ice sheets and thermal expansion of warming ocean waters; during the Last Interglacial Period, the former contributed much more to rising sea levels than the latter, a University of Arizona-led team of researchers has found; the results further suggest that ocean levels continue to rise long after warming of the atmosphere levels off
-
-
U.S. West Coast is rapidly eroding, with pace to accelerate

The stormy conditions of the 2009-10 El Nino winter eroded beaches from San Diego to Seattle to often unprecedented levels; the higher sea levels expected due to global warming, and potentially even stronger winter storms, will likely to contribute to increased rates of beach and bluff erosion along much of the U.S. West Coast
-
-
Preparing for the worst
Nearly three quarters (73 percent) of companies surveyed by AT&T are calling business continuity a priority in 2011, and almost half of them are seriously thinking about using cloud technology to help them deal with terrorism threats, security breaches, the problems that come when the power goes out or the weather turns extreme
-
-
Japan's prime minister pushes to end nuke program
Japan could soon be following in the footsteps of Germany and shut down its nuclear energy plants; at a televised press conference on Wednesday, Prime Minister Naota Kan pushed to end Japan’s nuclear program; “Japan should aim for a society that does not depend on nuclear energy,” Kan said
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
