-
SFO launches program to battle human traffickers

San Francisco International Airport is now home to the first program in the nation that trains airport personnel in identifying and stopping human traffickers
-
-
Dodge Durango Special Service available for police fleets
Chrysler unveils the Dodge Durango Special Service SUV, which is specially designed to handle the rigors of everyday use by police and fire departments and fleet customers
-
-
Updated solution allows quick, secure information sharing
Visual Alert 2 enables law enforcement agencies to get real-time access to police records through Pennsylvania’s Law Enforcement Justice Information System (LEJIS) and other authorized information sharing networks while the department maintains secure control of the information it shares
-
-
Bolstering police anti-child porn technology
Microsoft Corp. and NetClean the other day announced a joint effort to combat the sexual exploitation of children by making Microsoft PhotoDNA technology available and accessible to law enforcement agencies worldwide to help enhance child sex abuse investigations
-
-
Innovative CCTV protects copper cables
The theft of copper cables has cost the British economy an estimated £770 million a year over the last few years; British company which rely on copper cables to deliver their services are deploying an innovative CCTV to combat the thieves
-
-
U.K. police learning to battle cartels in El Paso
This week law enforcement officers from the United Kingdom are in El Paso, Texas to train with DHS; the special agents from the U.K.’s Serious Organized Crime Agency are in town specifically to learn how to combat the growing threat of trafficking
-
-
No racial profiling, abuse by Secure Communities
The Earl Warren Institute at the University of California, Berkeley Law School claimed that DHS Secure Communities program suffers from a disturbing pattern of abuse of authority by ICE, including wrongful arrests of thousands of U.S. citizens, a pattern of racial profiling against Latinos, and denial of due process for aliens in removal proceedings; a new study by the Center for Immigration Studies says this is not the case
-
-
Company develops telephone line “fingerprint” detector
Researchers at Pindrop, a new security company, have developed technology that can read telephone line “fingerprints” to prevent fraud and identify a caller
-
-
FBI increasingly concerned with “sovereign citizen” movement

Over the past decade, the FBI has grown increasingly concerned with the “sovereign citizen” movement; since 2000, sovereign citizens have killed six police officers and violent battles with law enforcement agents are on the rise; the U.S. National Counterterrorism Center classified the movement as a major threat alongside Islamic extremism
-
-
Taser rolls out redesigned wearable cameras
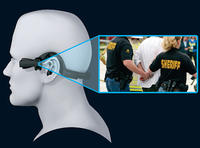
Last week Taser, the manufacturers of the electric stun guns, unveiled its newly remodeled wearable camera system which is sleeker and more advanced than its predecessor; the Axon Flex, introduced less than a year after the company rolled out its first wearable cameras, represents a significant upgrade
-
-
London holds massive Olympic security drill

Last week, in preparation for the London 2012 Olympic Games, more than 2,500 government officials, local police, and emergency responders participated in a two-day long emergency drill that simulated a terrorist attack on the city’s transportation network
-
-
Anthrax-decontamination foam used in meth lab cleanup
The meth cleanup problem in the United States is a big one; the U.S. Drug Enforcement Administration lists thousands of locations where law enforcement agencies have found chemicals or paraphernalia indicating the presence of either clandestine drug laboratories or dumpsites; Sandia’s decontamination foam, originally developed to deal with anthrax, is now also a meth eraser
-
-
Surveillance truck helps Fort Lauderdale keep streets safe
Police in Fort Lauderdale, Florida are trying a new approach to fighting crime – blatantly telling criminals they are under surveillance
-
-
In Keene, N.H., locals oppose military equipment for police
With the help of a $285,933 DHS grant, local police in Keene, New Hampshire were all set to purchase a new armored vehicle until local residents got wind of the plan; the citizens of the quiet New Hampshire town of 23,000, which has only seen two murders since 1999, questioned why police needed such an expensive military-type truck and balked at the militarization of a local force; with federal counterterrorism money continuing to pour into local communities, lawmakers and residents across the country will have to grapple with the same issues as Keene and determine what kind of police force they want to have patrolling the streets
-
-
Accenture develops crime management system for Norway
Accenture is developing a new national crime management system for the Norwegian National Police Directorate (POD) to support police investigations and criminal prosecutions in Norway; the crime management system will enable the Norwegian police force to manage, link, and analyze case information and intelligence for more reliability and consistency across law enforcement, police investigations, border management, emergency response, and case administration
-
More headlines
The long view
Why Was Pacific Northwest Home to So Many Serial Killers?
Ted Bundy, Gary Ridgway, George Russell, Israel Keyes, and Robert Lee Yates were serial killers who grew up in the Pacific Northwest in the shadow of smelters which spewed plumes of lead, arsenic, and cadmium into the air. As a young man, Charles Manson spent ten years at a nearby prison, where lead has seeped into the soil. The idea of a correlation between early exposure to lead and higher crime rates is not new. Fraser doesn’t explicitly support the lead-crime hypothesis, but in a nimble, haunting narrative, she argues that the connections between an unfettered pollution and violent crime warrant scrutiny.
