-
Improving nuclear power plant safety by looking at nature
Within the nuclear industry, hazardous salt solutions can arise within industrial containment vessels. The salt solution precipitates out, forming structures with strange morphologies that bear a resemblance to stalagmites. If left unchecked, they could build up and cause a problem in the nuclear containment chamber. Currently, these containment chambers are checked regularly to prevent this from happening. Taking inspiration from nature, researchers have created a versatile model to predict how stalagmite-like structures form in nuclear processing plants — as well as how lime scale builds up in kettles.
-
-
Risks of terrorists attacking, or using materials from, a nuclear power plant are low: Experts

Energy analysts who support new nuclear power plants construction insist that the probability of a terrorist nuclear attack by land, sea, or air is extremely low. They reject arguments by nuclear power opponents that terrorist groups may one day attack a nuclear plant, or build an improvised nuclear bomb using materials stolen from a nuclear power plant – and that governments should, therefore, end construction of new nuclear power plants. Climate scientists supporting reduction in CO2 emissions wrote that “There is no credible path to climate stabilization that does not include a substantial role for nuclear power.”
-
-
Washington State supports new Hanford project, but worries about cost
The state of Washington is supporting a new facility which would lessen the load on the Hanford vitrification (vit) plant to process nuclear waste, but has expressed concerns about how the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) will pay for the project. Only rough estimates of the cost of the project – called LAWPS, or the Low-Activity Waste Pretreatment System — have been made, but these estimates run between $243 million and $375 million, though that number does not include infrastructure costs such as the addition of roadways and utility services.
-
-
New light shed on reactor fuel behavior during severe nuclear reactor accidents
UO2 is the primary fuel component in the majority of existing nuclear reactors, but little is known about the molten state because of its extremely high melting point. Until now, the extremely high temperature and chemical reactivity of the melt have hindered studies of molten UO2. This lack of fundamental information has made it difficult to evaluate issues associated with the interaction of molten UO2 with a reactor’s zirconium cladding and steel containment vessel. A new discovery about the atomic structure of uranium dioxide will help scientists select the best computational model to simulate severe nuclear reactor accidents.
-
-
U.S. planning expansion of nuclear production in the face of safety concerns

Despite the release of a damning report regarding the 14 February nuclear waste accident at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) near Carlsbad, New Mexico by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), the government is planning ramped-up production of nuclear weapons cores, a move which is raising red flags for those calling for reform of nuclear production and storage procedures.
-
-
A second drum at nuke waste repository poses radiation leak danger

At a recent meeting of the New Mexico Legislature’s Radioactive and Hazardous Materials Committee in Carlsbad, officials were informed that a second waste drum containing nuclear materials, could also contain the same mix of ingredients as the waste drum from Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) which caused a radiation leak at the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) in February.
-
-
Preparing the next generation of nuclear emergency responders
The catastrophic failure of Japan’s Fukushima I Nuclear Power Plant in March 2011 was a turning point in how the scientific community viewed nuclear emergencies. Up to then, the emphasis had been on prevention, not response. Virginia Tech’s Sonja Schmid has won a 2014 National Science Foundation Faculty Early Development (CAREER) Award to study the prospects and problems of creating a global nuclear emergency response plan. Key issues to be addressed in her research are how to convince the world that any nuclear accident is everybody’s problem and how to mobilize an effective international response.
-
-
Strengthening the armor for nuclear-waste eating microbes
A microbe developed to clean up nuclear waste and patented by a Michigan State University researcher has just been improved. Researchers had identified that Geobacter bacteria’s tiny conductive hair-like appendages, or pili, did the yeoman’s share of remediation. By increasing the strength of the pili nanowires, she improved their ability to clean up uranium and other toxic wastes.
-
-
No Fukushima radiation found in California’s coastal areas
Following the 11 March 2011 Fukushima disaster, researches wanted to see whether radioactivity could be found in Bay Area precipitation. They collected weeks’ worth of rainwater around UC Berkeley Campus to find out. The results: low levels of a number of different radioactive nuclei produced by the fission of uranium-235 including, cesium-134, cesium-137, and iodine-131. “The levels we saw were detectable, but low and not a health hazard to anyone,” said UC Berkeley’s nuclear engineering professor Eric Norman.
-
-
Seismic faults make Diablo Canyon a nuclear catastrophe in waiting: Experts
Sunday’s magnitude-6 earthquake in Northern California has renewed focus on the dangers of Diablo Canyon, considered by many as a nuclear catastrophe in waiting. In 2008 authorities discovered the Shoreline fault, which lies about 650 yards from the plant’s reactors. Surveys have mapped a network of other faults around the reactors. Diablo Canyon’s owner released research in 2011 which determined that any of the three nearby faults — the Shoreline, Los Osos, and San Luis Bay — is capable of producing significantly more shaking during an earthquake than was accounted for in the design of the plant’s most vulnerable equipment.
-
-
Testing the shelf-life of nuclear reactors’ components
The structural components of advanced reactors such as the sodium fast reactor and the traveling wave nuclear reactor must be able to withstand the extreme levels of radioactivity from the fission reaction itself at temperatures well above 400 Celsius. Unfortunately, standard tests of such components are expensive, require increasingly rare test reactors and test periods that are impractical. Researchers have devised a quick way to test the structural materials used to build nuclear reactors by using high-energy beams of charged particles (ions).
-
-
Hopes for quicker, cheaper ways to build nuclear power plants dim
Promises of building a more cost effective U.S. nuclear industry continue to face setbacks as alternative energy sources like natural gas become cheaper for utilities, while new models for nuclear plants face cost overruns.Nuclear reactor developers sought to build new plants using prefabricated Lego-like blocks to save time and reduce labor costs, butanalysts consider the designs for the new nuclear reactors to be difficult or impossible to build.
-
-
U.S. nuclear plant licensees should seek, act on nuclear plant hazards information
A new report concludes that the overarching lesson learned from the 2011 Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident is that nuclear plant licensees and their regulators must actively seek out and act on new information about hazards with the potential to affect the safety of nuclear plants. The committee that wrote the report examined the causes of the Japan accident and identified findings and recommendations for improving nuclear plant safety and offsite emergency responses to nuclear plant accidents in the United States.
-
-
DOE chief to visit WIPP to discuss funding for recovery efforts
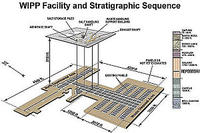
Energy Secretary Ernest Moniz will visit Carlsbad, New Mexico on 12 August to discuss funding for the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP) recovery efforts.Traces of americium and plutonium were released from a nuclear waste drum on 14 February and were detected in the air almost a half-mile outside WIPP. On 15 May, the DOE confirmed that the damage occurred on a waste drum from Los Alamos National Laboratory.
-
-
Fire shuts down nuclear repository, but DOE still recognizes operator for “excellent” performance
Five days after an underground truck fire closed the Waste Isolation Pilot Plant (WIPP), the Energy Department (DOE) awarded Nuclear Waste Partnership (NWP), the operating contractor of the nuclear repository, $1.9 million for “excellent” performance during the past year.Shortly after the truck fire, WIPP was shut down because of radiation leak, Still, “No federal or contractor official has lost their job, been transferred, been moved off the WIPP contract or otherwise held accountable. No leadership has changed at the federal level. No company has lost a contract,” noted an industry observer.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
