-
NY State: Religious grounds no longer allowed to exempt children from vaccination
New York is the latest state where parents can no longer refuse to vaccinate children on religious grounds. Both houses of the New York State Assembly passed the measure Thursday and Governor Andrew Cuomo signed it immediately.
-
-
Texas vaccine exemption rates have reached an all-time high. Did Texas make it too easy for parents to opt out?
Texas has resisted recent attempts to change its vaccine laws, allowing parents to get their children exemptions for “reasons of conscience.” Use our lookup tool to see how exemption rates have changed in school districts and private schools across the state.
-
-
Congress passes legislation authorizing critical biodefense programs
Last week the House passed the Pandemic and All-Hazards Preparedness and Advancing Innovation Act. The bill reauthorizes existing statute governing public health efforts at the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS).
-
-
Ebola outbreak spreads to Uganda – it should never have happened
The DRC is where the Ebola virus was first discovered in 1976. And the country is no stranger to this menace – this is the ninth time it has had to contain the disease. Still, this outbreak is the second largest on record – and the second to have crossed into another country.
-
-
As measles cases crack 1,000, a look at what to do
Measles was declared eliminated in the U.S. in 2000, but by early June, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention reported 1,022 cases in 28 states, the most since 1992. The disease is occurring in clusters of unvaccinated people who, for religious, personal, or medical reasons, have refused to be vaccinated or to have their children vaccinated. “What we haven’t seen before — or at least it’s much more intense now — is the extent to which a foreign power, Russia, is utilizing the sense of division in our country, using social media, websites targeting low-information communities, isolated communities, to propagate an unhealthy status for Americans, says a national security expert.
-
-
Experts urge vaccination as U.S. measles cases top 1,000
Federal officials yesterday said U.S. measles cases have reached 1,001, the first time since 1992 that cases have been in quadruple figures, while experts continued to urge vaccination and underscored the safety of the vaccine.
-
-
Climate change already affecting global food production—unequally
The world’s top 10 crops — barley, cassava, maize, oil palm, rapeseed, rice, sorghum, soybean, sugarcane, and wheat — supply a combined 83 percent of all calories produced on cropland. Yields have long been projected to decrease in future climate conditions. Now, new research shows climate change has already affected production of these key energy sources — and some regions and countries are faring far worse than others.
-
-
Possible European origin of the Spanish Influenza

What happens when a military historian and a virologist get together to discuss the 1918 pandemic? What you get is a fascinating insight into a possible European origin and all sorts of things we may have overlooked.
-
-
U.S. measles cases top record, putting measles elimination status at risk
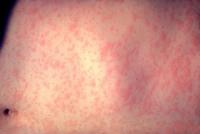
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) said Thursday that 971 cases of measles have been reported this year, topping the 1994 modern-record level, and it warned that the United States could lose its measles elimination status. Amid the growing measles crisis, the conspiracy-fueled anti-vaccination campaign of misinformation continues unabated on social media. DHS mulls a travel ban on measles-infected individuals.
-
-
The U.S. drinking water supply is mostly safe, but that’s not good enough

Most Americans take clean drinking water for granted as a convenience of modern life. The United States has one of the world’s safest drinking water supplies, but new challenges constantly emerge. As a scientist specializing in water quality, I believe water providers and regulators can’t afford to be complacent.
-
-
The “anti-vaxxer” movement and disinformation are fueling the spread of preventable diseases
Outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases, including measles, mumps and whooping cough, have again become an issue in Western and developed countries. Developing or conflict-ridden countries have far more cases of malaria and other diseases, but infection rates in the United States and Europe are on the rise. The number of cases is lower than in developing countries, but outbreaks in economically advanced countries can create sudden and sharp disruptions. Stratfor says that one key factor driving these outbreaks is a growing “anti-vaxxer” movement, which has encouraged an increasing number of people to avoid immunizations. Simply put, the more unvaccinated people there are, the more likely disease outbreaks are to occur. Influential political parties and public figures in the United States and Europe have expressed skepticism over the effectiveness and safety of vaccines and the rights of the government to regulate personal health decisions. These ideas have spread through social media and other communications channels, and ill-informed campaigns frequently cite scientific studies that have been soundly debunked. Subversive Russian social media campaigns have also contributed to the growth of the “anti-vaxxer” movement in recent years. The vaccine controversy is one of many divisive issues that the Kremlin has been exploiting to sow dissension in Western countries, particularly during election seasons. A 2018 study published in the American Journal of Public Health found that Russian troll farms had been spreading such disinformation. Numerous politicians and public health officials have pointed out Moscow’s efforts.
-
-
Crowds, social gatherings facilitate disease transmission
Large gatherings — from music festivals to religious pilgrimages to sporting events — have long been known to increase risks of infectious disease outbreaks. Now results from a new study associate even small-scale community gatherings with increased transmission of diarrheal diseases.
-
-
U.S. measles total climbs by 60 to reach 940 cases
The nation’s number of measles cases continues to climb steadily, with 60 more cases reported over the last week, raising this year’s total to 940 cases. Meanwhile, in global measles development, European officials today warned of a high risk of more widespread circulation due to gaps in vaccine coverage.
-
-
Biodefense Manhattan Project
The Blue Ribbon Study Panel on Biodefense will hold a day-long meeting to discuss a national, public-private research and development initiative to defend the United States against biological threats. The discussants will be “representatives from the same sorts of organizations that contributed to the original Manhattan Project,” the Blue Ribbon Panel says.
-
-
Antibiotics found in some of the world's rivers exceed “safe” levels
Concentrations of antibiotics found in some of the world’s rivers exceed “safe” levels by up to 300 times, the first ever global study has discovered. Researchers looked for 14 commonly used antibiotics in rivers in 72 countries across six continents and found antibiotics at 65 percent of the sites monitored.
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
