-
Virus movement in Wisconsin groundwater
Drinking water taken from a deep aquifer protected by a semi-permeable layer of rock should be safe because the water is protected from many contaminants, including viruses — but is it safe? University of Wisconsin scientists find virus particles in many deep Madison, Wisconsin water wells, raising questions about how viruses, which should not survive more than two years underground, reached so deep and survive for so long
-
-
11,000 California parents refuse basic vaccinations for their children
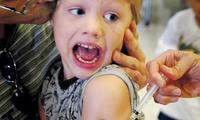
Even with the massive whooping cough outbreak last year in California that sickened more than 9,100 people and killed ten babies, over 11,000 hesitant parents chose not to vaccinate their children against the infectious disease; with record numbers of children going unvaccinated, there have been an increasing number of outbreaks of highly infectious diseases like measles and whooping cough
-
-
HHS proposes new rule regarding toxins
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has issued a proposed rule regarding the biennial review of the possession, use, and transfer of select agents and toxins, according to Secretary Kathleen Sebelius
-
-
Listeria outbreak grows worse, 18 dead and 100 sick

The nation’s deadliest food-borne outbreak in a decade continues to grow worse with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reporting a total of eighteen deaths from listeria-infected cantaloupe
-
-
Food safety grant to fund research on preventing food-borne illnesses
A $1.3 million grant to develop a new food-safety training program for government and industry has been awarded by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to the University of California, Davis, School of Veterinary Medicine
-
-
Anthrax vaccine contract worth up to $1.25 billion over five years
Emergent BioSolutions has been awarded a contract to supply the U.S. government with FDA-licensed anthrax vaccine; the 5-year contract a has a total value of up to $1.25 billion; the first 8.5 million doses will be delivered before the end of the year
-
-
New Zealand relaxes passenger X-ray screening requirement
To save money and speed up the processing of international passengers, New Zealand no longer requires 100 percent screening of bags of passengers entering the country; Kiwi farmers are worried about the move carry the risk of introducing animal disease into the country; the 100 percent screening mandate was imposed after a foot and mouth outbreak in 2001
-
-
U.S. inspects only 2 percent of all imported food
Each year one in six Americans — 48 million people — gets sick, 128,000 are hospitalized, and 3,000 die from foodborne diseases; the FDA uses a risk-based system to isolate foods with high risk of contamination, but physically inspects only about 2 percent of all imported food
-
-
Millions of yet-to-be-described viruses found in raw sewage

There are roughly 1.8 million species of organisms on planet Earth, and each one is host to untold numbers of unique viruses, but only about 3,000 have been identified to date; a new study reveals a vast world of unseen viral diversity that exists right under our nose — in ordinary raw sewage, to be precise
-
-
Report: anthrax antibiotic should be stockpiled locally
A new report describes a plan for the United States to be better prepared in the event of a bioterrorist attack using anthrax; the report recommends that public health officials in high-risk areas should consider stockpile anthrax antibiotics in local locations to make it easier to dispense quickly to an area of need, rather than continuing to use the single national stockpile
-
-
Contaminated cantaloupe outbreak deadliest in decade

The recent listeria outbreak that has sickened seventy-two people and killed as many as sixteen, is shaping up to be the deadliest U.S. food-borne disease outbreak in more than a decade
-
-
Elusive killer parasite being traced in Peru
Chagas disease, primarily seen in South America, Central America, and Mexico, is the most deadly parasitic disease in the Americas; Penn epidemiological study takes snap shot of long-term Chagas disease outbreak
-
-
Real-time disease monitoring can help improve diagnoses
Discovering epidemics or knowing when one is brewing is particularly difficult at the local level as doctors lack a broader perspective of what is occurring; to help provide local doctors with better information that could help stem the spread of infectious diseases, public health officials are pushing for the creation of a real-time national disease monitoring system
-
-
Study finds traces Japanese radiation in U.S. rain and food
A recently published government study found that following the nuclear accident at the Fukushima Daiichi power plant in Japan, elevated levels of radiation were detected in U.S. rain water as well as vegetables and milk
-
-
Japanese attenuated smallpox vaccine shows promise in U.S. trial
An attenuated smallpox vaccine that was developed in Japan in the 1970s compared well with a conventional smallpox vaccine in a phase 1-2 clinical trial in the United States
-
More headlines
The long view
A Shining Star in a Contentious Legacy: Could Marty Makary Be the Saving Grace of a Divisive Presidency?
While much of the Trump administration has sparked controversy, the FDA’s consumer-first reforms may be remembered as its brightest legacy. From AI-driven drug reviews to bans on artificial dyes, the FDA’s agenda resonates with the public in ways few Trump-era policies have.
