-
Transforming deadly chemicals into harmless dirt

Destroying bulk stores of chemical warfare agents is a challenge for the U.S. and international community. Current methods of eradication, such as incineration or hydrolysis, are not fully agnostic, require significant amounts of water and create hazardous waste that requires further processing. DARPA’s Agnostic Compact Demilitarization of Chemical Agents (ACDC) program recently awarded two contracts to develop prototypes of a transportable disposal system able to convert dangerous chemicals into safe output, such as harmless soil, using minimal consumables and creating no hazardous waste.
-
-
Pairing seismic data, radionuclide fluid-flow models to detect underground nuclear tests

Underground nuclear weapon testing produces radionuclide gases that may seep to the surface, which is affected by many factors. These include fractures in the rock caused by the explosion’s shock waves that create pathways for the gas to escape plus the effect of changes in atmospheric pressure that affect the gases’ movement. Scientists have developed a new, more thorough method for detecting underground nuclear explosions (UNEs) by coupling two fundamental elements — seismic models with gas-flow models — to create a more complete picture of how an explosion’s evidence (radionuclide gases) seep to the surface.
-
-
Locust-inspired robot traverses rocky terrain, assists in search and rescue

Since the 1980s, advanced robotic platforms have provided assistance to crisis intervention teams in the wake of man-made and natural disasters. The objective of such robots, in various sizes and shapes, has been to intervene where humans cannot and send life-saving data to rescue teams in the field. A new, locust-inspired robot, can jump eleven feet high — more than twice the height of similar-sized robots — and cover a horizontal distance of 4.5 feet in one leap. The researchers believe the robot will perform well in search-and-rescue missions and in reconnaissance operations in rough terrain.
-
-
The believers: String theory explains Santa Claus
Some argue that the laws of physics should prevent Santa Claus from delivering all his gifts and that Santa would burn up in the atmosphere if he tried. The Norwegian Internet magazine, forskning.no, has put together a team of four top researchers to look into the case, and the panel’s conclusion is clear: Santa can do the job and Christmas is saved.
-
-
The skeptics: Laws of traditional physics would foil Santa's effort to carry out mission

Santa has 31 hours to visit 378 million Christian children; at the rate of 3.5 children per household. Assuming at least one good child per home, this comes to 108 million homes. If each child receives no more than a medium sized Lego set (two pounds), the sleigh would be carrying more than 500 thousand tons of cargo, not counting Santa himself. Santa would thus need at least 360,000 Reindeer to pull the sleigh. Since Santa must visit 108 million homes in 31 hours, he will have to travel at 650 miles per second — 3,000 times the speed of sound, but at that speed, the lead pair of Reindeer would absorb 14.3 quintillion joules of energy per second each and vaporize — indeed, the entire Reindeer team would be vaporized within 4.26 thousandths of a second. Santa himself would be subjected to forces of 17,500 Gs. A 250 pound Santa (which seems ludicrously slim) would be pinned to the back of the sleigh by 4,315,015 pounds of force, and be crushed.
-
-
U.S., Israel to co-develop technologies for first responders

Some $12 million will be funneled to collaborative Israeli-American projects for the development of advanced technologies for first responders over the next three years. The agreement brings together the Israeli Ministry of Public Security and the U.S. Department of Homeland Security in a drive to better equip and prepare both countries’ national rescue forces including fire, police, and first-aid units. Each side will invest equally in the project.
-
-
Making the power grid more resilient, flexible
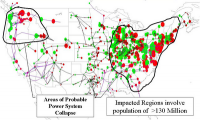
“The biggest and most complex machine ever built by humankind” – this is how one researcher describes the U.S. power grid. A research team has been charged with the formidable task of transforming that big and complex machine from the inside out. Inverters convert DC (direct current) electricity to AC (alternating current) electricity, the kind that forms the basis of today’s power grid. To integrate more inverter-based distributed generation into the grid, the researchers are developing a dynamic distribution system (DDS) that supplements centralized power plants, instead of replacing them.
-
-
Idaho to become U.S. geothermal research hot spot

For all the talk about energy shortages, the fact is the Earth is giant ball of energy that has been producing heat ever since the solar system was formed billions of years ago. The temperature at the core — 6,000 degrees Celsius — is roughly the same as the surface of the sun. All that heat radiates outward through the Earth’s mantle and crust. Less than 1 percent of the electricity in the United States comes from geothermal sources, and energy specialists believe that geothermal power should make a much greater contribution to U.S. electricity. A new consortium plans to pump water into the rock about 8,000 to 12,000 feet deep, fracture the rock and capture heat, then bring heated, pressurized water back to the surface to generate energy.
-
-
DHS S&T calls on non-traditional performers to offer solutions to tough threats

DHS Science and Technology Directorate (S&T) last week announced its first Innovation Other Transaction Solicitation (OTS) aimed at non-traditional performers such as technology start-ups to offer solutions to some of the toughest threats facing DHS and the homeland security mission. Awarded through Other Transaction Solicitation HSHQDC-16-R-B0005, the first call for proposals is looking for solutions to improve situational awareness and security measures for protecting Internet of Things (IoT) domains.
-
-
Matching bullets to wounds using organ-specific protein signatures found on projectiles
Forensic medicine has long employed molecular biology to link, for instance, tiny amounts of organic material to a suspect. Yet, such methods are less useful when it comes to finding out which shot or stab wound was the cause of death. They enable a weapon to be linked to the victim, but not the projectile to the wound. Researchers have developed a method which enables them more accurately to reconstruct crimes involving sharp blades or firearms.
-
-
Detecting, identifying explosives with single test
A new test for detecting multiple explosives simultaneously has been developed. The proof-of-concept sensor is designed quickly to identify and quantify five commonly used explosives in solution to help track toxic contamination in waste water and improve the safety of public spaces.
-
-
Fibers from natural fats make bulletproof vests stronger and greener
Bulletproof vests and other super-strong materials could soon become even tougher and more environmentally friendly at the same time with the help of extra firm, or “al dente,” fibers. These materials, which are powerful enough to stop speeding bullets, can also be used for many other tasks that require strength.
-
-
Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) technology for on-site detection
Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering (SERS) technology currently is applied using chemical analysis of materials, such as scanning at airports to identify what materials may be inside of glass vials. Researchers want to expand SERS for use in biological applications that could employ antibodies for purposes such as identifying viruses, water toxins, or pathogens in food samples. The researchers work on developing a small hand-held device that allows users to take a sample, put it in a glass vial and insert into the instrument for rapid identification.
-
-
New material enables more efficient desalination
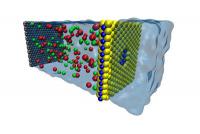
Engineers have found an energy-efficient material for removing salt from seawater. The material, a nanometer-thick sheet of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) riddled with tiny holes called nanopores, is specially designed to let high volumes of water through but keep salt and other contaminates out, a process called desalination.
-
-
Wireless technology enables advanced up protective clothing
Combining the latest advances in sensor and wireless technology with comfortable protective clothing has opened up new partnership possibilities across a range of sectors. Numerous end users stand to benefit from the inclusion of smart technology in protective clothing. One French start-up has pioneered intelligent active protection systems for ski racers. Further advances may see the use of advanced protective clothing by soldiers and first responders.
-
More headlines
The long view
Risk Assessment with Machine Learning
Researchers utilize geological survey data and machine learning algorithms for accurately predicting liquefaction risk in earthquake-prone areas.
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
New Approach Detects Adversarial Attacks in Multimodal AI Systems
New vulnerabilities have emerged with the rapid advancement and adoption of multimodal foundational AI models, significantly expanding the potential for cybersecurity attacks. Topological signatures key to revealing attacks, identifying origins of threats.
