-
Best way to stop a killer asteroid? Form a committee

The United Nations (UN) has adopted several recommendations of a new asteroid defense plan, the first steps in preventing Earth from being struck by an asteroid. The recommendations were a response to an asteroid strike earlier this year in Chelyabinsk, Russia. This object injured thousands and was around seventeen meters across. We have only found 1 percent of these “killer” asteroids, meaning there are hundreds of times more out there than we know of. One of them, sooner or later, will have our name written on it. For a global threat we need a global response, as well as a global share of the blame if it goes wrong.
-
-
Urban underground water can be used for sustainable energy
Vast energy sources are slumbering below big cities. Sustainable energies for heating in winter and cooling in summer may be extracted from heated groundwater aquifers. Researchers developed an analytical heat flux model and found that increasing heat in the underground is mainly caused by an increase in surface temperatures and heat release from buildings.
-
-
Helping first responders identify chemical, biological, and radiological agents
The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) has expanded the reach and capabilities of its rapid urban plume modeling and hazard assessment system, CT-Analyst, by providing a commercial license to Valencia, California-based Safe Environment Engineering (SEE) for the fields of use of public safety, industrial safety and monitoring, and environmental monitoring. CT Analyst is a tool designed to provide first responders with fast and accurate predictions of chemical, biological, and radiological agent airborne transport in urban environments. CT Analyst will be integrated into the existing product line of SEE’s Lifeline MultiMeterViewer software suite.
-
-
Video imaging system for remote detection of hidden threats
By adapting superconducting technology used in advanced telescope cameras, researchers have built a prototype video imaging system for detecting hidden weapons and other threats at distances up to twenty-eight meters away.
-
-
Dolphin-inspired radar system detects hidden surveillance, explosive devices

Scientists, inspired by the way dolphins hunt using bubble nets, have developed a new kind of radar that can detect hidden surveillance equipment and explosives. The twin inverted pulse radar (TWIPR) is able to distinguish true targets, such as certain types of electronic circuits that may be used in explosive or espionage devices, from clutter (for example, other metallic items like pipes, drinks cans, or nails) which may be mistaken for a genuine target by traditional radar and metal detectors.
-
-
New spectrometry standard for handheld chemical detectors
When it comes to detectors for dangerous chemicals, toxins, or nefarious germs, smaller and faster is better. Size and speed, however, must still allow for accuracy, especially when measurements by different instruments must give the same result. The recent publication of a new standard provides confidence that results from handheld chemical detectors can be compared, apples-to-apples.
-
-
Squeezing light improves performance of MEMS sensors
Microelectromechanical systems, known as MEMS, are ubiquitous in modern military systems such as gyroscopes for navigation, tiny microphones for lightweight radios, and medical biosensors for assessing the wounded. Such applications benefit from the portability, low power, and low cost of MEMS devices. The use of MEMS sensors is now commonplace, but they still operate many orders of magnitude below their theoretical performance limits, due to two obstacles: thermal fluctuations and random quantum fluctuations, a barrier known as the standard quantum limit.
-
-
Acoustic detection identifies IEDs – and their explosive yield
A number of different tools are currently used for explosives detection. These range from dogs and honeybees to mass spectrometry, gas chromatography, and specially designed X-ray machines.A new acoustic detection system, consisting of a phased acoustic array that focuses an intense sonic beam at a suspected improvised explosive device, can determine the difference between those that contain low-yield and high-yield explosives.
-
-
Innovative technique to detect fingerprints
Researchers have developed an innovative product that uses fluorescence to detect fingerprints. This new product, Lumicyano, will make it possible to highlight fingerprints directly, more rapidly, and at a lower cost, avoiding the cumbersome processes required until now.
-
-
Police departments adopt sophisticated, cheap-to-operate surveillance technology

Advancements in surveillance technology have been adopted not only by the National Security Agency (N.S.A) or other federal intelligence agencies. Local police departments have also incorporated the latest surveillance technologies into their work, allowing them to track individuals for different purposes.
-
-
Innovative salmonella sensing system
Foodborne illnesses making one in six Americans — or forty-eight million people — sick each year. Of these people sickened, 128,000 end up in the hospital, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, while 3,000 die. A new approach to detecting food contamination enables real-time testing of food and processing plant equipment.
-
-
Sea power: extracting energy from ocean waves
As sources of renewable energy, sun and wind have one major disadvantage: it is not always sunny or windy. Waves in the ocean, on the other hand, are never still. Researchers are now aiming to use waves to produce energy by making use of contact electrification between a patterned plastic nanoarray and water.
-
-
Compact, high-power terahertz source at room temperature developed
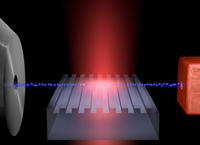
Terahertz (THz) radiation — radiation in the wavelength range of 30 to 300 microns — is gaining attention due to its applications in security screening, medical and industrial imaging, agricultural inspection, astronomical research, and other areas. Traditional methods of generating terahertz radiation usually involve large and expensive instruments, some of which also require cryogenic cooling. Researchers have developed a compact, room-temperature terahertz source with an output power of 215 microwatts.
-
-
Reducing urban water leakage
No resource is more fundamental to life and human society than water. Yet, globally, 25 to 30 percent of drinking water is lost every year due to leakages in urban water distribution systems. An EU-funded project is proposing an innovative solution for the automatic detection, sealing, and curing of typical network pipes, without digging up pavements and roads.
-
-
Reducing security threats from explosives
Researchers, as part of the Awareness and Localization of Explosives-Related Threats center (ALERT), a DHS Center of Excellence, are working on ways to detect explosives and neutralize their impact. The researchers are developing portable detectors as well as larger systems to scan for explosives. Some technologies will analyze the spectrum of light shining through vaporized samples; others will analyze solid residues.
-
More headlines
The long view
Risk Assessment with Machine Learning
Researchers utilize geological survey data and machine learning algorithms for accurately predicting liquefaction risk in earthquake-prone areas.
Bookshelf: Smartphones Shape War in Hyperconnected World
The smartphone is helping to shape the conduct and representation of contemporary war. A new book argues that as an operative device, the smartphone is now “being used as a central weapon of war.”
New Approach Detects Adversarial Attacks in Multimodal AI Systems
New vulnerabilities have emerged with the rapid advancement and adoption of multimodal foundational AI models, significantly expanding the potential for cybersecurity attacks. Topological signatures key to revealing attacks, identifying origins of threats.
