-
Senator Hatch champions tech industry’s priorities in immigration reform

As the Senate Judiciary Committee continues to consider the bipartisan immigration reform bill, both supporters and opponents of the bill agree that one senator has emerged as a key voice on the issue: the 79-year old Orrin Hatch (R-Utah). Hatch has emerged as a champion of the U.S. technology industry, and while he supports the broad goal of immigration reform, he insists on shaping the legislation so it addresses the priorities and preferences of the tech industry, priorities and preferences which he sees as essential not only for the health of the industry, but for the health of the U.S. economy more generally.
-
-
Compressing air for renewable energy storage
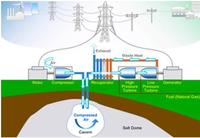
Enough Northwest wind energy to power about 85,000 homes each month could be stored in porous rocks deep underground for later use, according to a new, comprehensive study. Researchers identified two unique methods for this energy storage approach and two eastern Washington locations to put them into practice.
-
-
Quickly identifying chemical, biological warfare agents
For more than fifty years, researchers have been studying exactly how aspirin affects the human body. Despite thousands of publications on the topic, our understanding is still incomplete. Meanwhile, novel chemical and biological weapons have historically been mass produced within a year of discovery. Using current methods and technologies, researchers would require decades of study to gain a robust understanding of how new threat agents exert effects on human biological systems. DARPA wants to close this capability gap, which leaves U.S. forces vulnerable.
-
-
Terahertz technology helps to see more with less
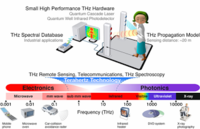
Terahertz technology is an emerging field which promises to improve a host of useful applications, ranging from passenger scanning at airports to huge digital data transfers. Terahertz radiation sits between the frequency bands of microwaves and infrared radiation, and it can easily penetrate many materials, including biological tissue. The energy carried by terahertz radiation is low enough to pose no risk to the subject or object under investigation.
-
-
Seeking new ideas for mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs)
Troops operating in forward locations without telecommunication infrastructure often rely on a mobile ad hoc network (MANET) to communicate and share data. A constraint with current MANETs is they can only scale to around fifty nodes before network services become ineffective. DARPA is exploring new technologies unencumbered by Internet Protocols (IP) which could be the key to enabling large MANETs. The Internet facilitated far-reaching technical advances, but in this technology area the Internet may be the roadblock.
-
-
Smartphone app locates gunfire source

For the last decade, the Department of Defense has spent millions of dollars to develop sophisticated sniper location systems which are installed in military vehicles and require dedicated sensor arrays. Scientists have now developed a smartphone app that tracks gunfire and points in the direction the shot came from.
-
-
New fertilizer can be used to grow food – but not build bombs

Ammonium nitrate fertilizer is used in agriculture, but when mixed with a fuel such as diesel, it is highly explosive. It was used in about 65 percent of the 16,300 homemade IEDs in Afghanistan in 2012.About 1,900 troops were killed or wounded in IED attacks in 2012, 60 percent of American combat casualties. There have been more than 17,000 global IED incidents in 123 countries in the past two years. Timothy McVeigh used ammonium nitrate in Oklahoma City in 1995. Scientists have developed a fertilizer that helps plants grow but cannot detonate a bomb.
-
-
DOE seizes $21 million from Fisker after company fails to make monthly payment on loan
The administration seized $21 million from auto company Fisker Automotive, less than a month after the automaker laid off three quarters of its employees due to financial and production problems. Fisker, based in Anaheim, California, was awarded a $192 million loan as part of a program started by the Obama administration to boost electric cars and other alternative-fuel vehicles.
-
-
Winner announced in the first DARPA FANG Challenge

The Ground Systems team outpaces more than 200 teams and 1,000 participants, submitting the winning mobility in the Fast Adaptable Next-Generation Ground Vehicle (FANG) Mobility/Drivetrain Challenge, and drivetrain subsystem design and claiming the $1 million prize.
-
-
New submarine hunting program reaches milestones
DARPA’s Distributed Agile Submarine Hunting (DASH) Program has tested two complementary prototype systems as part of its Phase 2 development effort. The prototypes demonstrated functional sonar, communications, and mobility at deep depths. The successful tests furthered DASH’s goals to apply advances in deep-ocean distributed sonar to help find and track quiet submarines.
-
-
DARPA shows smaller pixels, smaller thermal cameras for soldiers
The U.S. military uses long-wave infrared (LWIR) cameras as thermal imagers to detect humans at night. These cameras are usually mounted on vehicles as they are too large to be carried by a single soldier and are too expensive for individual deployment. DARPA researchers, however, recently demonstrated a new five-micron pixel LWIR camera that could make this class of camera smaller and less expensive.
-
-
Robot makes inspecting power lines simple, inexpensive

Mechanical engineers invented a robot designed to scoot along utility lines, searching for damage and other problems that require repairs. Made of off-the-shelf electronics and plastic parts printed on an inexpensive 3D printer, the SkySweeper prototype could be scaled up for less than $1,000, making it significantly more economical than the two models of robots currently used to inspect power lines.
-
-
Footwear safety reflectors help in detecting bioterror threats

Tiny versions of the reflectors on sneakers and bicycle fenders that help ensure the safety of runners and bikers at night are moving toward another role in detecting bioterrorism threats and diagnosing everyday infectious diseases, scientists said the other day.
-
-
Future computers will identify users by thoughts, not passwords

Instead of typing your password, in the future you may only have to think your password, according to researchers. A new study explores the feasibility of brainwave-based computer authentication as a substitute for passwords.
-
-
More border security means more business opportunities for tech companies

At last month’s Border Security Expo in Phoenix, both start-ups and established companies showed off their inventions in an effort to pitch projects to federal agencies. Two themes emerged in the show: the expo demonstrated that many of the systems and weapons systems that were used in the Iraq and Afghanistan wars are now becoming available to local, state, and federal law enforcement agencies – and companies expressed concern about the impact the federal budget cuts will have on their pockets.
-
More headlines
The long view
Are We Ready for a ‘DeepSeek for Bioweapons’?
Anthropic’s Claude 4 is a warning sign: AI that can help build bioweapons is coming, and could be widely available soon. Steven Adler writes that we need to be prepared for the consequences: “like a freely downloadable ‘DeepSeek for bioweapons,’ available across the internet, loadable to the computer of any amateur scientist who wishes to cause mass harm. With Anthropic’s Claude Opus 4 having finally triggered this level of safety risk, the clock is now ticking.”
Bookshelf: Preserving the U.S. Technological Republic
The United States since its founding has always been a technological republic, one whose place in the world has been made possible and advanced by its capacity for innovation. But our present advantage cannot be taken for granted.
Autonomous Weapon Systems: No Human-in-the-Loop Required, and Other Myths Dispelled
“The United States has a strong policy on autonomy in weapon systems that simultaneously enables their development and deployment and ensures they could be used in an effective manner, meaning the systems work as intended, with the same minimal risk of accidents or errors that all weapon systems have,” Michael Horowitz writes.
Ukraine Drone Strikes on Russian Airbase Reveal Any Country Is Vulnerable to the Same Kind of Attack
Air defense systems are built on the assumption that threats come from above and from beyond national borders. But Ukraine’s coordinated drone strike on 1 June on five airbases deep inside Russian territory exposed what happens when states are attacked from below and from within. In low-level airspace, visibility drops, responsibility fragments, and detection tools lose their edge. Drones arrive unannounced, response times lag, coordination breaks.
Shots to the Dome—Why We Can’t Model US Missile Defense on Israel’s “Iron Dome”
Starting an arms race where the costs are stacked against you at a time when debt-to-GDP is approaching an all-time high seems reckless. All in all, the idea behind Golden Dome is still quite undercooked.
Our Online World Relies on Encryption. What Happens If It Fails?
Quantum computers will make traditional data encryption techniques obsolete; BU researchers have turned to physics to come up with better defenses.
Virtual Models Paving the Way for Advanced Nuclear Reactors
Computer models predict how reactors will behave, helping operators make decisions in real time. The digital twin technology using graph-neural networks may boost nuclear reactor efficiency and reliability.
Critical Minerals Don’t Belong in Landfills – Microwave Tech Offers a Cleaner Way to Reclaim Them from E-waste
E-waste recycling focuses on retrieving steel, copper, aluminum, but ignores tiny specks of critical materials. Once technology becomes available to recover these tiny but valuable specks of critical materials quickly and affordably, the U.S. can transform domestic recycling and take a big step toward solving its shortage of critical materials.
Microbes That Extract Rare Earth Elements Also Can Capture Carbon
A small but mighty microbe can safely extract the rare earth and other critical elements for building everything from satellites to solar panels – and it has another superpower: capturing carbon dioxide.
Virtual Models Paving the Way for Advanced Nuclear Reactors
Computer models predict how reactors will behave, helping operators make decisions in real time. The digital twin technology using graph-neural networks may boost nuclear reactor efficiency and reliability.
Critical Minerals Don’t Belong in Landfills – Microwave Tech Offers a Cleaner Way to Reclaim Them from E-waste
E-waste recycling focuses on retrieving steel, copper, aluminum, but ignores tiny specks of critical materials. Once technology becomes available to recover these tiny but valuable specks of critical materials quickly and affordably, the U.S. can transform domestic recycling and take a big step toward solving its shortage of critical materials.
Microbes That Extract Rare Earth Elements Also Can Capture Carbon
A small but mighty microbe can safely extract the rare earth and other critical elements for building everything from satellites to solar panels – and it has another superpower: capturing carbon dioxide.
