-
Companies hiring hackers to harden defenses

To burglar-proof your home, it is best hire a burglar as a consultant, as he is more likely to find the security vulnerabilities and demonstrate how they can be exploited; following this approach, companies large and small are now hiring hackers to test the companies’ security system vulnerabilities and find ways to harden these systems to withstand intrusion
-
-
WWII-like message encryption now available for e-mail security
A Singapore-based company offers an e-mail encryption system based on the Verman cipher, or one-time pad, which was invented in 1917 and used by spies in the Second World War; the Vernam cipher is unbreakable because it produces completely random cipher-text that secures data so that even the most powerful super computers can not break the encryption when it is used properly
-
-
Cambridge first year student wins U.K. Cybersecrity Challenge competition
Cyber Security Challenge U.K. announces a winner and unveils this year’s new Challenge program (open for registrations as of yesterday); the winner, Jonathan Millican, competed with thousands of registered candidates in 6-month competition
-
-
Anonymous retaliates, takes down Interpol site

In retaliation for the arrest of twenty-five suspected members of the hacktivist collective known as Anonymous, the group briefly took down Interpol’s website on Tuesday
-
-
Cryptographic attack shows importance of bug-free software
Researchers have developed an attack that can circumvent the security OpenSSL should provide; the attack worked on a very specific version of the OpenSSL software, and only when a specific set of options were used
-
-
HP wins $47M contract to support HSPD-12 implementation
On Monday the U.S. General Services Administration (GSA) announced it had awarded Hewlett Packard a one-year contract worth as much as $47 million to support government-compliance with Homeland Security Presidential Directive-12 (HSPD-12)
-
-
DHS to work with Netherlands on cybersecurity
On Wednesday DHS Secretary Janet Napolitano signed a letter of intent to work with the Netherlands on several critical cybersecurity initiatives
-
-
Quantum physics makes possible perfectly secure cloud computing
Computer data processing and storage are increasingly done in the cloud; the challenge in cloud-based system is to ensure that clients’ data stays private; researchers have now shown that perfectly secure cloud computing can be achieved with quantum computers
-
-
Quantum technique for secret messaging
Quantum cryptography is the ultimate secret message service; new research shows it can counter even the ultimate paranoid scenario: when the equipment or even the operator is in the control of a malicious power
-
-
Satellite telephony is unsafe
In some regions of the world standard cell phone communication is still not available; in war zones, developing countries and on the high seas, satellite phones are used instead; the system, using an encryption algorithms of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), was considered unbreakable; in less than an hour, and with simple equipment, researchers found the crypto key which is needed to intercept telephone conversations
-
-
Sandia addresses complex DNS vulnerabilities
A Sandia researcher has developed a visualization tool to help network administrators within the federal government and global IT community better understand Domain Name System Security (DNSSEC) and also help them troubleshoot problems
-
-
Signcryption technology tightens cybersecurity
Signcryption is a data security technology by which confidentiality is protected and authenticity is achieved seamlessly at the same time; it has now been formally recognized as an international standard by the International Organization of Standardization (ISO)
-
-
New Apple facial recognition tech could make passwords obsolete
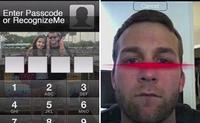
Passwords could become a thing of the past for Apple iPhone and iPad users; the tech company recently revealed a patent application for what it is calling “Low Threshold Face Recognition,” a tool that would allow users to unlock their phones by simply picking up the device and pointing it at their face
-
-
DHS, Idaho lab win cybersecurity innovation award
The Controls Systems Security Program (CSSP) at DHS and Idaho National Laboratory have created a series of training programs for managerial and technical people in the critical infrastructure sector that are packed with up-to-date information on cyber threats and mitigations for vulnerabilities
-
-
$3 million NSF grant for research into assured data provenance
The National Science Foundation supports funds new cyber security research into assured data provenance, the discipline of computer science concerned with the integrity and privacy of data sources, contents, and successive transformations
-
More headlines
The long view
Researchers Develop AI Agent That Solves Cybersecurity Challenges Autonomously
New framework called EnIGMA demonstrates improved performance in automated vulnerability detection using interactive tools.
