-
Thorium holds promise of safer, cleaner nuclear power
Thorium as nuclear fuels has drawbacks, but its main advantage includes generating far less toxic residue. The majority of the mineral is used during the fission process, and it can burn existing stockpiles of plutonium and hazardous waste, saving the need to transport it and bury the waste in concrete. If thorium becomes available as a source of energy in the future, the world will rely less on coal and gas, and wind turbines will become a thing of the past. The risk of a global energy crunch will decrease considerably.
-
-
Black carbon’s contribution to climate change underestimated
Black carbon is the second largest man-made contributor to global warming and its influence on climate has been greatly underestimated, according to the first quantitative and comprehensive analysis of this issue; black carbon is believed to have a warming effect of about 1.1 Watts per square meter (W/m²), approximately two thirds of the effect of the largest man made contributor to global warming, carbon dioxide.
-
-
Black carbon’s contribution to climate change underestimated

Black carbon is the second largest man-made contributor to global warming and its influence on climate has been greatly underestimated, according to the first quantitative and comprehensive analysis of this issue; black carbon is believed to have a warming effect of about 1.1 Watts per square meter (W/m²), approximately two thirds of the effect of the largest man made contributor to global warming, carbon dioxide.
-
-
NASA: 2012 sustained long-term climate warming trend
NASA scientists say 2012 was the ninth warmest of any year since 1880, continuing a long-term trend of rising global temperatures. With the exception of 1998, the nine warmest years in the 132-year record all have occurred since 2000, with 2010 and 2005 ranking as the hottest years on record. Scientists emphasize that weather patterns always will cause fluctuations in average temperature from year to year, but the continued increase in greenhouse gas levels in Earth’s atmosphere assures a long-term rise in global temperatures. Each successive year will not necessarily be warmer than the year before, but on the current course of greenhouse gas increases, scientists expect each successive decade to be warmer than the previous decade.
-
-
Global demand for food and energy is growing, and so does land and water “grabbing”

As world food and energy demands grow, nations and some corporations increasingly are looking to acquire quality agricultural land for food production. Some nations are gaining land by buying up property — and accompanying water resources — in other, generally less wealthy countries.
-
-
Better screening for bacteria for safer food
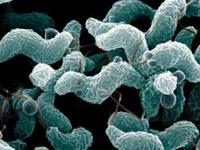
There are around 5.4 million cases of food-borne gastroenteritis in Australia every year. Of these cases, it is estimated that around 200,000 are associated with the bacteria Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Chicken meat and other foods will be able to be screened for bacteria even faster and more effectively than ever, thanks to breakthrough nanobiotechnology research.
-
-
Global warming threatens U.K. diet
The number of days with temperatures over 32 degrees C has more than doubled in some parts of France over the last fifty years. Many other land areas show similar increases. By the 2020s, temperatures over 32 degrees C could occur over large areas of France where previously they were uncommon. Maize yields are reduced significantly for each day with temperatures over around 32 degrees Celsius. The United Kingdom imports more maize from France than anywhere else in the world, and declining crop yields in France mean that U.K. consumers will have to pay more for maize-based foods, or change their diets.
-
-
Drought, heat turn hundreds of U.S. counties into disaster areas

The U.S. Agriculture Department (USDA) last week said that drought conditions and heat necessitated designating 597 counties in fourteen states as primary natural disaster areas. The affected counties have suffered severe drought for eight consecutive weeks, which qualified them for the automatic designation. 2012 had been the hottest year on record for the continental United States: the year’s average temperature of 55.3 degrees Fahrenheit across the Lower 48, which was more than 3.2 degrees warmer than the average for the twentieth century.
-
-
Tiny helpers: Atom-thick flakes help clean up radioactive waste, fracking sites
Graphene oxide has a remarkable ability quickly to remove radioactive material from contaminated water. Researchers determined that microscopic, atom-thick flakes of graphene oxide bind quickly to natural and human-made radionuclides and condense them into solids. The discovery could be a boon in the cleanup of contaminated sites like the Fukushima nuclear plants, and it could also cut the cost of hydraulic fracturing (“fracking”) for oil and gas recovery and help reboot American mining of rare earth metals.
-
-
Students develop low-cost water filtering system for African nation
Every year, 3.4 million people die from lack of access to fresh water globally; in East Africa, daily routines include women venturing miles to secure fresh water and bearing the heavy weight of water containers to secure less-than-desirable water; in an effort to bring fresh water to rural Kenyans, Penn State’s School of International Affairs (SIA) students have developed a ceramic water filtration system for parts of the sub Saharan African nation
-
-
Shoring up Long Island’s natural shore defenses against future storms

Sand and other coarse-grained sediments are vital to the naturally occurring barrier systems which dissipate storm surges, protect coastal residences, and shelter biologically diverse estuaries and ecosystems; a team of researchers is conducting marine geophysical surveys of the seafloor and shallow subsurface to assess the health of the offshore barrier system which protects the New York Harbor and southwestern Long Island region against damage from future storms
-
-
Fish zapping: shocking Asian carp out of Midwest waters not feasible
The several species known as Asian carp are not native to U.S. waterways but have been found in rivers throughout the Midwest; these fish are competing with native species for food and altering ecosystems; they are also dangerous to boaters and other river users since Asian carp can weigh up to sixty pounds and are known to jump out of the water during even minor disturbances; scientists had hoped to modify or expand low-voltage electrical barriers like those used around Chicago waterways to direct Asian carp from particular areas, but found that the level of electricity needed would be far too high
-
-
New York State power plants showing their age

New York State could face power plant closings in the near future as a result of updated environmental regulations and the fact that plants in the state are outdated and inefficient; a recent report concluded that New York’s coal and nuclear power plants, as well as steam and turbine plants that run on oil or gas, are on average older than others around the country
-
-
"Prophylactic dressing" for walls make buildings safer during earthquakes
In the case of earthquakes, only seconds may remain for a safe escape from buildings; debris falling down and obstructing the escape routes may even aggravate the situation; a new product extends the time for saving lives by reinforcing walls and keeping off the debris; an innovative building material manufacturer now has launched the mature innovation in the market
-
-
Assessing future sea level rise from ice sheets
Future sea level rise due to the melting of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets could be substantially larger than estimated in Climate Change 2007, the Fourth Assessment Report of the IPCC, according to new research
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
