-
WWII-like message encryption now available for e-mail security
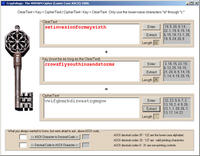
A Singapore-based company offers an e-mail encryption system based on the Verman cipher, or one-time pad, which was invented in 1917 and used by spies in the Second World War; the Vernam cipher is unbreakable because it produces completely random cipher-text that secures data so that even the most powerful super computers can not break the encryption when it is used properly
-
-
ACLU: Cell phone tracking by police widespread
ACLU obtains information from over 200 law enforcement agencies; finds widespread police use of cell phone location tracking along with variance in legal standards, technology used
-
-
DHS resisted calls for intelligence on Occupy movement
Internal documents released by DHS demonstrate the efforts made by the department to avoid gathering intelligence on last year’s Occupy movement
-
-
California bill would restrict data usage from license plate scanners

Legislation has been introduced in California to limit the use of data gathered by patrol car-mounted license plate readers, and the duration for which such data may be held; access to the data by other agencies and personnel would be limited as well
-
-
NATO commander target of persistent Facebook cyberattacks

The senior commander of NATO has been the target of repeated Facebook-based cyberattacks that are believed to have originated from China; Admiral James Stavridis is the subject of a campaign to gain information about him and his colleagues, friends, and family
-
-
Inquiring minds want to know
“It is not surprising to see more FOIA [Freedom of Information Act] requests sent in to an administration that has emphasized transparency… We’re making a strong effort to keep up with that demand by devoting more resources to it.”
White House spokesman Eric Schultz on why the Obama administration could not keep pace with the increasing number of people asking for documents, e-mails, photographs, and more under FOIA -
-
Google's new privacy policy
“On its best day, with every ounce of technology the U.S. government could muster, it could not know a fraction as much about any of us as Google does now.”
Shelly Palmer, technology analyst -
-
Experts: White House consumer privacy plan seriously flawed
Last week the White House announced its Consumer Privacy Bill of Rights, which would give consumers the right to exercise control over what personal data is collected and how it is used; an expert says more than thirty years of experience with control-based laws has demonstrated that they don’t work and they don’t protect consumer privacy
-
-
Growing pressure to investigate facial recognition technology
Concerned with the growing ubiquity of facial recognition technology, earlier this month, lawmakers sent a letter to the Federal Trade Commission urging the agency to “look further” into the technology
-
-
Cell phone hackers can track your location without your knowledge
Using a cheap phone, readily available equipment, and no direct help from a service provider, hackers could listen to unencrypted broadcast messages from cell phone towers
-
-
ACLU questions police tracking of cell phones

Civil rights advocates are increasingly uneasy with law enforcement agencies increasing use of cell phone triangulation to pinpoint an individual’s location; earlier this year, thirty-four ACLU affiliates from across the country filed open records requests from local law enforcement agencies requesting information on how authorities are tracking cell phones
-
-
Concern over DHS move to create giant information databank

In an effort to enhance DHS’ information sharing capabilities, the department is looking to construct an integrated database known as the “Federated Information Sharing System,” a move which has raised concerns from the American Civil Liberties Union
-
-
Interface could help Facebook members limit security leaks
Researchers develop a sign-up interface for Facebook apps could help members prevent personal information — and their friends’ information — from leaking out through third-party games and apps to hackers and identity thieves
-
-
British law enforcement exploits flaw in iTunes to spy

British law enforcement agencies and Apple are coming under sharp criticism after it was discovered that authorities exploited a security flaw in iTunes to spy on individuals
-
-
Digital DNA the new DNA
With the increasing ubiquity of computers, smart phones, and other electronic devices comes a torrent of “digital DNA,” which can be used to record an individual’s every move and even convict them of a crime
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
