-
Extreme weather events threaten U.S. national landmarks

Rising seas, floods, and wildfires are threatening the U.S. most cherished historic sites — from Ellis Island to the Everglades, Cape Canaveral to California’s César Chávez National Monument. Scientists say that today these sites face an uncertain future in a world of rising sea levels, more frequent wildfires, increased flooding, and other damaging effects of climate change. At some sites — such as Liberty and Ellis Islands and Cape Hatteras — steps have already been taken to prepare for these growing climate risks. At many other sites, such efforts have not yet begun.
-
-
Extreme weather exposes the toxic legacy of an industrial past
The increase in the number and intensity of extreme weather events in the United States carries with it yet another, more insidious danger: it forces to the surface toxic lead from long-shuttered smelters. Lead smelters had mostly closed down in the United States by the 1980s, but they left behind millions of tons of toxic waste. One example: In 2011, Joplin, Missouri suffered a devastating tornado which killed 158 people and flattened much of the city. Decades of lead processing in the Joplin area had created about 150 million tons of toxic wastes, with about 9 million tons still remaining after a federal Superfund cleanup. The 2011 tornado forced some of the buried lead to the surface, forcing Joplin to spend $3.5 million so far on lead clean up. The city now requires builders to test for lead, and clean up any traces, before beginning construction.
-
-
Rio builds a high tech integrated urban command center

Rio de Janeiro is one of the most densely populated cities in South America. Much of the city is vulnerable to flooding, and about three-quarters of Rio’s districts have areas at risk of landslides. High temperatures can make living situations unbearable. In addition, a high crime rate and poor infrastructure make the city difficult to govern. In preparation for the 2014 World Cup and 2016 Summer Olympics, authorities are looking to improve response times to disasters and establish a more efficient system to deal with the city’s many challenges. One of the solutions is a high tech integrated urban command center — Centro de Operações Preifetura do Rio de Janeiro (COR) – which unites Rio’s thirty departments and some private suppliers in a single monitoring room where operators can track real-time conditions of the city and coordinate a response to emergencies and disruptions.
-
-
Canada is not doing enough to prepare for, cope with natural, man-made disasters
The 2013 Alberta floods cost more than $6 billion, making it the worst weather disaster in Canada’s history. Before 1990, only three Canadian disasters exceeded $500 million, but in the past ten years alone nine disasters have exceeded that amount. Disaster management experts said that while it may be understandable that corporate and municipal budgets for disaster training and preparations have been reduced during the economic slowdown, corporate and government leaders in Canada must consider how such reductions would impact the ability of communities to build adequately resilience systems against potential natural and manmade disasters.
-
-
Rising sea levels will be too much, too fast for Florida
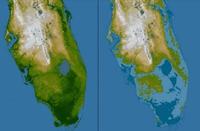
The U.S. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) published its assessment of sea level rise in 2012 as part of the National Climate Assessment. Including estimates based on limited and maximum melt of the Greenland and Antarctic ice sheets, it anticipated a raise of 4.1 to 6.6ft (1.25 to 2m) by 2100, reaching 2ft (0.6m) by around 2050 and 3ft (0.9m) by around 2075. This means that by the middle of this century most of the barrier islands of south Florida and the world will be abandoned and the people relocated, while low areas such as Sweetwater and Hialeah bordering the Everglades will be frequently flooded and increasingly difficult places to live. Florida will start to lose its freshwater resources, its infrastructure will begin to fail, and the risk of catastrophic storm surges and hurricane flooding will increase. Florida counties should be planning for their future to determine at what point the costs of maintaining functional infrastructure, insurance, and human health and safety becomes economically impossible. Already, there are areas and properties that will become unlivable within a 30-year mortgage cycle.
-
-
NOAA predicts near-normal or below-normal 2014 Atlantic hurricane season
In its 2014 Atlantic hurricane season outlook issued yesterday NOAA’s Climate Prediction Center is forecasting a near-normal or below-normal season. The main driver of this year’s outlook is the anticipated development of El Niño this summer. El Niño causes stronger wind shear, which reduces the number and intensity of tropical storms and hurricanes. El Niño can also strengthen the trade winds and increase the atmospheric stability across the tropical Atlantic, making it more difficult for cloud systems coming off of Africa to intensify into tropical storms.
-
-
Public-private partnership proposed to fund Calif. seismic early warning system
California state agencies federal agencies, are proposing a partnership between public and private agencies to build the $23.1 million earthquake early warning system in the state, and fund the $11.4 million annual operating budget. Governor Jerry Brown signed Senate Bill 135 in 2013 authorizing construction of the warning system, but the bill does not provide or allocate funding, despite a plan to have the system active in two years. The early warning system will provide Los Angeles residents up to a minute’s notice if a large earthquake is generated on the San Andreas Fault in the Salton Sea area. The system could also provide warnings for earthquakes that occur throughout California’s earthquake-prone landscape.
-
-
The next Bay Area’s Big One may be a cluster of major quakes
A cluster of closely timed earthquakes over 100 years in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries released as much accumulated stress on San Francisco Bay Area’s major faults as the Great 1906 San Francisco earthquake, suggesting two possible scenarios for the next “Big One” for the region, according to new research. “The plates are moving,” the study’s co-author said. “The stress is re-accumulating, and all of these faults have to catch up. How are they going to catch up?”
-
-
Pumping Central Valley’s ground water increases number of California’s earthquakes
Scientists have offered a new theory explaining the steady increase in the number of small earthquakes in parts of Central California. They say that the quakes are partly due to the pumping of groundwater. Groundwater is heavy, and depresses the Earth’s upper crust like a weight. Without that weight, the earth springs upward and the change in pressure can trigger more small earthquakes.
-
-
April storms lead to first billion-dollar losses of 2014

The outbreak of severe weather throughout the United States and other parts of the world in April will prove to have caused the largest economic losses since 2013, according to a report. During the month in the United States, at least 39 people were killed and 250 injured amid nearly 70 confirmed tornado touchdowns, which occurred across more than 20 states in the Plains, Mississippi Valley, Southeast, Midwest, and Mid-Atlantic.
-
-
Colorado tries to increase safety of urban development in wildfire-prone areas
Colorado continues to deal with the challenge of building new urban developments while reducing wildfire risks. There are currently 556,000 houses built in burn zones around the state, and the demand for water to sustain residents and industries continue to rise. A new study predicts that development will occupy 2.1 million acres in wildfire-prone forests by 2030, an increase from one million acres today — just as wildfires continue to burn roughly 900,000 acres a year since 2000, compared with just 200,000 acres a year in the 1990s.
-
-
Improving gloves to enhance first responders’ safety
Firefighters wear protective gloves called “structure gloves” to keep their hands safe on the job. The structure gloves currently used by firefighters, however, are not designed for the precision movements first responders must perform. There are many different types of structure gloves available, but none fully satisfies modern firefighters’ needs. Today’s compact tools often have small buttons that require nimble movements. Bulky gloves can make it difficult for firefighters to complete simple tasks without removing their gloves and compromising their safety. As advanced textile technology and materials continue to develop, the science behind firefighter structure gloves has adapted.
-
-
Limiting methane emissions would more quickly affect climate than limiting CO2
When discussing climate change, scientists point to “radiative forcing,” a measure of trapped heat in Earth’s atmosphere from man-made greenhouse gases. The current role of methane looms large, they say, contributing over 40 percent of current radiative forcing from all greenhouse gases. The role of methane as a driver of global warming is even more critical than this 40 percent value might indicate, they note, since the climate system responds much more quickly to reducing methane than to reducing carbon dioxide. The implication is that while it is true that in order to slow, or even reverse, global warming we must limit emissions of both carbon dioxide and methane, it makes more sense to concentrate now on limiting methane emissions because reducing methane emissions would buy society some critical decades of lower temperatures.
-
-
Fire experiments will test new firefighting tactics
Fire researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) will return to Spartanburg, South Carolina, on 15-21 May 2014, as part of a collaborative effort on a series of controlled-burn experiments in detached single-family homes slated for demolition. Measurements of temperature, total heat flux and other ground truth data gathered during the live fire experiments will help the NIST team and its partners to further assess the effectiveness of new fire-suppression tactics known as transitional fire attack.
-
-
Coral reefs offer valuable protection for coastal infrastructure
Growing natural hazards from coastal storms, flooding, and rising sea levels are leading to major investments worldwide in coastal defense structures such as seawalls and breakwaters. A new study shows that coral reefs can provide risk reduction benefits comparable to artificial defenses, and reef restoration and enhancement is a cost-effective alternative to manmade structures. Restoring coral reefs as a way to protect coastal infrastructure is also cheaper: the typical price for a tropical breakwater project is $197 million, compared with $129 million for restoring a reef.
-
- All
- Regional
- Water
- Biometrics
- Borders/Immig
- Business
- Cybersecurity
- Detection
- Disasters
- Government
- Infrastructure
- International
- Public health
- Public Safety
- Communication interoperabillity
- Emergency services
- Emergency medical services
- Fire
- First response
- IEDs
- Law Enforcement
- Law Enforcement Technology
- Military technology
- Nonlethal weapons
- Nuclear weapons
- Personal protection equipment
- Police
- Notification /alert systems
- Situational awareness
- Weapons systems
- Sci-Tech
- Sector Reports
- Surveillance
- Transportation
Advertising & Marketing: advertise@newswirepubs.com
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
Editorial: editor@newswirepubs.com
General: info@newswirepubs.com
2010-2011 © News Wire Publications, LLC News Wire Publications, LLC
220 Old Country Road | Suite 200 | Mineola | New York | 11501
Permissions and Policies
